Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Lithiated porous silicon nanowires stimulate periodontal regeneration
Lithiated porous silicon nanowires stimulate periodontal regeneration
Prelithiation can introduce controllable amounts of lithium within porous silicon, however it yields a highly reactive material unsuitable for biomedicine. In this study, the authors present a strategy to lithiate porous silicon nanowires, resulting in a biocompatible and bioresorbable material.
- Martti Kaasalainen
- , Ran Zhang
- & Ciro Chiappini
-
Article
| Open Access Autonomous artificial intelligence increases screening and follow-up for diabetic retinopathy in youth: the ACCESS randomized control trial
Autonomous artificial intelligence increases screening and follow-up for diabetic retinopathy in youth: the ACCESS randomized control trial
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that can be prevented through screening, yet adherence is low. Here, the authors show that autonomous AI increases diabetic eye exam completion in a diverse cohort of youth with diabetes.
- Risa M. Wolf
- , Roomasa Channa
- & Michael D. Abramoff
-
Article
| Open Access Gene-SGAN: discovering disease subtypes with imaging and genetic signatures via multi-view weakly-supervised deep clustering
Gene-SGAN: discovering disease subtypes with imaging and genetic signatures via multi-view weakly-supervised deep clustering
Many diseases can display distinct brain imaging phenotypes across individuals, potentially reflecting disease subtypes. However, biological interpretability is limited if the derived subtypes are not associated with genetic drivers or susceptibility factors. Here, the authors describe a deep-learning method that links imaging phenotypes with genetic factors, thereby conferring genetic correlations to the disease subtypes.
- Zhijian Yang
- , Junhao Wen
- & Christos Davatzikos
-
Article
| Open Access Convergence of resistance and evolutionary responses in Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica co-inhabiting chicken farms in China
Convergence of resistance and evolutionary responses in Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica co-inhabiting chicken farms in China
Bacteria in the same environment can share genetic material but the extent to which this influences development of antimicrobial resistance is unclear. Here, the authors investigate the evidence for co-evolution of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria found coexisting in animals and the environment in chicken farms and slaughterhouses in China.
- Michelle Baker
- , Xibin Zhang
- & Tania Dottorini
-
Article
| Open Access Quick model-based viscoelastic clot strength predictions from blood protein concentrations for cybermedical coagulation control
Quick model-based viscoelastic clot strength predictions from blood protein concentrations for cybermedical coagulation control
Available viscoelastic models of blood flow and blood coagulation are unsuited for a cybermedical input-output type of control system application. Here the authors present validated viscoelastic coagulation models that use quickly-measurable protein concentrations to forecast slow clot strength curves for future automation.
- Damon E. Ghetmiri
- , Alessia J. Venturi
- & Amor A. Menezes
-
Article
| Open Access AI co-pilot bronchoscope robot
AI co-pilot bronchoscope robot
The unequal distribution of medical resources means that bronchoscopic services are often unavailable in underdeveloped areas. Here, the authors present an AI co-pilot bronchoscope robot that features a user-friendly plug-and-play catheter and an AI-human shared control algorithm, to enable novice doctors to conduct lung examinations safely.
- Jingyu Zhang
- , Lilu Liu
- & Haojian Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic predictors of COVID-19 vaccination uptake and their interconnections over two years in Hong Kong
Dynamic predictors of COVID-19 vaccination uptake and their interconnections over two years in Hong Kong
Understanding factors associated with COVID-19 vaccine uptake in an evolving pandemic context is important for future vaccine campaigns. Here, the authors investigate the main drivers of vaccine hesitancy in Hong Kong at different stages of the pandemic, where uptake was initially low despite high availability.
- Jiehu Yuan
- , Yucan Xu
- & Qiuyan Liao
-
Article
| Open Access Efficacy of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BL-99 in the treatment of functional dyspepsia: a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial
Efficacy of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BL-99 in the treatment of functional dyspepsia: a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial
Functional dyspepsia (FD) is a common chronic gastrointestinal disorder. Here, in a randomized, parallel-group, positive-drug, and placebo-controlled clinical trial, the authors show that supplementation with the probiotic Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BL-99 (BL-99) improves FD clinical response rate and promotes accumulation of SCFA-producing microbiota.
- Qi Zhang
- , Guang Li
- & Fazheng Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Gut microbiota facilitate chronic spontaneous urticaria
Gut microbiota facilitate chronic spontaneous urticaria
Chronic spontaneous urticarial is an inflammatory skin disease which has been linked to intestinal dysbiosis. Here the authors implicate intestinal dysbiosis with the inflammatory response in a murine model of urticaria.
- Lei Zhu
- , Xingxing Jian
- & Jie Li
-
Article
| Open Access Mucosal TLR5 activation controls healthspan and longevity
Mucosal TLR5 activation controls healthspan and longevity
Understanding how the immune system’s functionality declines with age is crucial for addressing aging-related health issues. Here, the authors demonstrate that activating TLR5 in the mucosal layer can significantly improve healthspan and longevity, suggesting a novel approach for aging interventions.
- Jae Sung Lim
- , Eun Jae Jeon
- & Kyung A Cho
-
Article
| Open Access Incidence and transmission of respiratory syncytial virus in urban and rural South Africa, 2017-2018
Incidence and transmission of respiratory syncytial virus in urban and rural South Africa, 2017-2018
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) causes a high burden of disease in children, particularly in lower- and middle-income countries. In this prospective household-based observational cohort study in South Africa, the authors estimate the incidence of RSV and identify risk factors for transmission.
- Cheryl Cohen
- , Jackie Kleynhans
- & Stefano Tempia
-
Article
| Open Access Myeloid-derived grancalcin instigates obesity-induced insulin resistance and metabolic inflammation in male mice
Myeloid-derived grancalcin instigates obesity-induced insulin resistance and metabolic inflammation in male mice
The mechanism by which the cross-talk between bone and adipose tissue regulates metabolic homeostasis is unknown. Here, the authors show a mechanism whereby bone marrow factor GCA initiates adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance, showing how GCA targeting could potentially treat metainflammation.
- Tian Su
- , Yue He
- & Xianghang Luo
-
Article
| Open Access BCG vaccination-induced acquired control of mycobacterial growth differs from growth control preexisting to BCG vaccination
BCG vaccination-induced acquired control of mycobacterial growth differs from growth control preexisting to BCG vaccination
Bacillus Calmette-Guèrin vaccination prevents tuberculosis but some individuals control infection without immunization. Here the authors employ functional assessment of effector responses against mycobacteria to find that distinct gene expression profiles for pre-existing capacity to control and control induced by BCG vaccination.
- Krista E. van Meijgaarden
- , Wenchao Li
- & Simone A. Joosten
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitatively assessing early detection strategies for mitigating COVID-19 and future pandemics
Quantitatively assessing early detection strategies for mitigating COVID-19 and future pandemics
Monitoring samples from hospital patients, wastewater, or air travel may enable early detection of pathogens. Here, the authors assess how these surveillance systems could have impacted detection of COVID-19 and their potential benefits for detection of other emerging pathogens.
- Andrew Bo Liu
- , Daniel Lee
- & Michael Springer
-
Article
| Open AccessDietary circadian rhythms and cardiovascular disease risk in the prospective NutriNet-Santé cohort
The relation between daily meal and fasting timing with cardiovascular disease incidence remains unclear. Here, authors show that a later daily meal timing is associated with increased cardiovascular disease risk, especially in women. This study suggests that adopting earlier daily eating patterns may be beneficial for cardiovascular prevention.
- Anna Palomar-Cros
- , Valentina A. Andreeva
- & Bernard Srour
-
Article
| Open Access Deep learning-based phenotyping reclassifies combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma
Deep learning-based phenotyping reclassifies combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma
Combined hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinomas (cHCC-CCA) are challenging to diagnose, as they exhibit features of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICCA). Here, the authors use deep learning to re-classify cHCC-CCA tumours into HCC or ICCA based on histopathology images.
- Julien Calderaro
- , Narmin Ghaffari Laleh
- & Jakob Nikolas Kather
-
Article
| Open Access Effects of accelerometer-based sedentary time and physical activity on DEXA-measured fat mass in 6059 children
Effects of accelerometer-based sedentary time and physical activity on DEXA-measured fat mass in 6059 children
Childhood obesity remains a global epidemic. Here, using objective measurements, the authors show that sedentary time increased from 6 h/day in childhood to 9 h/day in young adulthood, and was cumulatively associated with increased total and trunk fat mass. Both light or moderate-to-vigorous physical activity similarly partly reversed risk.
- Andrew O. Agbaje
- , Wei Perng
- & Tomi-Pekka Tuomainen
-
Article
| Open Access A deep unrolled neural network for real-time MRI-guided brain intervention
A deep unrolled neural network for real-time MRI-guided brain intervention
Real-time MRI provides accurate navigation and targeting for neurological interventions. Here, the authors propose a deep unrolled neural network for MRI reconstruction that enables real-time monitoring of remote-controlled brain interventions and can be integrated into diagnostic scanners.
- Zhao He
- , Ya-Nan Zhu
- & Yuan Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Temperature-related death burden of various neurodegenerative diseases under climate warming: a nationwide modelling study
Temperature-related death burden of various neurodegenerative diseases under climate warming: a nationwide modelling study
Examining non-optimal temperatures’ influence on neurodegenerative diseases amid climate warming is vital for public health. Here, the authors project a notable net increase of death burden from neurodegenerative diseases after the mid-21st century.
- Peng Yin
- , Ya Gao
- & Haidong Kan
-
Article
| Open Access Phylogeny and molecular evolution of the first local monkeypox virus cluster in Guangdong Province, China
Phylogeny and molecular evolution of the first local monkeypox virus cluster in Guangdong Province, China
The first known local mpox outbreak in Guangdong Province, China occurred in June 2023. Here, the authors perform phylogenetic and molecular evolution analysis of ten mpox virus genome sequences from this outbreak, and place them in the context of other samples detected in surrounding regions.
- Jianhai Yu
- , Xin Zhang
- & Baisheng Li
-
Article
| Open Access High-throughput target trial emulation for Alzheimer’s disease drug repurposing with real-world data
High-throughput target trial emulation for Alzheimer’s disease drug repurposing with real-world data
Target trial emulation (TTE) simulates randomized controlled trials using real world data (RWD). Here, authors show the effectiveness of different TTE strategies to identify drug candidates that could be potentially repurposed to Alzheimer’s disease using two large scale RWD warehouses.
- Chengxi Zang
- , Hao Zhang
- & Fei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Interactions between climate change, urban infrastructure and mobility are driving dengue emergence in Vietnam
Interactions between climate change, urban infrastructure and mobility are driving dengue emergence in Vietnam
The geographic distribution of dengue has been expanding in recent decades, and Vietnam is one of the most severely affected countries. In this study, the authors use Bayesian hierarchical modelling to investigate the socio-environmental and climatic drivers of dengue incidence in Vietnam and how they vary across the country.
- Rory Gibb
- , Felipe J. Colón-González
- & Rachel Lowe
-
Comment
| Open Access Time for global health policy and research leaders to prioritize endometriosis
Time for global health policy and research leaders to prioritize endometriosis
Endometriosis is an incurable, under-diagnosed, systemic inflammatory disease affecting millions world-wide. Common symptoms include life-impacting pain, gastrointestinal/urinary symptoms, excessive fatigue, and infertility. Global public health policies are urgently needed to promote awareness, implement multidisciplinary care, and fund research for aetiology, biomarker discovery, and effective therapies for symptoms associated with endometriosis.
- Linda C. Giudice
- , Andrew W. Horne
- & Stacey A. Missmer
-
Article
| Open Access Estimating the potential impact and diagnostic requirements for SARS-CoV-2 test-and-treat programs
Estimating the potential impact and diagnostic requirements for SARS-CoV-2 test-and-treat programs
Antivirals are now available for treating COVID-19 but must be used early in the course of infection to be effective. Here, the authors use mathematical modelling to assess the potential public health impacts of antiviral use considering different levels of testing and country sociodemographic characteristics.
- Alvin X. Han
- , Emma Hannay
- & Colin A. Russell
-
Article
| Open Access True prevalence of long-COVID in a nationwide, population cohort study
True prevalence of long-COVID in a nationwide, population cohort study
Determining the prevalence of Long COVID is challenging because many symptoms attributed to the syndrome could have other causes. Here, the authors estimate the prevalence of Long COVID in Scotland by comparing rates of symptoms reported by people with and without history of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
- Claire E. Hastie
- , David J. Lowe
- & Jill P. Pell
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association analysis of left ventricular imaging-derived phenotypes identifies 72 risk loci and yields genetic insights into hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Genome-wide association analysis of left ventricular imaging-derived phenotypes identifies 72 risk loci and yields genetic insights into hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Changes of left ventricular structure are used to predict morbidity and mortality in cardiovascular diseases. Here the authors conducted a study using advanced deep learning technology to analyze left ventricular regional wall thickness (LVRWT) in a large population, identifying 72 significant genetic loci linked to LVRWT traits.
- Caibo Ning
- , Linyun Fan
- & Xiaoping Miao
-
Article
| Open Access TransformEHR: transformer-based encoder-decoder generative model to enhance prediction of disease outcomes using electronic health records
TransformEHR: transformer-based encoder-decoder generative model to enhance prediction of disease outcomes using electronic health records
Using AI to predict disease can improve interventions slow down or prevent disease. Here, the authors show that generative AI models built on the framework of Transformer, the model that also empowers ChatGPT, can achieve state-of-the-art performance on disease predictions based on longitudinal electronic records.
- Zhichao Yang
- , Avijit Mitra
- & Hong Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Data-driven grading of acute graft-versus-host disease
Data-driven grading of acute graft-versus-host disease
Acute GVHD severity grading is based on target organ assessments. Here, the authors show that data-driven grading can identify 12 distinct grades with specific aGVHD phenotypes, which are associated with clinical outcomes, and that their method outperformed conventional gradings.
- Evren Bayraktar
- , Theresa Graf
- & Amin T. Turki
-
Article
| Open Access Epidemiology, mortality, and health service use of local-level multimorbidity patterns in South Spain
Epidemiology, mortality, and health service use of local-level multimorbidity patterns in South Spain
Multimorbidity—the occurrence of chronic diseases together—represents a major challenge for healthcare systems. Here, the authors characterise multimorbidity patterns in a large dataset of patients residing in southern Spain and show the unequal distribution of multimorbidity patterns along different socioeconomic areas at the local level.
- Javier Alvarez-Galvez
- , Esther Ortega-Martin
- & Jesus Carretero-Bravo
-
Article
| Open Access A self-stabilized and water-responsive deliverable coenzyme-based polymer binary elastomer adhesive patch for treating oral ulcer
A self-stabilized and water-responsive deliverable coenzyme-based polymer binary elastomer adhesive patch for treating oral ulcer
The therapeutic benefits of biomaterials-based treatments for oral ulcer have been limited by the materials’ poor adhesion and short-time retention in oral cavity. Here, the authors report a polymer binary elastomer adhesive patch that allows water-responsive sustainable delivery of bioactive small molecules and durable adhesion to oral mucosal wounds to achieve efficient therapy of oral ulcer.
- Chunyan Cui
- , Li Mei
- & Wenguang Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Assessing the value of integrating national longitudinal shopping data into respiratory disease forecasting models
Assessing the value of integrating national longitudinal shopping data into respiratory disease forecasting models
Novel indicators of infectious disease prevalence could improve real-time surveillance and support healthcare planning. Here, the authors show that sales data for non-prescription medications from a UK high street retailer can improve the accuracy of models forecasting mortality from respiratory infections.
- Elizabeth Dolan
- , James Goulding
- & Laila J. Tata
-
Article
| Open Access Evaluation of the US COVID-19 Scenario Modeling Hub for informing pandemic response under uncertainty
Evaluation of the US COVID-19 Scenario Modeling Hub for informing pandemic response under uncertainty
The US COVID-19 Scenario Modeling Hub produced medium to long term projections based on different epidemic scenarios. In this study, the authors evaluate 14 rounds of projections by comparing them to the epidemic trajectories that occurred, and discuss lessons learned for future similar projects.
- Emily Howerton
- , Lucie Contamin
- & Justin Lessler
-
Article
| Open Access The burden of post-acute COVID-19 symptoms in a multinational network cohort analysis
The burden of post-acute COVID-19 symptoms in a multinational network cohort analysis
Post-acute COVID-19 condition is difficult to quantify because it includes a range of symptoms that may have other causes. In this study, the authors use primary care data from England and Catalonia, Spain, to estimate the incidence of the condition and identify symptoms that occur more frequently following infection than in uninfected controls.
- Kristin Kostka
- , Elena Roel
- & Annika M. Jödicke
-
Article
| Open Access The metabolic, virulence and antimicrobial resistance profiles of colonising Streptococcus pneumoniae shift after PCV13 introduction in urban Malawi
The metabolic, virulence and antimicrobial resistance profiles of colonising Streptococcus pneumoniae shift after PCV13 introduction in urban Malawi
Pneumococcal vaccination has been shown to promote emergence of non-vaccine S. pneumoniae serotypes. Here, the authors use data from Malawi to investigate whether vaccine introduction also results in changes in metabolic, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance profiles of circulating strains.
- Uri Obolski
- , Todd D. Swarthout
- & Robert S. Heyderman
-
Article
| Open Access Circadian disturbances and frailty risk in older adults
Circadian disturbances and frailty risk in older adults
The relationship between circadian function and frailty is not well understood. Here, the authors show that disturbances in circadian rest-activity rhythms were associated with an elevated frailty risk and faster progress of frailty in older adults.
- Ruixue Cai
- , Lei Gao
- & Peng Li
-
Article
| Open Access Impact of vaccinations, boosters and lockdowns on COVID-19 waves in French Polynesia
Impact of vaccinations, boosters and lockdowns on COVID-19 waves in French Polynesia
In this study, the authors develop a mathematical modelling framework to estimate the impacts of non-pharmaceutical interventions and vaccination on COVID-19 incidence. The model accounts for changes in SARS-CoV-2 variant and population immunity, and here they use it to investigate epidemic dynamics in French Polynesia.
- Lloyd A. C. Chapman
- , Maite Aubry
- & Adam J. Kucharski
-
Article
| Open Access Malaria surveillance reveals parasite relatedness, signatures of selection, and correlates of transmission across Senegal
Malaria surveillance reveals parasite relatedness, signatures of selection, and correlates of transmission across Senegal
Senegal has initiated a national sentinel surveillance program for malaria parasite genetics. Here, the authors report data from the first year of the program and use it to investigate local malaria incidence, patterns of transmission, and genetic loci under selection.
- Stephen F. Schaffner
- , Aida Badiane
- & Sarah K. Volkman
-
Article
| Open Access Automated temporalis muscle quantification and growth charts for children through adulthood
Automated temporalis muscle quantification and growth charts for children through adulthood
Temporalis muscle thickness is a promising marker of lean muscle mass but has had limited utility due to its unknown normal growth trajectory and lack of standardized measurement. Here, the authors develop an automated deep learning pipeline to accurately measure temporalis muscle thickness from routine brain magnetic resonance imaging.
- Anna Zapaishchykova
- , Kevin X. Liu
- & Benjamin H. Kann
-
Article
| Open Access Fetal biometry and amniotic fluid volume assessment end-to-end automation using Deep Learning
Fetal biometry and amniotic fluid volume assessment end-to-end automation using Deep Learning
Fetal biometry and amniotic fluid volume are essential but strenuous measurements in fetal ultrasound screening. Here, the authors show that deep learning models can automate these measurements with high accuracy, using a large and diverse dataset of Moroccan fetal ultrasound images.
- Saad Slimani
- , Salaheddine Hounka
- & El Houssine Bouyakhf
-
Comment
| Open Access The counterintuitive implications of superspreading diseases
The counterintuitive implications of superspreading diseases
The superspreading that characterized SARS and now COVID-19 can be rapidly quantified; however, its implications for outbreak control were never well understood. Recent studies point to its profound impact on outbreak dynamics and prospects for effective control of a future Disease X. These insights necessitate research into the mechanisms, impact and different modes of superspreading more widely.
- Bjarke Frost Nielsen
- , Kim Sneppen
- & Lone Simonsen
-
Comment
| Open AccessLessons for cross-species viral transmission surveillance from highly pathogenic avian influenza Korean cat shelter outbreaks
In this Comment, the authors describe recent outbreaks of highly pathogenic avian influenza in cat shelters in Seoul, South Korea. They discuss potential routes of transmission and describe implications for surveillance of spillover infections in animals in non-agricultural settings.
- Younjung Kim
- , Guillaume Fournié
- & Pierre Nouvellet
-
Article
| Open Access Cumulative effect of PM2.5 components is larger than the effect of PM2.5 mass on child health in India
Cumulative effect of PM2.5 components is larger than the effect of PM2.5 mass on child health in India
Health impact of air pollution is estimated using PM2.5 mass as exposure metric. Here authors show that the impacts on child health is underestimated in India using this metric relative to the cumulative impact of the various PM2.5 components.
- Ekta Chaudhary
- , Franciosalgeo George
- & Unnati Mehta
-
Article
| Open Access RNA N6-methyladenosine modification-based biomarkers for absorbed ionizing radiation dose estimation
RNA N6-methyladenosine modification-based biomarkers for absorbed ionizing radiation dose estimation
Radiation dosimetry are critical for the medical management of individuals exposed to ionizing radiation (IR). Here, authors show that the RNA m6A levels of Ncoa4, Ate1 and Fgf22 genes in peripheral blood cells could serve as dosimetry of IR exposure.
- Hongxia Chen
- , Xi Zhao
- & Gangqiao Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchical AI enables global interpretation of culture plates in the era of digital microbiology
Hierarchical AI enables global interpretation of culture plates in the era of digital microbiology
DeepColony is a multi-level AI solution for the interpretation of bacterial culturing images in clinical microbiology laboratory automations. Here, the authors show it allows presumptive identification and quantitation of relevant pathogens at both colony- and plate-level.
- Alberto Signoroni
- , Alessandro Ferrari
- & Karissa Culbreath
-
Article
| Open Access Effectiveness of the second COVID-19 booster against Omicron: a large-scale cohort study in Chile
Effectiveness of the second COVID-19 booster against Omicron: a large-scale cohort study in Chile
This study assesses the effectiveness of a second COVID-19 mRNA booster vaccine against severe disease using data from Chile. The authors find that the effectiveness of the second mRNA booster was high with a range of different background vaccination schemes, but there was evidence of waning over time.
- Alejandro Jara
- , Cristobal Cuadrado
- & Rafael Araos
-
Article
| Open Access Using drivers and transmission pathways to identify SARS-like coronavirus spillover risk hotspots
Using drivers and transmission pathways to identify SARS-like coronavirus spillover risk hotspots
Identification of areas with risk factors for spillover of viruses from animals to humans could assist with early detection of emerging infectious diseases. In this study, the authors characterise potential risks for spillover of SARS-like viruses from bats to humans and identify geographical regions in which multiple risk factors cluster together.
- Renata L. Muylaert
- , David A. Wilkinson
- & David T. S. Hayman
-
Article
| Open Access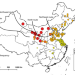 Mortality risks from a spectrum of causes associated with sand and dust storms in China
Mortality risks from a spectrum of causes associated with sand and dust storms in China
Sand and dust storms pose considerable health risks worldwide. Here, the authors conduct a nationwide multicenter time-series study to examine sand and dust storm-associated mortality risks.
- Can Zhang
- , Meilin Yan
- & Tiantian Li
-
Article
| Open Access Reconstructing disease dynamics for mechanistic insights and clinical benefit
Reconstructing disease dynamics for mechanistic insights and clinical benefit
Understanding disease progression dynamics is critical for diagnostics and treatment, but capturing dynamics is difficult. Here, the authors present a method for modelling disease progression from high dimensional molecular data that enables patient stratification and high-risk disease state identification, showcased in bladder cancer.
- Amit Frishberg
- , Neta Milman
- & Shai S. Shen-Orr
-
Article
| Open Access Long-term health impacts of COVID-19 among 242,712 adults in England
Long-term health impacts of COVID-19 among 242,712 adults in England
The duration of symptomatic COVID-19 and its impacts on health and quality of life are not well understood. In this study, the authors report results from a survey of ~275,000 adults in England and find that persistent COVID-19 is relatively rare but is associated with poorer mental health and health-related quality of life.
- Christina J. Atchison
- , Bethan Davies
- & Paul Elliott

 A randomized trial looking at planning prompts to reduce opioid prescribing
A randomized trial looking at planning prompts to reduce opioid prescribing