Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid room-temperature phosphorescence chiral recognition of natural amino acids
Rapid room-temperature phosphorescence chiral recognition of natural amino acids
Chiral recognition of amino acids with luminescence, despite its advantages, is usually slow and lacks generality. Here, the authors demonstrate that L-phenylalanine derived benzamide can manifest the structural difference between the natural, left-handed amino acid and its right-handed counterpart via the difference in room-temperature phosphorescence, irrespective of the specific chemical structure.
- Xiaoyu Chen
- , Renlong Zhu
- & Guoqing Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Measuring sub-nanometer undulations at microsecond temporal resolution with metal- and graphene-induced energy transfer spectroscopy
Measuring sub-nanometer undulations at microsecond temporal resolution with metal- and graphene-induced energy transfer spectroscopy
Studying the fluctuations of biological membranes with high resolution is challenging. Here, the authors combine metal- and graphene-induced energy transfer (MIET/GIET) with fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) to monitor such fluctuations with nanometer and microsecond resolution.
- Tao Chen
- , Narain Karedla
- & Jörg Enderlein
-
Article
| Open Access Ratiometric fluorescent sensing of pyrophosphate with sp³-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes
Ratiometric fluorescent sensing of pyrophosphate with sp³-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes
Inorganic pyrophosphate is a key molecule in many biological processes. Here, the authors develop an optical sensor that enables its ratiometric detection in the near infrared with functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes.
- Simon Settele
- , C. Alexander Schrage
- & Jana Zaumseil
-
Article
| Open Access Dual-wavelength metalens enables Epi-fluorescence detection from single molecules
Dual-wavelength metalens enables Epi-fluorescence detection from single molecules
The requirement for sophisticated objective lenses hinders the miniaturisation of single molecule fluorescence spectroscopy for portable sensing applications. Here, the authors demonstrate a dual-wavelength metalens for real-time monitoring of individual fluorescent nanoparticles.
- Aleksandr Barulin
- , Yeseul Kim
- & Inki Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Hot luminescence from single-molecule chromophores electrically and mechanically self-decoupled by tripodal scaffolds
Hot luminescence from single-molecule chromophores electrically and mechanically self-decoupled by tripodal scaffolds
A fundamental challenge for molecular electronics is the change in photophysical properties of molecules upon direct electrical contact. Here, the authors observe hot luminescence emitted by single-molecule chromophores that are electrically and mechanically self-decoupled by a tripodal scaffold.
- Vibhuti Rai
- , Nico Balzer
- & Michal Valášek
-
Article
| Open Access Sharp zero-phonon lines of single organic molecules on a hexagonal boron-nitride surface
Sharp zero-phonon lines of single organic molecules on a hexagonal boron-nitride surface
Low-temperature spectroscopy of single fluorescent molecules can be of use to study dynamics in the nano-environment around them. Here, Smit et al. show that the fluorescence wavelength of molecules on the surface of hexagonal boron-nitride is particularly sensitive to how clean this surface is.
- Robert Smit
- , Arash Tebyani
- & Michel Orrit
-
Article
| Open Access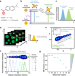 Biomolecular condensates modulate membrane lipid packing and hydration
Biomolecular condensates modulate membrane lipid packing and hydration
Nano-environmental probes and advance imaging microscopy provide deep insight into protein phase separation and the interaction of condensates with membranes, revealing that wetting by condensates can modulate membrane lipid packing and hydration.
- Agustín Mangiarotti
- , Macarena Siri
- & Rumiana Dimova
-
Article
| Open Access Multicolor lifetime imaging and its application to HIV-1 uptake
Multicolor lifetime imaging and its application to HIV-1 uptake
Multicolor imaging employing genetically-encodable fluorescent proteins permits spatiotemporal live cell imaging of multiple cues. Here, authors use multicolor lifetime imaging to visualize quadruple-labelled human immunodeficiency viruses within cellular contexts.
- Tobias Starling
- , Irene Carlon-Andres
- & Sergi Padilla-Parra
-
Article
| Open Access Altering the spectroscopy, electronic structure, and bonding of organometallic curium(III) upon coordination of 4,4′−bipyridine
Altering the spectroscopy, electronic structure, and bonding of organometallic curium(III) upon coordination of 4,4′−bipyridine
Despite the distinct electronic properties of the wide variety Cm3+ compounds that have been prepared to date, no singlecrystal structural characterization of a complex containing a Cm−C bond has been reported. Here the authors report the synthesis of a Cm complex bearing trimethylsilylcyclopentadienyl and 4,4’-bipyridine ligands with a low energy emission and identify the 4,4’-bipyridine ligand as the primary quenching agent.
- Brian N. Long
- , María J. Beltrán-Leíva
- & Thomas E. Albrecht-Schönzart
-
Article
| Open Access In-plane and out-of-plane excitonic coupling in 2D molecular crystals
In-plane and out-of-plane excitonic coupling in 2D molecular crystals
The mixing between Frenkel and charge-transfer characters in molecular excitons is difficult to analyze. Here, the authors demonstrate the onset and evolution of the mixing using 2D perylene molecular crystals by measuring the reorientation of emission transition dipoles with varying thicknesses.
- Dogyeong Kim
- , Sol Lee
- & Sunmin Ryu
-
Article
| Open Access All-optical control of high-purity trions in nanoscale waveguide
All-optical control of high-purity trions in nanoscale waveguide
The authors induce a nanoscale strain gradient in monolayer MoS2 suspended on a waveguide and take advantage of propagating surface plasmon polaritons to localize hot electrons in the suspended area. They funnel excitons in the waveguide, facilitating all-optical control of exciton-to-trion conversion.
- Hyeongwoo Lee
- , Yeonjeong Koo
- & Kyoung-Duck Park
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of Chiral-selective room-temperature phosphorescence enhancement via chirality-dependent energy transfer
Observation of Chiral-selective room-temperature phosphorescence enhancement via chirality-dependent energy transfer
Despite increasing interest in organic room temperature phosphorescence, it can still be challenging to determine mechanism and develop practical applications. Here, the authors report room temperature phosphorescent systems from chiral components, with strong phosphorescence observed only when both host and guest had the same chirality.
- Biao Chen
- , Wenhuan Huang
- & Guoqing Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access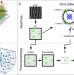 Real-time single-molecule 3D tracking in E. coli based on cross-entropy minimization
Real-time single-molecule 3D tracking in E. coli based on cross-entropy minimization
Single-molecule 3D tracking is critical to understand macromolecular dynamics but achieving this at a sub-millisecond resolution remains challenging. Here the authors present a 3D tracking method based on cross-entropy minimization and the true excitation point spread function.
- Elias Amselem
- , Bo Broadwater
- & Johan Elf
-
Article
| Open Access Theoretical and experimental analysis of circularly polarized luminescence spectrophotometers for artifact-free measurements using a single CCD camera
Theoretical and experimental analysis of circularly polarized luminescence spectrophotometers for artifact-free measurements using a single CCD camera
The authors present an artifact-free circularly polarized luminescence spectrophotometer using a single camera and two polarization encoding paths. The spectra are measured in a few seconds without the need of calibration by inverting the role of the paths.
- Bruno Baguenard
- , Amina Bensalah-Ledoux
- & Stéphan Guy
-
Article
| Open Access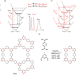 Red edge effect and chromoselective photocatalysis with amorphous covalent triazine-based frameworks
Red edge effect and chromoselective photocatalysis with amorphous covalent triazine-based frameworks
Chromoselective catalysis offers an intriguing opportunity to enable a specific reaction pathway in photocatalysis. Here, the authors look into the ability of covalent triazine frameworks to enable the synthesis of different organic compounds by using safer red light instead of harsh UV light.
- Yajun Zou
- , Sara Abednatanzi
- & Aleksandr Savateev
-
Article
| Open Access Ultraviolet optical horn antennas for label-free detection of single proteins
Ultraviolet optical horn antennas for label-free detection of single proteins
The authors introduce optical horn antennas, a nanophotonic platform combining plasmonic enhancement, efficient collection and background screening, for detection of UV autofluorescence from single proteins. They demonstrate label-free monitoring of protein unfolding and dissociation upon denaturation.
- Aleksandr Barulin
- , Prithu Roy
- & Jérôme Wenger
-
Article
| Open Access Comparing ultrastable lasers at 7 × 10−17 fractional frequency instability through a 2220 km optical fibre network
Comparing ultrastable lasers at 7 × 10−17 fractional frequency instability through a 2220 km optical fibre network
Precision measurement plays an important role in frequency metrology and optical communications. Here the authors compare two geographically separate ultrastable lasers at 7 × 10−17 fractional frequency instability over a 2220 km optical fibre link and these measurements can be useful for dissemination of ultrastable light to distant optical clocks.
- M. Schioppo
- , J. Kronjäger
- & G. Grosche
-
Article
| Open Access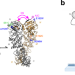 Two-colour single-molecule photoinduced electron transfer fluorescence imaging microscopy of chaperone dynamics
Two-colour single-molecule photoinduced electron transfer fluorescence imaging microscopy of chaperone dynamics
Revealing mechanisms of complex protein machines requires simultaneous exploration of multiple structural coordinates. Here the authors report two-colour fluorescence microscopy combined with photoinduced electron transfer probes to simultaneously detect two structural coordinates in single protein molecules.
- Jonathan Schubert
- , Andrea Schulze
- & Hannes Neuweiler
-
Article
| Open Access Structures of prokaryotic ubiquitin-like protein Pup in complex with depupylase Dop reveal the mechanism of catalytic phosphate formation
Structures of prokaryotic ubiquitin-like protein Pup in complex with depupylase Dop reveal the mechanism of catalytic phosphate formation
Pupylation is a bacterial post-translational protein modification, where the small ubiquitin-like protein Pup is covalently attached to lysine side chains of target proteins, which is a reversible process and depupylation is catalysed by the depupylase enzyme, Dop. Here, the authors present crystal structures of Dop in different functional states, which together with biochemical experiments provide insights into the catalytic mechanism of this enzyme.
- Hengjun Cui
- , Andreas U. Müller
- & Eilika Weber-Ban
-
Article
| Open Access Vacancy control in acene blends links exothermic singlet fission to coherence
Vacancy control in acene blends links exothermic singlet fission to coherence
A complete understanding of singlet fission (SF) in molecular materials will enable the design of optimised optoelectronic devices. Here, the authors use vacancy control in acene-based blends to link coherent and incoherent SF pathways to energetics.
- Clemens Zeiser
- , Chad Cruz
- & Katharina Broch
-
Article
| Open Access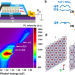 Strong interaction between interlayer excitons and correlated electrons in WSe2/WS2 moiré superlattice
Strong interaction between interlayer excitons and correlated electrons in WSe2/WS2 moiré superlattice
Heterobilayers of transition metal dichalcogenides host moiré superlattices that give rise to strong electron interactions. Here, the authors study the photoluminescence from interlayer excitons in a WS2/WSe2 heterobilayer to reveal the onset of various correlated insulating states.
- Shengnan Miao
- , Tianmeng Wang
- & Su-Fei Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Exciton-acoustic phonon coupling revealed by resonant excitation of single perovskite nanocrystals
Exciton-acoustic phonon coupling revealed by resonant excitation of single perovskite nanocrystals
In order to develop perovskite nanocrystals as a single-photon source, there is a need to understand the complex exciton photo-physics. Here, the authors employ resonant and near-resonant excitation technique to study single CsPbI3 nanocrystal that allows them to probe the continuous and size-quantised acoustic-phonon modes.
- Yan Lv
- , Chunyang Yin
- & Min Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Probing intramolecular vibronic coupling through vibronic-state imaging
Probing intramolecular vibronic coupling through vibronic-state imaging
Vibronic coupling is a key feature of molecular electronic transitions, but its visualization in real space is an experimental challenge. Here the authors, using scanning tunneling microscopy induced luminescence, resolve the effect of vibronic coupling with different modes on the electron distributions in real space in a single pentacene molecule.
- Fan-Fang Kong
- , Xiao-Jun Tian
- & J. G. Hou
-
Article
| Open Access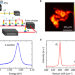 Exciton–phonon coupling strength in single-layer MoSe2 at room temperature
Exciton–phonon coupling strength in single-layer MoSe2 at room temperature
The exciton–phonon coupling (EXPC) affects the opto-electronic properties of atomically thin semiconductors. Here, the authors develop two-dimensional micro-spectroscopy to determine the EXPC of monolayer MoSe2.
- Donghai Li
- , Chiara Trovatello
- & Tobias Brixner
-
Article
| Open Access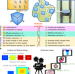 Imaging spatiotemporal evolution of molecules and active sites in zeolite catalyst during methanol-to-olefins reaction
Imaging spatiotemporal evolution of molecules and active sites in zeolite catalyst during methanol-to-olefins reaction
Imaging zeolites in catalysis relies on the use of probe molecules or model catalysts. Here the authors show the synergy of a multiscale reaction-diffusion model and structured illumination microscopy to illustrate spatiotemporal evolution of molecules and acid sites in SAPO-34 zeolites in methanol-to-olefins reaction.
- Mingbin Gao
- , Hua Li
- & Zhongmin Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Phonon-exciton Interactions in WSe2 under a quantizing magnetic field
Phonon-exciton Interactions in WSe2 under a quantizing magnetic field
An out-of-plane magnetic field is expected to strongly modify exciton-phonon interactions in atomically thin transitional metal dichalcogenides. Here, the authors show that the phonon-exciton interaction in monolayer WSe2 lifts the inter-Landau-level transition selection rules for dark trions.
- Zhipeng Li
- , Tianmeng Wang
- & Su-Fei Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Deciphering nanoconfinement effects on molecular orientation and reaction intermediate by single molecule imaging
Deciphering nanoconfinement effects on molecular orientation and reaction intermediate by single molecule imaging
Nanoconfinement effects on changing molecular transport and reaction kinetics in heterogeneous catalysis have been widely recognized. Here, the authors design a core-shell nanocatalyst with aligned linear nanopores to uncover nanoconfinement effects on catalytic activity and adsorption strength by single molecule imaging.
- Bin Dong
- , Yuchen Pei
- & Ning Fang
-
Article
| Open Access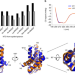 Methionine in a protein hydrophobic core drives tight interactions required for assembly of spider silk
Methionine in a protein hydrophobic core drives tight interactions required for assembly of spider silk
Spider silk is of interest in material science research. Here the authors show that the tight binding of a spider silk protein domain relies on the amino acid methionine, which is abundant in the domain core where it facilitates dynamic shape adaption of the binding interface.
- Julia C. Heiby
- , Benedikt Goretzki
- & Hannes Neuweiler
-
Article
| Open Access Non-aromatic annulene-based aggregation-induced emission system via aromaticity reversal process
Non-aromatic annulene-based aggregation-induced emission system via aromaticity reversal process
Molecular systems displaying aggregation-induced emission (AIE) have important biomedical and optoelectronic applications. Here the authors report a further mechanism for AIE, through aromaticity reversal from the ground state to the excited state, in the non-aromatic annulene derivative of cyclooctatetrathiophene.
- Zheng Zhao
- , Xiaoyan Zheng
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Emerging photoluminescence from the dark-exciton phonon replica in monolayer WSe2
Emerging photoluminescence from the dark-exciton phonon replica in monolayer WSe2
The long lifetime and spin properties of dark excitons in atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides offer opportunities to explore light-matter interactions beyond electric dipole transitions. Here, the authors demonstrate that the coupling of the dark exciton and an optically silent chiral phonon enables the intrinsic photoluminescence of the dark-exciton replica in monolayer WSe2
- Zhipeng Li
- , Tianmeng Wang
- & Su-Fei Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Microscopic insight into non-radiative decay in perovskite semiconductors from temperature-dependent luminescence blinking
Microscopic insight into non-radiative decay in perovskite semiconductors from temperature-dependent luminescence blinking
The mechanism of the non-radiative recombination in halide perovskite nanocrystals has not been fully understood. Here Gerhard et al. resolve the contributions of individual recombination centers by photoluminescence blinking measurements and identify ion migration as the underlying mechanism.
- Marina Gerhard
- , Boris Louis
- & Ivan G. Scheblykin
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative optical assessment of photonic and electronic properties in halide perovskite
Quantitative optical assessment of photonic and electronic properties in halide perovskite
The electronic and photonic contributions to the power conversion efficiency in solar cell devices are often hard to disentangle. Here Bercegol et al. develop a purely optical method to quantitatively decouple and assess the electronic and photonic processes in halide perovskite solar cells.
- Adrien Bercegol
- , Daniel Ory
- & Laurent Lombez
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule trapping and spectroscopy reveals photophysical heterogeneity of phycobilisomes quenched by Orange Carotenoid Protein
Single-molecule trapping and spectroscopy reveals photophysical heterogeneity of phycobilisomes quenched by Orange Carotenoid Protein
Upon photoactivation the Orange Carotenoid Protein (OCP) binds to the phycobilisome and prevents damage by thermally dissipating excess energy. Here authors use an Anti-Brownian ELectrokinetic trap to determine the photophysics of single OCP-quenched phycobilisomes and observe two distinct OCP-quenched states with either one or two OCPs bound.
- Allison H. Squires
- , Peter D. Dahlberg
- & W. E. Moerner
-
Article
| Open Access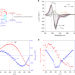 In situ monitoring of molecular aggregation using circular dichroism
In situ monitoring of molecular aggregation using circular dichroism
Molecular aggregation is a widespread and important process in physiological metabolism, but details regarding conformational changes during the process are hard to probe. Here, the authors use circular dichroism to monitor in-situ the conformational changes occurring during molecular aggregation.
- Haoke Zhang
- , Xiaoyan Zheng
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Valley coherent exciton-polaritons in a monolayer semiconductor
Valley coherent exciton-polaritons in a monolayer semiconductor
The short exciton life time in atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides poses limitations to efficient control of the valley pseudospin and coherence. Here, the authors manipulate the exciton coherence in a WSe2 monolayer embedded in an optical microcavity in the strong light-matter coupling regime.
- S. Dufferwiel
- , T. P. Lyons
- & A. I. Tartakovskii
-
Article
| Open Access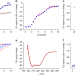 Two-step self-assembly of a spider silk molecular clamp
Two-step self-assembly of a spider silk molecular clamp
Molecular details that underlie mechanical properties of spider silk are of great interest to material scientists. Here, the authors report a previously unknown three-state mechanism of folding and an expanded structure of a spider silk protein that may contribute to elasticity of spider silk.
- Charlotte Rat
- , Julia C. Heiby
- & Hannes Neuweiler
-
Article
| Open Access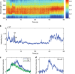 Superresolution mapping of energy landscape for single charge carriers in plastic semiconductors
Superresolution mapping of energy landscape for single charge carriers in plastic semiconductors
To understand the complex nanoscale structure-property relationships in conjugated polymers for device applications, new methods for tracking charge transport are required. Here, the authors employ superresolution mapping to study the charge carrier dynamics in conjugated polymer nanoparticles.
- Yifei Jiang
- & Jason McNeill
-
Article
| Open Access Spatially-resolved fluorescence-detected two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy probes varying excitonic structure in photosynthetic bacteria
Spatially-resolved fluorescence-detected two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy probes varying excitonic structure in photosynthetic bacteria
2D electronic spectroscopy enables a spatially-averaged view of the electronic structure of a heterogeneous system. Here, the authors extend it to sub-micron resolution and ~106 times better sensitivity, to resolve spatially varying excitonic structure in a heterogeneous mixture of photosynthetic cells.
- Vivek Tiwari
- , Yassel Acosta Matutes
- & Jennifer P. Ogilvie
-
Article
| Open Access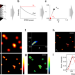 Exploiting the tunability of stimulated emission depletion microscopy for super-resolution imaging of nuclear structures
Exploiting the tunability of stimulated emission depletion microscopy for super-resolution imaging of nuclear structures
A known limitation of super-resolution STED microscopy is the need of high laser power which can cause photobleaching and phototoxicity. Here the authors further optimize this method and show that modulating STED intensity during acquisition results in an enhanced resolution and reduced background.
- Maria J. Sarmento
- , Michele Oneto
- & Luca Lanzanò
-
Article
| Open Access Domino-like multi-emissions across red and near infrared from solid-state 2-/2,6-aryl substituted BODIPY dyes
Domino-like multi-emissions across red and near infrared from solid-state 2-/2,6-aryl substituted BODIPY dyes
The class of BODIPY dyes has high solubility and high quantum yields and is widely used in imaging applications. Here Tian et al. synthesize new dye molecules and demonstrate extended emission properties and application scope controllable both by the excitation wavelength and aggregation states.
- Dan Tian
- , Fen Qi
- & Wei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Selective manipulation of electronically excited states through strong light–matter interactions
Selective manipulation of electronically excited states through strong light–matter interactions
Manipulating energy levels in molecules could allow applications such as improving organic LEDs. Here, the authors show evidence that reversed intersystem crossing can be enhanced in Erythrosine B coupled to a cavity by selectively manipulating the energy of the singlet state.
- Kati Stranius
- , Manuel Hertzog
- & Karl Börjesson
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasensitive reversible chromophore reaction of BODIPY functions as high ratio double turn on probe
Ultrasensitive reversible chromophore reaction of BODIPY functions as high ratio double turn on probe
BODIPY dyes, though widely explored, have not been pursued as chromophore reaction based chemical probes. Here, the authors synthesize a meso-naked BODIPY core flanked with two electron-withdrawing groups, which undergoes a reversible change in conjugated structure in the presence of base and functions as a dual signal and ultrahigh turn-on ratio chemical probe.
- Dehui Hu
- , Tao Zhang
- & Guoqiang Yang
-
Article
| Open Access A volumetric three-dimensional digital light photoactivatable dye display
A volumetric three-dimensional digital light photoactivatable dye display
Despite living in a three-dimensional world, almost all information in our society is conveyed in a two-dimensional format. Here, the authors provide a technique for the generation of spatially accurate and high-resolution three-dimensional images using fluorescent photoswitch chemistry.
- Shreya K. Patel
- , Jian Cao
- & Alexander R. Lippert
-
Article
| Open Access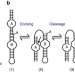 Pressure modulates the self-cleavage step of the hairpin ribozyme
Pressure modulates the self-cleavage step of the hairpin ribozyme
Studying the reactivity of ribozymes under extreme pressure could provide insights to optimize biocatalytic RNA design. Here, the authors show that at high pressure the transesterification step of the hairpin ribozyme self-cleavage reaction accelerates, while the overall process is slower.
- Caroline Schuabb
- , Narendra Kumar
- & Roland Winter
-
Article
| Open Access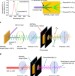 Quantification of re-absorption and re-emission processes to determine photon recycling efficiency in perovskite single crystals
Quantification of re-absorption and re-emission processes to determine photon recycling efficiency in perovskite single crystals
Fanget al. develop a method to determine the photon recycling efficiency for organic-inorganic hybrid single crystal perovskites by differentiating between emitted and re-absorbed photons based on their polarization difference. For these systems efficiencies of less than 0.5% are reported.
- Yanjun Fang
- , Haotong Wei
- & Jinsong Huang
-
Article
| Open Access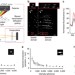 Multi-dimensional super-resolution imaging enables surface hydrophobicity mapping
Multi-dimensional super-resolution imaging enables surface hydrophobicity mapping
Many super-resolution imaging techniques use fluorescence emission intensity to obtain precise positional information, but other spectral information is ignored. Here, the authors develop a method that records the spectrum and position of single dye molecules to map the hydrophobicity of a surface.
- Marie N. Bongiovanni
- , Julien Godet
- & Steven F. Lee
-
Article
| Open Access 3D visualization of additive occlusion and tunable full-spectrum fluorescence in calcite
3D visualization of additive occlusion and tunable full-spectrum fluorescence in calcite
Introducing organic guests to a crystal is a convenient way to tailor its properties. Here, the authors occlude fluorescent dyes within calcite to reveal that additives can occupy distinct zones of a crystal, and strategically embed green, blue, and red dyes to create white fluorescent calcite.
- David C. Green
- , Johannes Ihli
- & Fiona C. Meldrum
-
Article
| Open Access Super-resolution spectroscopic microscopy via photon localization
Super-resolution spectroscopic microscopy via photon localization
Photon localization microscopy uses stochastic emission events from fluorescent molecules to enable super-resolution imaging, but spectroscopic information is lost. Here, the authors improve the spatial resolution of this technique with a method that also detects each blink’s fluorescence spectrum.
- Biqin Dong
- , Luay Almassalha
- & Hao F. Zhang

 Giant magneto-photoluminescence at ultralow field in organic microcrystal arrays for on-chip optical magnetometer
Giant magneto-photoluminescence at ultralow field in organic microcrystal arrays for on-chip optical magnetometer