Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Leukaemia cell of origin identified by chromatin landscape of bulk tumour cells
Leukaemia cell of origin identified by chromatin landscape of bulk tumour cells
A tumour’s cell of origin may influence tumour progression and response to therapy. Here, the authors demonstrate that the cell of origin determines the aggressiveness of AML in a mouse model and identify unique biomarkers of the specific leukaemia cell of origin by profiling open chromatin regions of AML samples.
- Joshy George
- , Asli Uyar
- & Jennifer J. Trowbridge
-
Article
| Open Access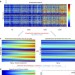 Early role of vascular dysregulation on late-onset Alzheimer’s disease based on multifactorial data-driven analysis
Early role of vascular dysregulation on late-onset Alzheimer’s disease based on multifactorial data-driven analysis
Late-onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD) is a complex multi-factorial disorder. Here, the authors perform a data-driven analysis of LOAD progression, including multimodal brain imaging, plasma and CSF biomarkers, and find vascular dysfunction is among the earliest and strongest altered events.
- Y. Iturria-Medina
- , R. C. Sotero
- & Ansgar J. Furst
-
Article
| Open Access Translation control during prolonged mTORC1 inhibition mediated by 4E-BP3
Translation control during prolonged mTORC1 inhibition mediated by 4E-BP3
The eIF4E-binding proteins (4E-BPs) are critical repressors of cap-dependent translation via mTOR, a pathway frequently hyperactivated in cancer. Here the authors show that 4E-BP3 specifically mediates the cap-dependent translation repression and antiproliferative effects of prolonged pharmacological mTOR inhibition.
- Yoshinori Tsukumo
- , Tommy Alain
- & Nahum Sonenberg
-
Article
| Open Access Exosomal microRNA miR-92a concentration in serum reflects human brown fat activity
Exosomal microRNA miR-92a concentration in serum reflects human brown fat activity
Exosomes are RNA-containing lipid vesicles with roles in inter-tissue crosstalk. Here the authors show that exosome release from brown adipocytes is increased upon thermogenic activation, both in vitro and in vivo, and demonstrate that serum levels of exosomal miR-92 reflect brown fat activity in humans.
- Yong Chen
- , Joschka J. Buyel
- & Alexander Pfeifer
-
Article
| Open Access Blood-based biomarkers of age-associated epigenetic changes in human islets associate with insulin secretion and diabetes
Blood-based biomarkers of age-associated epigenetic changes in human islets associate with insulin secretion and diabetes
Aging is associated with impaired pancreatic islet function, increased risk of type 2 diabetes, and changes in DNA methylation. Here the authors find blood-based biomarkers that reflect age-associated DNA methylation changes in human pancreatic islets associated with insulin secretion and diabetes.
- Karl Bacos
- , Linn Gillberg
- & Charlotte Ling
-
Article
| Open Access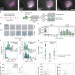 Single-cell differences in matrix gene expression do not predict matrix deposition
Single-cell differences in matrix gene expression do not predict matrix deposition
Regenerative tissue engineering with mesenchymal stem cells is hampered by bulk methods of assessing differentiation status and a general assumption that expression of individual markers of stem cell differentiation correlate with functional capacity. Here the authors debunk this assumption by applying single-cell techniques to disassociate aggrecan mRNA abundance and matrix deposition.
- Allison J. Cote
- , Claire M. McLeod
- & Robert L. Mauck
-
Article
| Open Access Common and rare variants associating with serum levels of creatine kinase and lactate dehydrogenase
Common and rare variants associating with serum levels of creatine kinase and lactate dehydrogenase
Creatine kinase (CK) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) are biomarkers of tissue damages including myopathy and myocardial infarction. Here, Patrick Sulem and colleagues perform a genome-wide association study to identify common and rare genetic variants that associates with serum CK or LDH levels.
- Ragnar P. Kristjansson
- , Asmundur Oddsson
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article
| Open Access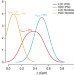 Non-CG DNA methylation is a biomarker for assessing endodermal differentiation capacity in pluripotent stem cells
Non-CG DNA methylation is a biomarker for assessing endodermal differentiation capacity in pluripotent stem cells
The methylation of non-CpG residues is a poorly understood marker of pluripotent cells, gradually lost as cells differentiate. Here the authors show non-CG methylation can be used as a marker of differentiation potential.
- Lee M. Butcher
- , Mitsuteru Ito
- & Stephan Beck
-
Article
| Open Access Frequent alterations in cytoskeleton remodelling genes in primary and metastatic lung adenocarcinomas
Frequent alterations in cytoskeleton remodelling genes in primary and metastatic lung adenocarcinomas
Despite lung adenocarcinoma having a high global mortality, the genetic mutations present in Asian patients are uncharacterized. Here the authors use genomic and transcriptomic analysis to identify thirteen significantly affected genes, including RHPN2, GLI3, MRC2, TP53 and IQGAP3.
- Kui Wu
- , Xin Zhang
- & Jianxing He
-
Article
| Open Access Fibrocyte-like cells mediate acquired resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy with bevacizumab
Fibrocyte-like cells mediate acquired resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy with bevacizumab
Acquired resistance to anti-angiogenic drugs, including bevacizumab, may occur in cancer patients. In this study the authors identify in the tumour microenvironment, fibrocyte-like cells derived from the bone marrow that mediate the resistance to bevacizumab through the production of FGF2.
- Atsushi Mitsuhashi
- , Hisatsugu Goto
- & Yasuhiko Nishioka
-
Article
| Open Access Cerebrospinal fluid-derived circulating tumour DNA better represents the genomic alterations of brain tumours than plasma
Cerebrospinal fluid-derived circulating tumour DNA better represents the genomic alterations of brain tumours than plasma
DNA circulating in the plasma of cancer patients carries features of the primary tumour, however such DNA is found in low levels in brain cancer patients. Here, the authors show that circulating tumour DNA can be detected in the cerebral spinal fluid of cancer patients and that this better recapitulates the primary tumour compared to DNA from the plasma.
- Leticia De Mattos-Arruda
- , Regina Mayor
- & Joan Seoane
-
Article
| Open Access MAP3K8/TPL-2/COT is a potential predictive marker for MEK inhibitor treatment in high-grade serous ovarian carcinomas
MAP3K8/TPL-2/COT is a potential predictive marker for MEK inhibitor treatment in high-grade serous ovarian carcinomas
The identification of pharmaceutically targetable biomarkers is essential for improving therapeutic options for cancer patients. In this study, the authors identify MAP3K8 as a potential predictive marker for MEK inhibitor treatment in patients with aggressive ovarian cancer.
- Tina Gruosso
- , Camille Garnier
- & Fatima Mechta-Grigoriou
-
Article
| Open Access Immunological biomarkers predict HIV-1 viral rebound after treatment interruption
Immunological biomarkers predict HIV-1 viral rebound after treatment interruption
In some HIV-1-infected individuals, viraemia remains undetectable after antiretroviral treatment, but which of these patients will experience viral rebound is difficult to predict. Here the authors show that T cell exhaustion markers before treatment are predictive of shorter time to viral rebound.
- Jacob Hurst
- , Matthias Hoffmann
- & John Frater
-
Article
| Open Access EZH2-mediated loss of miR-622 determines CXCR4 activation in hepatocellular carcinoma
EZH2-mediated loss of miR-622 determines CXCR4 activation in hepatocellular carcinoma
Chemokines and their receptors have key roles in tumorigenesis. Here, the authors demonstrate that CXRC4 is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and is associated with poor prognosis and, mechanistically CXCR4 is increased in expression via EZH2 repression of microRNA-622.
- Haiou Liu
- , Yidong Liu
- & Jiejie Xu
-
Article
| Open Access STAT3 regulated ARF expression suppresses prostate cancer metastasis
STAT3 regulated ARF expression suppresses prostate cancer metastasis
IL6-STAT3 signaling is activated in prostate cancer, however inhibiting this pathway has not lead to a survival advantage in patients. Here, Pencik et al.show that loss of the IL6-STAT3 axis in mice and humans leads to metastasis due to loss of ARF, unravelling STAT3 and ARF as potential prognostic markers in prostate cancer.
- Jan Pencik
- , Michaela Schlederer
- & Lukas Kenner
-
Article
| Open Access Desialylation is a mechanism of Fc-independent platelet clearance and a therapeutic target in immune thrombocytopenia
Desialylation is a mechanism of Fc-independent platelet clearance and a therapeutic target in immune thrombocytopenia
Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is caused by autoantibody-mediated platelet clearance, but refractoriness to current immunomodulatory therapies is common. Here the authors show that desialylated platelets can be cleared via hepatic Ashwell–Morell receptor, a process that can be attenuated by sialidase inhibitors, suggesting a new therapy for ITP.
- June Li
- , Dianne E. van der Wal
- & Heyu Ni
-
Article
| Open Access UCHL1 provides diagnostic and antimetastatic strategies due to its deubiquitinating effect on HIF-1α
UCHL1 provides diagnostic and antimetastatic strategies due to its deubiquitinating effect on HIF-1α
When stabilized, HIF-1 can activate adaptation to hypoxia and metastasis. Here the authors show that upregulation of Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase-L1 in human cancers promotes metastasis and correlates with poor prognosis because of its role in opposing ubiquitin-mediated degradation of HIF-1.
- Yoko Goto
- , Lihua Zeng
- & Hiroshi Harada
-
Article |
 Low MITF/AXL ratio predicts early resistance to multiple targeted drugs in melanoma
Low MITF/AXL ratio predicts early resistance to multiple targeted drugs in melanoma
Increased expression of MITF transcription factor is thought to promote melanoma progression and kinase inhibitor resistance. Here Muller et al. show that MITF loss is also common in melanomas and confers kinase inhibitor resistance due to upregulation of AXL and other receptor tyrosine kinases.
- Judith Müller
- , Oscar Krijgsman
- & Daniel S. Peeper
-
Article
| Open Access Strong effects of genetic and lifestyle factors on biomarker variation and use of personalized cutoffs
Strong effects of genetic and lifestyle factors on biomarker variation and use of personalized cutoffs
Protein biomarkers could play an important role in the diagnosis and management of diseases. Here the authors investigate the impact of genetic, clinical and lifestyle factors on 92 protein biomarkers for cancer and inflammation and suggest that personalized biomarker thresholds should be used in cancer management.
- Stefan Enroth
- , Åsa Johansson
- & Ulf Gyllensten
-
Article
| Open Access Alarmin S100A8/S100A9 as a biomarker for molecular imaging of local inflammatory activity
Alarmin S100A8/S100A9 as a biomarker for molecular imaging of local inflammatory activity
Alarmins are locally released during inflammation and are early amplifiers of inflammation. Here Vogl et al.show that the alarmin S100A8/S100A9 can be used as a sensitive marker to detect subclinical inflammation and follow disease progression in a variety of disease models.
- Thomas Vogl
- , Michel Eisenblätter
- & Johannes Roth
-
Article |
 Angiotensin II plasma levels are linked to disease severity and predict fatal outcomes in H7N9-infected patients
Angiotensin II plasma levels are linked to disease severity and predict fatal outcomes in H7N9-infected patients
An avian influenza H7N9 virus causes severe human disease, including acute and often lethal respiratory failure. Here, the authors report that plasma levels of angiotensin II, a regulatory peptide of the renin–angiotensin system, are associated with disease severity and fatal outcome in infected patients.
- Fengming Huang
- , Jing Guo
- & Lanjuan Li
-
Article
| Open Access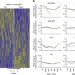 Maternal nutrition at conception modulates DNA methylation of human metastable epialleles
Maternal nutrition at conception modulates DNA methylation of human metastable epialleles
Maternal diet affects DNA methylation in the developing offspring, leading to phenotypic changes. Here, Dominguez-Salas et al. exploit seasonal variation in the diet of Gambian women to show that maternal methyl donor nutrient status around the time of conception predicts methylation levels at metastable epialleles in infants.
- Paula Dominguez-Salas
- , Sophie E. Moore
- & Branwen J. Hennig
-
Article
| Open Access Exhaustion of nucleus pulposus progenitor cells with ageing and degeneration of the intervertebral disc
Exhaustion of nucleus pulposus progenitor cells with ageing and degeneration of the intervertebral disc
Back pain and sciatica are often caused by intervertebral disc degeneration. Sakai and colleagues identify a subset of nucleus pulposus progenitor cells from the intervertebral disc and show that loss of these progenitor cells correlates with ageing and intervertebral disc degeneration.
- Daisuke Sakai
- , Yoshihiko Nakamura
- & Joji Mochida
-
Article |
 Alternative α-synuclein transcript usage as a convergent mechanism in Parkinson's disease pathology
Alternative α-synuclein transcript usage as a convergent mechanism in Parkinson's disease pathology
The protein α-synuclein is implicated in Parkinson's disease. Rhinn and colleagues perform gene expression analysis and find that specific α-synuclein transcripts are preferentially associated with Parkinson's disease, and that they potentiate the accumulation of α-synuclein protein.
- Herve Rhinn
- , Liang Qiang
- & Asa Abeliovich
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of high-quality cancer prognostic markers and metastasis network modules
Identification of high-quality cancer prognostic markers and metastasis network modules
There has been great interest in attempting to identify gene expression signatures that predict cancer survival. In this study a new algorithm is developed to analyse gene expression datasets that accurately classify both ER+ and ER− breast cancers into low- and high-risk groups.
- Jie Li
- , Anne E.G. Lenferink
- & Edwin Wang

 Cutaneous wound healing through paradoxical MAPK activation by BRAF inhibitors
Cutaneous wound healing through paradoxical MAPK activation by BRAF inhibitors