Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access De novo identification of essential protein domains from CRISPR-Cas9 tiling-sgRNA knockout screens
De novo identification of essential protein domains from CRISPR-Cas9 tiling-sgRNA knockout screens
Tiling-sgRNA designs allow the in situ evaluation of protein domain functions. Here the authors present ProTiler - a computational method to predict CRISPR knockout hyper-sensitive regions, revealing previously unannotated domains.
- Wei He
- , Liang Zhang
- & Han Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Strain-level metagenomic assignment and compositional estimation for long reads with MetaMaps
Strain-level metagenomic assignment and compositional estimation for long reads with MetaMaps
Sequencing platforms, such as Oxford Nanopore or Pacific Biosciences generate long-read data that preserve long-range genomic information but have high error rates. Here, the authors develop MetaMaps, a computational tool for strain-level metagenomic assignment and compositional estimation using long reads.
- Alexander T. Dilthey
- , Chirag Jain
- & Adam M. Phillippy
-
Article
| Open Access A tessellation-based colocalization analysis approach for single-molecule localization microscopy
A tessellation-based colocalization analysis approach for single-molecule localization microscopy
Multicolour single-molecule localization microscopy lacks a standard analysis method. Here Levet et al. introduce Coloc-Tesseler, a parameter-free colocalisation analysis method based on tessellation analysis for the efficient analysis of multicolour SMLM data.
- Florian Levet
- , Guillaume Julien
- & Jean-Baptiste Sibarita
-
Article
| Open Access Complete deconvolution of cellular mixtures based on linearity of transcriptional signatures
Complete deconvolution of cellular mixtures based on linearity of transcriptional signatures
Complete gene expression deconvolution remains a challenging problem. Here, the authors provide a solution based on the recognition that expression levels of cell type specific genes are mutually linear across mixtures and mutually linear gene clusters correspond to cell type-specific signatures.
- Konstantin Zaitsev
- , Monika Bambouskova
- & Maxim N. Artyomov
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell trajectories reconstruction, exploration and mapping of omics data with STREAM
Single-cell trajectories reconstruction, exploration and mapping of omics data with STREAM
The increasing accessibility of single cell omics technologies beyond transcriptomics demands parallel advances in analysis. Here, the authors introduce STREAM, a pipeline for reconstruction and visualization of differentiation trajectories from both single-cell RNA-seq and ATAC-seq data.
- Huidong Chen
- , Luca Albergante
- & Luca Pinello
-
Article
| Open Access Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets
Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets
With the increasing obtainability of multi-OMICs data comes the need for easy to use data analysis tools. Here, the authors introduce Metascape, a biologist-oriented portal that provides a gene list annotation, enrichment and interactome resource and enables integrated analysis of multi-OMICs datasets.
- Yingyao Zhou
- , Bin Zhou
- & Sumit K. Chanda
-
Article
| Open Access Topological scoring of protein interaction networks
Topological scoring of protein interaction networks
Inferring direct protein−protein interactions (PPIs) and modules in PPI networks remains a challenge. Here, the authors introduce an algorithm to infer potential direct PPIs from quantitative proteomic AP-MS data by identifying enriched interactions of each bait relative to the other baits.
- Mihaela E. Sardiu
- , Joshua M. Gilmore
- & Michael P. Washburn
-
Article
| Open Access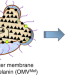 Bioengineered bacterial vesicles as biological nano-heaters for optoacoustic imaging
Bioengineered bacterial vesicles as biological nano-heaters for optoacoustic imaging
Bacterial outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) are increasingly used as carriers for drug delivery. Here the authors encapsulate biopolymer melanin into OMVs, extending their use to optoacoustic imaging both in vitro and in vivo, and demonstrate the potential of this tool for photothermal therapy applications.
- Vipul Gujrati
- , Jaya Prakash
- & Vasilis Ntziachristos
-
Article
| Open Access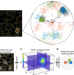 Ultrafast data mining of molecular assemblies in multiplexed high-density super-resolution images
Ultrafast data mining of molecular assemblies in multiplexed high-density super-resolution images
Analyzing the organization of molecular complexes in multi-color single-molecule localization microscopy data requires heavy computation resources that are impractical for laboratory computers. Here the authors develop a coordinate-based Triple-Correlation algorithm with improved speed and reduced computational cost.
- Yandong Yin
- , Wei Ting Chelsea Lee
- & Eli Rothenberg
-
Article
| Open Access Why rankings of biomedical image analysis competitions should be interpreted with care
Why rankings of biomedical image analysis competitions should be interpreted with care
Biomedical image analysis challenges have increased in the last ten years, but common practices have not been established yet. Here the authors analyze 150 recent challenges and demonstrate that outcome varies based on the metrics used and that limited information reporting hampers reproducibility.
- Lena Maier-Hein
- , Matthias Eisenmann
- & Annette Kopp-Schneider
-
Article
| Open Access Improved estimation of cancer dependencies from large-scale RNAi screens using model-based normalization and data integration
Improved estimation of cancer dependencies from large-scale RNAi screens using model-based normalization and data integration
Integrated analyses of multiple large-scale screenings can be complicated by batch effects and technical artefacts. McFarland et al. introduce DEMETER2, a hierarchical model coupled with model-based normalization, which allows the assessment of differential dependencies across genes and cell lines.
- James M. McFarland
- , Zandra V. Ho
- & Aviad Tsherniak
-
Article
| Open Access Functional equivalence of genome sequencing analysis pipelines enables harmonized variant calling across human genetics projects
Functional equivalence of genome sequencing analysis pipelines enables harmonized variant calling across human genetics projects
Sharing of whole genome sequencing (WGS) data improves study scale and power, but data from different groups are often incompatible. Here, US genome centers and NIH programs define WGS data processing standards and a flexible validation method, facilitating collaboration in human genetics research.
- Allison A. Regier
- , Yossi Farjoun
- & Ira M. Hall
-
Article
| Open Access LISA improves statistical analysis for fMRI
LISA improves statistical analysis for fMRI
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) is a powerful technique for measuring human brain activity, but the statistical analysis of fMRI data can be difficult. Here, the authors introduce a new fMRI analysis tool, LISA, which provides increased statistical power compared to existing techniques.
- Gabriele Lohmann
- , Johannes Stelzer
- & Klaus Scheffler
-
Article
| Open Access GraphDDP: a graph-embedding approach to detect differentiation pathways in single-cell-data using prior class knowledge
GraphDDP: a graph-embedding approach to detect differentiation pathways in single-cell-data using prior class knowledge
Inference and representation of differentiation trajectories from single cell RNA-seq data remains a challenge. Here, the authors offer a visualization approach that captures both continuous differentiation trajectories and discrete clusters representing metastable states along the trajectories.
- Fabrizio Costa
- , Dominic Grün
- & Rolf Backofen
-
Article
| Open Access Detection and removal of barcode swapping in single-cell RNA-seq data
Detection and removal of barcode swapping in single-cell RNA-seq data
DNA barcode swapping results in mislabelling of sequencing reads between multiplexed samples. Here, the authors investigate the severity and consequences of barcode swapping for single-cell RNA-seq data, and develop a computational method to exclude swapped reads.
- Jonathan A. Griffiths
- , Arianne C. Richard
- & John C. Marioni
-
Article
| Open Access Massive mining of publicly available RNA-seq data from human and mouse
Massive mining of publicly available RNA-seq data from human and mouse
Publicly available RNA-seq data is provided mostly in raw form, resulting in a barrier for integrative analyses. Here, Lachmann et al. develop a high-throughput processing infrastructure and search database (ARCHS4) that provides processed RNA-seq data for 187,946 publicly available mouse and human samples to support exploration and reuse.
- Alexander Lachmann
- , Denis Torre
- & Avi Ma’ayan
-
Article
| Open Access High-throughput immune repertoire analysis with IGoR
High-throughput immune repertoire analysis with IGoR
B and T cell receptor diversity can be studied by high-throughput immune receptor sequencing. Here, the authors develop a software tool, IGoR, that calculates the likelihoods of potential V(D)J recombination and somatic hypermutation scenarios from raw immune sequence reads.
- Quentin Marcou
- , Thierry Mora
- & Aleksandra M. Walczak
-
Article
| Open Access Probability of phenotypically detectable protein damage by ENU-induced mutations in the Mutagenetix database
Probability of phenotypically detectable protein damage by ENU-induced mutations in the Mutagenetix database
Programs such as PolyPhen-2 predict the relative severity of damage by missense mutations. Here, Wang et al estimate probabilities that putative null or missense alleles would reduce protein function to cause detectable phenotype by analyzing data from ENU-induced mouse mutations.
- Tao Wang
- , Chun Hui Bu
- & Bruce Beutler
-
Article
| Open Access Post-transcriptional 3´-UTR cleavage of mRNA transcripts generates thousands of stable uncapped autonomous RNA fragments
Post-transcriptional 3´-UTR cleavage of mRNA transcripts generates thousands of stable uncapped autonomous RNA fragments
Most mammalian genes contain alternative polyadenylation sites. Here, the authors provide evidence that mRNA can be cleaved post-transcriptionally to generate mRNAs with shorter 3-´UTRs and stable autonomous uncapped 3´-UTR sequences.
- Yuval Malka
- , Avital Steiman-Shimony
- & Michael Berger
-
Article
| Open Access Algorithm for post-clustering curation of DNA amplicon data yields reliable biodiversity estimates
Algorithm for post-clustering curation of DNA amplicon data yields reliable biodiversity estimates
A central problem in biodiversity estimation from genetic markers is the ability of algorithms to retain ‘true’ species while discarding artefacts. Here, the authors present a new post-clusturing curation algorithm using OTU co-occurrences to estimate plant biodiversity from soil samples.
- Tobias Guldberg Frøslev
- , Rasmus Kjøller
- & Anders Johannes Hansen
-
Article
| Open Access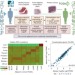 Comprehensive analysis of normal adjacent to tumor transcriptomes
Comprehensive analysis of normal adjacent to tumor transcriptomes
Normal tissue adjacent to the tumour (NAT) is often used as a control in cancer studies. Here, the authors analyse across cancer types the transcriptomes of healthy, NAT, and tumour tissues, and find that NAT presents a unique state, potentially due to inflammatory response of the NAT to the tumour tissue.
- Dvir Aran
- , Roman Camarda
- & Atul J. Butte
-
Article
| Open Access Accurate immune repertoire sequencing reveals malaria infection driven antibody lineage diversification in young children
Accurate immune repertoire sequencing reveals malaria infection driven antibody lineage diversification in young children
Somatic hypermutation of antibodies can occur in infants but are difficult to track. Here the authors present a new method called MIDCIRS for deep quantitative repertoire sequencing with few cells, and show infants as young as 3 months can expand antibody lineage complexity in response to malaria infection.
- Ben S. Wendel
- , Chenfeng He
- & Ning Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access A hybrid cloud read aligner based on MinHash and kmer voting that preserves privacy
A hybrid cloud read aligner based on MinHash and kmer voting that preserves privacy
Outsourcing computation for genomic data processing offers the ability to allocate massive computing power and storage on demand. Here, Popic and Batzoglou develop a hybrid cloud aligner for sequence read mapping that preserves privacy with competitive accuracy and speed.
- Victoria Popic
- & Serafim Batzoglou
-
Article
| Open Access Subsampling scaling
Subsampling scaling
We can often observe only a small fraction of a system, which leads to biases in the inference of its global properties. Here, the authors develop a framework that enables overcoming subsampling effects, apply it to recordings from developing neural networks, and find that neural networks become critical as they mature.
- A. Levina
- & V. Priesemann
-
Article
| Open Access In silico Pathway Activation Network Decomposition Analysis (iPANDA) as a method for biomarker development
In silico Pathway Activation Network Decomposition Analysis (iPANDA) as a method for biomarker development
Pathway analysis aids interpretation of large-scale gene expression data, but existing algorithms fall short of providing robust pathway identification. The method introduced here includes coexpression analysis and gene importance estimation to robustly identify relevant pathways and biomarkers for patient stratification.
- Ivan V. Ozerov
- , Ksenia V. Lezhnina
- & Alex Zhavoronkov
-
Article
| Open Access Comparative survey of the relative impact of mRNA features on local ribosome profiling read density
Comparative survey of the relative impact of mRNA features on local ribosome profiling read density
Ribosome profiling data can suffer from uneven coverage which hampers estimation of elongation rates. Connor et al.present an enhanced data smoothing method for Ribo-seq data and highlight significant variability in sequence determinants of ribosome density in publicly available data sets.
- Patrick B. F. O’Connor
- , Dmitry E. Andreev
- & Pavel V. Baranov
-
Article
| Open Access Extraction and analysis of signatures from the Gene Expression Omnibus by the crowd
Extraction and analysis of signatures from the Gene Expression Omnibus by the crowd
A wealth of gene expression data is publicly available, yet is little use without additional human curation. Ma’ayan and colleagues report a crowdsourcing project involving over 70 participants to annotate and analyse thousands of human disease-related gene expression datasets.
- Zichen Wang
- , Caroline D. Monteiro
- & Avi Ma’ayan
-
Article
| Open Access reChIP-seq reveals widespread bivalency of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 in CD4+ memory T cells
reChIP-seq reveals widespread bivalency of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 in CD4+ memory T cells
Co-localizing chromatin modifications and regulators can exert a combinatorial effect on chromatin structure and function. Here the authors describe reChIP-seq and normR to identify co-localizing proteins in an unbiased genome-wide manner.
- Sarah Kinkley
- , Johannes Helmuth
- & Ho-Ryun Chung
-
Article
| Open Access Information processing using a single dynamical node as complex system
Information processing using a single dynamical node as complex system
The paradigm of reservoir computing shows that, like the human brain, complex networks can perform efficient information processing. Here, a simple delay dynamical system is demonstrated that can efficiently perform computations capable of replacing a complex network in reservoir computing.
- L. Appeltant
- , M.C. Soriano
- & I. Fischer

 A systematic evaluation of single cell RNA-seq analysis pipelines
A systematic evaluation of single cell RNA-seq analysis pipelines