Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access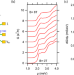 Electron pairing and nematicity in LaAlO3/SrTiO3 nanostructures
Electron pairing and nematicity in LaAlO3/SrTiO3 nanostructures
SrTiO3-based heterostructures display intriguing low-temperature transport features. Here the authors study LaAlO3/SrTiO3 nanoscale crossbar devices, revealing correlations between electron pairing without superconductivity, anomalous Hall effect, and electronic nematicity, suggesting a shared microscopic origin.
- Aditi Nethwewala
- , Hyungwoo Lee
- & Jeremy Levy
-
Article
| Open Access Apparent nonlinear damping triggered by quantum fluctuations
Apparent nonlinear damping triggered by quantum fluctuations
Nonlinear damping is a ubiquitous phenomenon in technological applications involving oscillators, but its origin is sometimes poorly understood. Here, the authors highlight how the interplay between quantum noise and Kerr anharmonicity introduces an effect resembling nonlinear damping.
- Mario F. Gely
- , Adrián Sanz Mora
- & Gary A. Steele
-
Article
| Open Access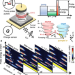 Time, momentum, and energy resolved pump-probe tunneling spectroscopy of two-dimensional electron systems
Time, momentum, and energy resolved pump-probe tunneling spectroscopy of two-dimensional electron systems
Pump-probe techniques—where a system is driven into a nonequilibrium state and then studied as a function of time—provide rich information about the behaviour of charge carriers and their interactions. Here, Yoo et al extend this class of techniques by injecting electrons at a selected energy and observing their decay in energy and momentum space.
- H. M. Yoo
- , M. Korkusinski
- & R. C. Ashoori
-
Article
| Open Access Phase biasing of a Josephson junction using Rashba–Edelstein effect
Phase biasing of a Josephson junction using Rashba–Edelstein effect
The authors study transport in Nb-(Pt/Cu)-Nb Josephson junctions (JJ), where Pt/Cu is a Rashba interface. Due to the Rashba–Edelstein effect, a charge current leads to a non-equilibrium spin moment at the Pt/Cu interface, which can be measured from a shift of the Fraunhofer pattern of the JJ.
- Tapas Senapati
- , Ashwin Kumar Karnad
- & Kartik Senapati
-
Article
| Open Access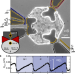 Observing the universal screening of a Kondo impurity
Observing the universal screening of a Kondo impurity
Previous work on charge Kondo circuits, in which a spin is formed by two degenerate charge states of a metallic island, has been limited to transport measurements of multi-channel Kondo problems. Piquard et al. use thermodynamic measurements via a charge sensor to study the evolution of a single Kondo impurity.
- C. Piquard
- , P. Glidic
- & F. Pierre
-
Article
| Open Access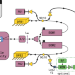 Frequency stable and low phase noise THz synthesis for precision spectroscopy
Frequency stable and low phase noise THz synthesis for precision spectroscopy
The authors demonstrate a very stable yet broadly tunable photonic THz source, characterized from 2 GHz to 1.4 THz. A very narrow Lamb dip feature is observed in a water absorption line, showcasing its potential for sub-kHz resolution spectroscopy.
- Léo Djevahirdjian
- , Loïc Lechevallier
- & Samir Kassi
-
Article
| Open Access Heat current-driven topological spin texture transformations and helical q-vector switching
Heat current-driven topological spin texture transformations and helical q-vector switching
Topological spin textures, such as skyrmions and antiskyrmions are of interest for use in information storage, owing to their inherent robustness. Critical to this use is the ability to manipulate these spin textures. Here, Yasin et al. demonstrate heat current driven transformation of a topological spin texture in a ferromagnet at room temperature.
- Fehmi Sami Yasin
- , Jan Masell
- & Xiuzhen Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Phase-engineering the Andreev band structure of a three-terminal Josephson junction
Phase-engineering the Andreev band structure of a three-terminal Josephson junction
The authors study Andreev bound states (ABSs) in 3-terminal InAs/Al Josephson-junction devices. They find signatures of hybridization between two ABSs, with band structure tunable by electric currents that generate magnetic fluxes threading superconducting loops in the device.
- Marco Coraiola
- , Daniel Z. Haxell
- & Fabrizio Nichele
-
Article
| Open Access Room-temperature high-speed electrical modulation of excitonic distribution in a monolayer semiconductor
Room-temperature high-speed electrical modulation of excitonic distribution in a monolayer semiconductor
2D excitonic devices hold potential for on-chip optoelectronic applications. Here, the authors report high-speed in-plane electrical modulations of the excitonic distribution in monolayer semiconductor/Au electrode junctions, showing switching times as low as 5 ns at room temperature.
- Guangpeng Zhu
- , Lan Zhang
- & Qihua Xiong
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-scale molecular dynamics simulations of enhanced energy transfer in organic molecules under strong coupling
Multi-scale molecular dynamics simulations of enhanced energy transfer in organic molecules under strong coupling
Placing an organic material in an optical cavity can enhance exciton transport, but the mechanism is poorly understood. Here, using molecular dynamics simulations, the authors obtained atomistic insights into that mechanism.
- Ilia Sokolovskii
- , Ruth H. Tichauer
- & Gerrit Groenhof
-
Article
| Open Access In-situ electro-responsive through-space coupling enabling foldamers as volatile memory elements
In-situ electro-responsive through-space coupling enabling foldamers as volatile memory elements
Molecular electronics holds promise for building memristor at nanoscales for in-memory computing. Li et al. design tailored foldamers with furan-benzene and thiophene-benzene stacking to achieve voltage triggered quantum interference switching for potential random number generator application.
- Jinshi Li
- , Pingchuan Shen
- & Zujin Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access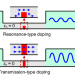 Transmission-type photonic doping for high-efficiency epsilon-near-zero supercoupling
Transmission-type photonic doping for high-efficiency epsilon-near-zero supercoupling
The authors present a transmission-type doping approach to reduce resonant losses in photonic doping. Assisted by the approach, proximate ideal epsilon-near-zero (ENZ) supercoupling with neartotal energy transmission and zero-phase advance is achieved in experiments.
- Wendi Yan
- , Ziheng Zhou
- & Yue Li
-
Article
| Open Access An anisotropic van der Waals dielectric for symmetry engineering in functionalized heterointerfaces
An anisotropic van der Waals dielectric for symmetry engineering in functionalized heterointerfaces
Here, the authors demonstrate that a layered anisotropic dielectric material, SiP2, can break the rotational symmetry of 2D MoS2, leading to linearly polarized photoluminescence emission and conductance anisotropy ratios up to 1000 in gated SiP2/MoS2 heterostructures.
- Zeya Li
- , Junwei Huang
- & Hongtao Yuan
-
Article
| Open Access Synergistic correlated states and nontrivial topology in coupled graphene-insulator heterostructures
Synergistic correlated states and nontrivial topology in coupled graphene-insulator heterostructures
Here, the authors theoretically predict the formation of synergistic correlated and topological states in Coulomb-coupled and gate-tunable graphene/insulator heterostructures, proposing a number of promising substrate candidates and a possible explanation for recent experimental observations in graphene/CrOCl heterostructures.
- Xin Lu
- , Shihao Zhang
- & Jianpeng Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Noise resilient exceptional-point voltmeters enabled by oscillation quenching phenomena
Noise resilient exceptional-point voltmeters enabled by oscillation quenching phenomena
Here the authors demonstrate a nonlinear exceptional-point sensing platform. They harness oscillation quenching phenomena to overcome the noise-sensitivity of techniques based on exceptional point degeneracies.
- Arunn Suntharalingam
- , Lucas Fernández-Alcázar
- & Tsampikos Kottos
-
Article
| Open Access Non-volatile optoelectronic memory based on a photosensitive dielectric
Non-volatile optoelectronic memory based on a photosensitive dielectric
Designing high efficient optoelectronic memory remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a novel optoelectronic memory device based on a photosensitive dielectric that is an insulator in dark and a semiconductor under irradiation with multilevel storage ability, low energy consumption and good compatibility.
- Rui Zhu
- , Huili Liang
- & Zengxia Mei
-
Article
| Open Access Impact of inherent energy barrier on spin-orbit torques in magnetic-metal/semimetal heterojunctions
Impact of inherent energy barrier on spin-orbit torques in magnetic-metal/semimetal heterojunctions
Many proposed spintronic devices, where spin, rather than charge is used for information processing, rely on the combination of multiple materials, for example, heavy metals and magnetic materials in spin-orbit torque devices. Here, Gao et al. show how the interface between a ferromagnet and a semimetal, Ni81Fe19/Bi0.1Sb0.9, can result in a barrier-mediated spin-orbit torques
- Tenghua Gao
- , Alireza Qaiumzadeh
- & Kazuya Ando
-
Article
| Open Access Superscattering emerging from the physics of bound states in the continuum
Superscattering emerging from the physics of bound states in the continuum
The scattering of light by small particles plays a central role in a myriad of fields. Here, the authors demonstrate a super dipole resonance that arises when two resonant modes of a small particle interfere, overcoming a widely accepted limitation to the cross section.
- Adrià Canós Valero
- , Hadi K. Shamkhi
- & Alexander S. Shalin
-
Article
| Open Access Adiabatic topological photonic interfaces
Adiabatic topological photonic interfaces
Smooth topological photonic interfaces lead to less localized boundary modes which improves their guiding characteristics in both spin- and valley Hall metasurfaces. The modes become insensitive to the lattice details, showcasing improved bandgap crossing and longer propagation distances.
- Anton Vakulenko
- , Svetlana Kiriushechkina
- & Alexander B. Khanikaev
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid topological photonic crystals
Hybrid topological photonic crystals
Owing to the nonequilibrium nature, photonic topological phenomena can involve multiple band gaps. Here the authors report on the discovery of a class of hybrid topological photonic crystals that host quantum anomalous Hall and valley Hall phases simultaneously.
- Yanan Wang
- , Hai-Xiao Wang
- & Guang-Yu Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Topotactic fabrication of transition metal dichalcogenide superconducting nanocircuits
Topotactic fabrication of transition metal dichalcogenide superconducting nanocircuits
The practical device application of transition-metal dichalcogenide superconductors (TMDSCs) is limited by their environmental instability. Here, the authors report a generic, non-destructive, and scalable strategy to fabricate TMDSC nanocircuits via the topotactic conversion of prepatterned metallic precursors.
- Xiaohan Wang
- , Hao Wang
- & Peiheng Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Strong bulk photovoltaic effect in engineered edge-embedded van der Waals structures
Strong bulk photovoltaic effect in engineered edge-embedded van der Waals structures
The bulk photovoltaic effect (BPVE) is a nonlinear optical effect offering a promising approach to overcome the limitations of conventional photovoltaics. Here, the authors report the observation of BPVE-induced photocurrents at the edges of 2D semiconductors embedded in various van der Waals heterostructures.
- Zihan Liang
- , Xin Zhou
- & Xiaolong Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Inductively shunted transmons exhibit noise insensitive plasmon states and a fluxon decay exceeding 3 hours
Inductively shunted transmons exhibit noise insensitive plasmon states and a fluxon decay exceeding 3 hours
Alternative superconducting qubit designs with improved performance are attracting attention. Here the authors introduce an inductively shunted transmon qubit that offers protection against flux noise and measures quantum tunneling between fluxon states that are shown to be stable for hours.
- F. Hassani
- , M. Peruzzo
- & J. M. Fink
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous electronic transport in high-mobility Corbino rings
Anomalous electronic transport in high-mobility Corbino rings
Metallic resistance of two-dimensional electron gases normally increases with temperature increasing. Here, the authors find a resistance decrease with increasing temperature at very low temperatures in two-dimensional electron metal described by Fermi liquid theory.
- Sujatha Vijayakrishnan
- , F. Poitevin
- & G. Gervais
-
Article
| Open Access Spin current driven by ultrafast magnetization of FeRh
Spin current driven by ultrafast magnetization of FeRh
In some magnetic materials, it is possible to magnetize or demagnetize the system on extremely short timescales. The angular momentum carried by the magnetic state must be generated or dissipated. Here, Kang et al find a significant correlation between spin current and the magnetization dynamics in the ultrafast magnetization processes, implying angular momentum transfer from electrons to magnons.
- Kyuhwe Kang
- , Hiroki Omura
- & Gyung-Min Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent optical control of a superconducting microwave cavity via electro-optical dynamical back-action
Coherent optical control of a superconducting microwave cavity via electro-optical dynamical back-action
Electro-optical interfaces are promising for quantum networks of superconducting circuits. Here the authors demonstrate a coherent optical control of a superconducting microwave resonator in the unity cooperativity regime of cavity electro-optics.
- Liu Qiu
- , Rishabh Sahu
- & Johannes M. Fink
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of hot-electron-enhanced thermoelectric effects in silicon nanodevices
Direct observation of hot-electron-enhanced thermoelectric effects in silicon nanodevices
Thermoelectric property of silicon itself is important for the thermal management of post-Moore nanoelectronics. Here, Xue et al directly observe unconventional thermoelectric cooling/heating effects enhanced by hot electrons in silicon nanodevices.
- Huanyi Xue
- , Ruijie Qian
- & Wei Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum bath suppression in a superconducting circuit by immersion cooling
Quantum bath suppression in a superconducting circuit by immersion cooling
Removing excess energy (cooling) and reducing noise in superconducting quantum circuits is central to improved coherence. Lucas et al. demonstrate cooling of a superconducting resonator and its noisy environment to sub-mK temperatures by immersion in liquid 3He.
- M. Lucas
- , A. V. Danilov
- & S. E. de Graaf
-
Article
| Open Access Non-Hermitian control between absorption and transparency in perfect zero-reflection magnonics
Non-Hermitian control between absorption and transparency in perfect zero-reflection magnonics
Absorption, transmission and reflection are three processes characterizing optical devices. Absorption allows for signal conversion and transmission is important for signal transfer, however, reflection is frequently detrimental to device performance. Here, Qian et al demonstrate a magnonic device with controllable absorption and transmission while maintain zero reflection.
- Jie Qian
- , C. H. Meng
- & C. -M. Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental demonstration of a skyrmion-enhanced strain-mediated physical reservoir computing system
Experimental demonstration of a skyrmion-enhanced strain-mediated physical reservoir computing system
An energy-efficient physical reservoir is crucial for reservoir computing (RC). Here the authors demonstrate an all-electric skyrmion-enhanced strain-mediated physical RC system and achieve a benchmark chaotic time series prediction.
- Yiming Sun
- , Tao Lin
- & Weisheng Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Electrostatic control of the proximity effect in the bulk of semiconductor-superconductor hybrids
Electrostatic control of the proximity effect in the bulk of semiconductor-superconductor hybrids
The proximity effect in semiconductor-superconductor nanowires is expected to generate an induced gap in the semiconductor. Here, the authors study the superconducting proximity effect in InSb nanowires with an Al/Pt shell, demonstrating control of the induced gap using electric and magnetic fields.
- Nick van Loo
- , Grzegorz P. Mazur
- & Leo P. Kouwenhoven
-
Article
| Open Access Thermally stable threshold selector based on CuAg alloy for energy-efficient memory and neuromorphic computing applications
Thermally stable threshold selector based on CuAg alloy for energy-efficient memory and neuromorphic computing applications
Designing efficient selector devices remains a challenge. Here, the authors propose a CuAg alloy-based selector with excellent ON/OFF ratio and thermal stability. It can effectively suppress the sneak-path current in 1S1R arrays, making it suitable for storage class memory and neuromorphic computing applications.
- Xi Zhou
- , Liang Zhao
- & Dongdong Li
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-state data storage in a two-dimensional stripy antiferromagnet implemented by magnetoelectric effect
Multi-state data storage in a two-dimensional stripy antiferromagnet implemented by magnetoelectric effect
In a magneto-electric material, the magnetic and electric properties are coupled. This coupling allows the magnetic order to be controlled by electric stimuli, making magnetoelectric materials promising candidates for new data storage technologies. Here Gu et al demonstrate a magnetoelectric effect in a van der Waals antiferromagnetic CrOCl which persists down to monolayer, and using this realize a multi-state data storage device.
- Pingfan Gu
- , Cong Wang
- & Yu Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Gate-tunable superconducting diode effect in a three-terminal Josephson device
Gate-tunable superconducting diode effect in a three-terminal Josephson device
Non-reciprocal critical current in a Josephson junction device is known as the Josephson diode effect. Here, the authors observe such an effect in 3-terminal Josephson devices based on InAs two-dimensional electron gas proximitized by an epitaxial Al layer.
- Mohit Gupta
- , Gino V. Graziano
- & Vlad S. Pribiag
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable directional photon scattering from a pair of superconducting qubits
Tunable directional photon scattering from a pair of superconducting qubits
The two frequency-modulated superconducting qubits act as a trembling mirror for microwave photons with on-demand tunable directionality.
- Elena S. Redchenko
- , Alexander V. Poshakinskiy
- & Johannes M. Fink
-
Article
| Open Access Field-free spin-orbit torque switching via out-of-plane spin-polarization induced by an antiferromagnetic insulator/heavy metal interface
Field-free spin-orbit torque switching via out-of-plane spin-polarization induced by an antiferromagnetic insulator/heavy metal interface
Electrically switching perpendicular magnetized ferromagnets using spin-orbit torques without assisting magnetic fields is a major goal for spintronics. Recently, several works have proposed using out-of-plane spin polarized currents to achieve this, but these rely on antiferromagnetic metals with low Neel temperatures. Here, Wang et al show that such out-of-plane spin polarization driven switching can be achieved using the interface of an antiferromagnetic insulator and a heavy metal.
- Mengxi Wang
- , Jun Zhou
- & Yong Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Emission enhancement of erbium in a reverse nanofocusing waveguide
Emission enhancement of erbium in a reverse nanofocusing waveguide
Emission enhancement and extraction from quantum emitters is a major challenge for photon sources in e.g. quantum photonic networks. Here the authors propose a broadband waveguide platform which allows to boost, extract, and guide quantum emission within integrated photonic networks.
- Nicholas A. Güsken
- , Ming Fu
- & Rupert F. Oulton
-
Article
| Open Access A sensory memory processing system with multi-wavelength synaptic-polychromatic light emission for multi-modal information recognition
A sensory memory processing system with multi-wavelength synaptic-polychromatic light emission for multi-modal information recognition
Multimodal cognitive computing task is an important research content in the field of AI. Here, the authors propose an efficient sensory memory processing system, which can process sensory information and generate synapse-like and multiwavelength light-emitting output for efficient multimodal information recognition.
- Liuting Shan
- , Qizhen Chen
- & Huipeng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Probing spin dynamics of ultra-thin van der Waals magnets via photon-magnon coupling
Probing spin dynamics of ultra-thin van der Waals magnets via photon-magnon coupling
van der Waals magnetic materials, which retain magnetism down to a single two-dimensional layer of atoms, have great technological potential for spin-based information processing, however, typical approaches to measure their spin dynamics are often hampered by the small number of spins in a single atomic layer compared to three dimensional materials. Here, Zollitsch et al present a methodology for the detection of spin dynamics in van der Waals magnets via photon-magnon coupling between it and a superconducting resonator, with potential to resolve spin dynamics down to a single monolayer.
- Christoph W. Zollitsch
- , Safe Khan
- & Hidekazu Kurebayashi
-
Article
| Open Access High-efficiency and stable short-delayed fluorescence emitters with hybrid long- and short-range charge-transfer excitations
High-efficiency and stable short-delayed fluorescence emitters with hybrid long- and short-range charge-transfer excitations
To possess a small singlet-triplet energy gap and a large oscillator strength simultaneously is critical for efficient thermally activated delayed fluorescent emitters. Here, the authors attach an multiresonance-acceptor onto a sterically-uncrowded donor for realizing a device efficiency of 40.4%.
- Guoyun Meng
- , Hengyi Dai
- & Lian Duan
-
Review Article
| Open Access How to characterize figures of merit of two-dimensional photodetectors
How to characterize figures of merit of two-dimensional photodetectors
The lack of a standardized approach for the characterization of the performance of 2D photodetectors represents an important obstacle towards their industrialization. Here, the authors propose practical guidelines to characterize their figures of merit and analyse common situations where their performance can be misestimated.
- Fang Wang
- , Tao Zhang
- & Weida Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Superfluid response of an atomically thin gate-tuned van der Waals superconductor
Superfluid response of an atomically thin gate-tuned van der Waals superconductor
Superconductivity has been discovered in atomically thin two-dimensional van der Waals materials by resistance measurements, but magnetic measurements are lacking. Here, the authors use a micron-scale SQUID magnetometer to measure the superfluid response of exfoliated MoS2.
- Alexander Jarjour
- , G. M. Ferguson
- & Katja C. Nowack
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance vertical field-effect organic photovoltaics
High-performance vertical field-effect organic photovoltaics
The device efficiency of organic solar cells is usually limited by the inherent energy loss during carrier transport. Here, authors integrate bulk heterojunction organic photovoltaic with vertical field effect transistor, leading to reduced energy loss below 0.2 eV as controlled by the gate voltage.
- Xiaomin Wu
- , Changsong Gao
- & Huipeng Chen
-
Article
| Open Access A self-adaptive hardware with resistive switching synapses for experience-based neurocomputing
A self-adaptive hardware with resistive switching synapses for experience-based neurocomputing
A big challenge for artificial intelligence is to gain the ability of learning by experience like biological systems. Here Bianchi et al. propose a hardware neural network based on resistive-switching synaptic arrays which dynamically adapt to the environment for autonomous exploration.
- S. Bianchi
- , I. Muñoz-Martin
- & D. Ielmini
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanical overtone frequency combs
Mechanical overtone frequency combs
The authors combined optical traps and frequency combs to create new acoustic technology – a mechanical frequency comb. The generation of this comb does not require any precision control, making it uniquely positioned for sensing, metrology, and quantum technology.
- Matthijs H. J. de Jong
- , Adarsh Ganesan
- & Richard A. Norte
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-micron spin-based magnetic field imaging with an organic light emitting diode
Sub-micron spin-based magnetic field imaging with an organic light emitting diode
Previous demonstrations of electrically and optically detected magnetic resonance in OLED materials have established these systems as promising candidates for magnetic field sensing. Here the authors present an integrated OLED-based device for magnetic field imaging with sub-micron resolution.
- Rugang Geng
- , Adrian Mena
- & Dane R. McCamey
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid spin Hall nano-oscillators based on ferromagnetic metal/ferrimagnetic insulator heterostructures
Hybrid spin Hall nano-oscillators based on ferromagnetic metal/ferrimagnetic insulator heterostructures
Spin-hall nano-oscillators have potential for use in neuromorphic computing applications. Normally they are based around combination platinum and permalloy. Here, the authors combine a permalloy ferromagnet with a low magnetic damping ferrimagnet, leading to significantly improved performance.
- Haowen Ren
- , Xin Yu Zheng
- & Andrew D. Kent
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum enhanced radio detection and ranging with solid spins
Quantum enhanced radio detection and ranging with solid spins
Quantum sensors based on NV centers in diamond are well established, however the sensitivity of detection of high-frequency radio signals has been limited. Here the authors use nanoscale field-focusing to enhance sensitivity and demonstrate ranging for GHz radio signals in an interferometer set-up.
- Xiang-Dong Chen
- , En-Hui Wang
- & Fang-Wen Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale imaging of super-high-frequency microelectromechanical resonators with femtometer sensitivity
Nanoscale imaging of super-high-frequency microelectromechanical resonators with femtometer sensitivity
Implementing MEMS resonators calls for detailed microscopic understanding of the devices and imperfections from microfabrication. Lee et al. imaged super-high-frequency acoustic resonators with a spatial resolution of 100 nm and a displacement sensitivity of 10 fm/√Hz. Individual overtones, spurious modes, and acoustic leakage are also visualized and analyzed.
- Daehun Lee
- , Shahin Jahanbani
- & Keji Lai

 Thermal and electrostatic tuning of surface phonon-polaritons in LaAlO3/SrTiO3 heterostructures
Thermal and electrostatic tuning of surface phonon-polaritons in LaAlO3/SrTiO3 heterostructures