Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial-goosebump-driven microactuation
Artificial-goosebump-driven microactuation
Light-induced artificial goosebumps on liquid crystal elastomer skin are used to precisely manipulate passive microstructures, achieving a localized and controllable system for programmable micromachines.
- Mingchao Zhang
- , Aniket Pal
- & Metin Sitti
-
News & Views |
 A cutting-edge solution for adhesives
A cutting-edge solution for adhesives
Metamaterial adhesives with nonlinear cut architectures provide strong and reversible adhesion, directionality and spatially programmable adhesive strength.
- Geonjun Choi
- & Hoon Eui Jeong
-
Article |
 Operando electron microscopy investigation of polar domain dynamics in twisted van der Waals homobilayers
Operando electron microscopy investigation of polar domain dynamics in twisted van der Waals homobilayers
Polar domains have been observed in twist-stacked van der Waals layers, but their dynamics are unexplored. Here, using operando electron microscopy, it is found that polar domains in an antiferroelectric arrangement cannot transition to a ferroelectric state due to topological protection of the domain wall network.
- Kahyun Ko
- , Ayoung Yuk
- & Hyobin Yoo
-
Perspective |
 Nanocrystal phononics
Nanocrystal phononics
Colloidal nanocrystals can form into periodic superlattices exhibiting collective vibrations from the correlated motion of the nanocrystals. This Perspective discusses such collective vibrations and their as-of-yet untapped potential applications for phononic crystals, acoustic metamaterials and optomechanical systems.
- Maximilian Jansen
- , William A. Tisdale
- & Vanessa Wood
-
-
News & Views |
 Making smarter materials
Making smarter materials
Scientists have designed a foldable, mechanical analogue of integrated circuits that could be used as a platform to fabricate intelligent metamaterials.
- Christian D. Santangelo
-
News & Views |
 Topological properties that can be heard
Topological properties that can be heard
The introduction of crystalline defects experimentally reveals elusive signatures of topological phenomena in acoustic metamaterials.
- Marc Serra-Garcia
-
Editorial |
 Soft features for robotics
Soft features for robotics
Innovations in soft materials design and engineering are delivering promising functional components for advanced soft robotic applications.
-
News & Views |
 Popping, locking robots
Popping, locking robots
An interplay between deswelling and buckling in a polymer gel is harnessed to achieve sequential snap events for repeatable jumping motion, opening the door to autonomously moving soft robots.
- Johannes T. B. Overvelde
-
News & Views |
 The sound of Weyl hinges
The sound of Weyl hinges
Clever 3D-printed acoustic materials allow probing a new higher-order semimetallic topological phase using audible sound.
- R. Fleury
-
Article |
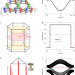 Higher-order topological semimetal in acoustic crystals
Higher-order topological semimetal in acoustic crystals
A second-order topological Weyl semimetal based on a 3D-printed acoustic crystal, exhibiting Weyl points, Fermi arc surface states, and hinge states, has been experimentally demonstrated.
- Qiang Wei
- , Xuewei Zhang
- & Suotang Jia
-
News & Views |
 An aluminium superinductor
An aluminium superinductor
Granular aluminium — a superconductor with high kinetic inductance — has been used to create a superinductor for a fluxonium superconducting qubit.
- Joel I-Jan Wang
- & William D. Oliver
-
Article |
 Shape-encoded dynamic assembly of mobile micromachines
Shape-encoded dynamic assembly of mobile micromachines
Mobile micromachines with advanced configurations and functions self-assembled through designed dielectrophoretic interactions between structural and motor units.
- Yunus Alapan
- , Berk Yigit
- & Metin Sitti
-
Letter |
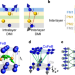 Symmetry-breaking interlayer Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interactions in synthetic antiferromagnets
Symmetry-breaking interlayer Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interactions in synthetic antiferromagnets
An interlayer Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction is observed in a synthetic antiferromagnet, with implications for achieving chiral spin textures in multilayered thin films.
- Amalio Fernández-Pacheco
- , Elena Vedmedenko
- & Russell P. Cowburn
-
News & Views |
 Trapping sound at corners
Trapping sound at corners
Higher-order topological acoustic metamaterials on kagome lattices, which host topologically protected corner states, can confine sound at corners. This may lead to applications of acoustic metamaterials in local acoustic field enhancement, trapping and manipulating of particles, and acoustic sensing and probing.
- Zhengyou Liu
-
Letter |
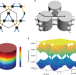 Acoustic higher-order topological insulator on a kagome lattice
Acoustic higher-order topological insulator on a kagome lattice
A second-order topological insulator in an acoustical metamaterial with a breathing kagome lattice, supporting one-dimensional edge states and zero-dimensional corner states is demonstrated.
- Haoran Xue
- , Yahui Yang
- & Baile Zhang
-
Article |
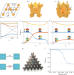 Observation of higher-order topological acoustic states protected by generalized chiral symmetry
Observation of higher-order topological acoustic states protected by generalized chiral symmetry
The physics of a second-order topological insulator, such as two-dimensional polarization, one-dimensional edge states and zero-dimensional corner states, are demonstrated experimentally in an acoustic breathing kagome lattice.
- Xiang Ni
- , Matthew Weiner
- & Alexander B. Khanikaev
-
Perspective |
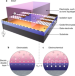 Electrolyte-based ionic control of functional oxides
Electrolyte-based ionic control of functional oxides
Electrolyte gating of complex oxides enables substantial control of electronic phase transitions, allowing electrical control of complex phenomena. Here, the role of both electrostatic and electrochemical mechanisms in this process is elucidated.
- Chris Leighton
-
Article |
 Thermal meta-device in analogue of zero-index photonics
Thermal meta-device in analogue of zero-index photonics
In this type of thermal cloak, when a fluid circulates around the object of interest, the temperature perturbation is minimized as the effective thermal conductivity of the fluid becomes very high due to convective effects.
- Ying Li
- , Ke-Jia Zhu
- & C.-W. Qiu
-
Article |
 On-chip valley topological materials for elastic wave manipulation
On-chip valley topological materials for elastic wave manipulation
Topologically protected edge states can be observed when combining two Si-based phononic crystals of opposite phases, as well as on-chip elastic wave splitting via partition of edges states at the intersection of topological channels.
- Mou Yan
- , Jiuyang Lu
- & Zhengyou Liu
-
Article |
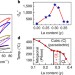 Electrostrain in excess of 1% in polycrystalline piezoelectrics
Electrostrain in excess of 1% in polycrystalline piezoelectrics
Electrostrain, an important value for actuators, larger than 1% is only achieved in single crystals. Here, a pseudo-ternary polycrystalline ferroelectric with spontaneous lattice strain has 1.3% electrostrain, which may enable cheaper piezoelectrics.
- Bastola Narayan
- , Jaskaran Singh Malhotra
- & Rajeev Ranjan
-
Article |
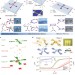 Morphable 3D mesostructures and microelectronic devices by multistable buckling mechanics
Morphable 3D mesostructures and microelectronic devices by multistable buckling mechanics
Reconfigurable electronic devices that can be shaped in two or more stable geometries modifying their functionalities have been realized by engineering the sequence in which the elastomeric substrates are mechanically buckled.
- Haoran Fu
- , Kewang Nan
- & John A. Rogers
-
News & Views |
 Living bandgaps
Living bandgaps
Sound waves drive the organization of particle scatterers into stable structures, exhibiting phononic band gaps that heal from disturbances and adapt to changes in the drive.
- Kyle J. M. Bishop
-
Article |
 Emergence of an enslaved phononic bandgap in a non-equilibrium pseudo-crystal
Emergence of an enslaved phononic bandgap in a non-equilibrium pseudo-crystal
The dynamic self-assembly of a pseudo-crystal, characterized by a phononic bandgap bound to the wavelength of an external coherent driving field.
- Nicolas Bachelard
- , Chad Ropp
- & Xiang Zhang
-
Letter |
 Surface phononic graphene
Surface phononic graphene
An artificial phononic graphene for surface acoustic waves on a LiNbO3 integrated platform allows for the experimental demonstration of pseudo-diffusion transport and a temporal beating effect similar to the ‘Zitterbewegung’ phenomenon.
- Si-Yuan Yu
- , Xiao-Chen Sun
- & Yan-Feng Chen
-
Letter |
 Observation of Aubry-type transition in finite atom chains via friction
Observation of Aubry-type transition in finite atom chains via friction
The transition from superlubricity to stick–slip behaviour of a chain of atoms on a periodic surface has now been directly studied experimentally, related to the Aubry transition.
- Alexei Bylinskii
- , Dorian Gangloff
- & Vladan Vuletić
-
Article |
 Ultra-sparse metasurface for high reflection of low-frequency sound based on artificial Mie resonances
Ultra-sparse metasurface for high reflection of low-frequency sound based on artificial Mie resonances
An ultraslow-fluid-like unit cell composed of acoustic channels, arranged in a zigzag shape, exhibits various tunable Mie resonances. It is used for the construction of a highly reflective metasurface that can efficiently block low-frequency sound.
- Y. Cheng
- , C. Zhou
- & X. J. Liu
-
Progress Article |
 Phonon wave interference and thermal bandgap materials
Phonon wave interference and thermal bandgap materials
Thermal vibrations in materials can be controlled via interference (in a similar way to light propagating in layered structures) to produce a thermal bandgap, an approach promising for thermoelectric applications.
- Martin Maldovan
-
Letter |
 Hybrid optical–electrical detection of donor electron spins with bound excitons in silicon
Hybrid optical–electrical detection of donor electron spins with bound excitons in silicon
A scheme of hybrid optical–electrical detection of an ensemble of donor electrons bound to phosphorus in silicon reveals electron spin Rabi oscillations and long coherence times, setting the foundations for a single-electron spin read-out technique.
- C. C. Lo
- , M. Urdampilleta
- & J. J. L. Morton
-
News & Views |
 Nearly perfect sound absorbers
Nearly perfect sound absorbers
Membrane-based acoustic resonators of subwavelength dimensions achieve nearly perfect acoustic absorption.
- Mathias Fink
-
Article |
 Acoustic metasurface with hybrid resonances
Acoustic metasurface with hybrid resonances
Acoustic impedance-matched surfaces do not reflect incident waves. Traditional means of acoustic absorption have so far resulted in imperfect impedance matching and bulky structures, or require costly and sophisticated electrical design. Inspired by electromagnetic metamaterials, a subwavelength acoustically reflecting surface with hybrid resonances and impedance-matched to airborne sound at tunable frequencies is now demonstrated.
- Guancong Ma
- , Min Yang
- & Ping Sheng
-
-
News & Views |
 Three rules of design
Three rules of design
By following three empirical rules it is possible to design and fabricate magnetic heterostructures or even devices whose magnetization can be controlled by means of circularly polarized femtosecond laser pulses, instead of applied magnetic fields.
- Alexey V. Kimel
-
News & Views |
 Positively 'negative' friction
Positively 'negative' friction
Friction classically decreases with decreasing load. Nanoscale measurements on chemically modified graphite now show an opposite trend related to local deformation, which could serve as a probe for determining the exfoliation energy of layered materials.
- Kathryn J. Wahl

 Giant electron-mediated phononic nonlinearity in semiconductor–piezoelectric heterostructures
Giant electron-mediated phononic nonlinearity in semiconductor–piezoelectric heterostructures Cubic boron arsenide under pressure
Cubic boron arsenide under pressure