Comment |
Featured
-
-
Letter |
 Scalable optical manufacture of dynamic structural colour in stretchable materials
Scalable optical manufacture of dynamic structural colour in stretchable materials
Desired for optical sensing or visual communications, structural colour-changing materials are hindered by the lack of scalable manufacturing. Here, by adapting Lippmann photography, large-area manufacturing of colour patterns in photosensitive elastomers is realized.
- Benjamin Harvey Miller
- , Helen Liu
- & Mathias Kolle
-
Article |
 Efficient and low-voltage vertical organic permeable base light-emitting transistors
Efficient and low-voltage vertical organic permeable base light-emitting transistors
Vertical organic light-emitting transistors are realized by using a porous base electrode in the centre of the device, which improves efficiency and reduces operating voltage by regulating charge transport and forming an optical microcavity.
- Zhongbin Wu
- , Yuan Liu
- & Karl Leo
-
Article |
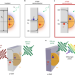 Ultrafast hot-hole injection modifies hot-electron dynamics in Au/p-GaN heterostructures
Ultrafast hot-hole injection modifies hot-electron dynamics in Au/p-GaN heterostructures
Photo-excited gold nanoparticles are shown to provide ultrafast and efficient hot-hole injection to the valence band of p-type GaN, substantially altering hot-electron dynamics in the nanoparticles and forming a basis to design hot-hole-based optoelectronics.
- Giulia Tagliabue
- , Joseph S. DuChene
- & Harry A. Atwater
-
Review Article |
 Nanophotonic engineering of far-field thermal emitters
Nanophotonic engineering of far-field thermal emitters
This Review covers the basic physics of thermal emission, ways to engineer the thermal field radiated by hot objects in the far field and applications, such as thermophotovoltaics, radiative cooling, camouflage and privacy.
- Denis G. Baranov
- , Yuzhe Xiao
- & Mikhail A. Kats
-
Letter |
 Emissive and charge-generating donor–acceptor interfaces for organic optoelectronics with low voltage losses
Emissive and charge-generating donor–acceptor interfaces for organic optoelectronics with low voltage losses
Charge-transfer states with comparable recombination and charge-splitting rates are shown to be a key ingredient for donor–acceptor organic blends that perform well in both light-emitting and photovoltaic applications.
- Sascha Ullbrich
- , Johannes Benduhn
- & Koen Vandewal
-
Article |
 Fully textured monolithic perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells with 25.2% power conversion efficiency
Fully textured monolithic perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells with 25.2% power conversion efficiency
An optimized two-step deposition process allows the formation of uniform layers of metal halide perovskites on textured silicon layers, enabling tandem silicon/perovskite solar cells with improved optical design and efficiency.
- Florent Sahli
- , Jérémie Werner
- & Christophe Ballif
-
Editorial |
 As thin as it gets
As thin as it gets
As the family of 2D materials expands to include transition metal dichalcogenides and Xenes, novel fundamental properties and applications come to light.
-
News & Views |
 Shrinking the camera size
Shrinking the camera size
A miniaturized camera has been developed by integrating a planar metasurface lens doublet with a CMOS image sensor. The metasurface lens doublet corrects the monochromatic aberration and thus delivers nearly diffraction-limited image quality over a wide field of view.
- Cheng Sun
-
Article |
 Solution-based electrical doping of semiconducting polymer films over a limited depth
Solution-based electrical doping of semiconducting polymer films over a limited depth
A solution process for the diffusion of dopants in organic semiconducting films over a limited depth has been developed. The method is applied to single polymers and donor–acceptor mixtures, and for the realization of single-layer solar cells.
- Vladimir A. Kolesov
- , Canek Fuentes-Hernandez
- & Bernard Kippelen
-
Article |
 Direct–indirect character of the bandgap in methylammonium lead iodide perovskite
Direct–indirect character of the bandgap in methylammonium lead iodide perovskite
Time-resolved photo-conductance and microwave conductance investigations reveal that methylammonium lead iodide perovskites have an indirect bandgap at temperatures relevant to photovoltaic applications.
- Eline M. Hutter
- , María C. Gélvez-Rueda
- & Tom J. Savenije
-
Letter |
 A sub-femtojoule electrical spin-switch based on optically trapped polariton condensates
A sub-femtojoule electrical spin-switch based on optically trapped polariton condensates
The spin-switching of optically induced polariton condensates can be externally controlled with an electric field, with switching energies below 0.5 fJ.
- Alexander Dreismann
- , Hamid Ohadi
- & Jeremy J. Baumberg
-
News & Views |
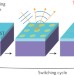 To scatter or not to scatter
To scatter or not to scatter
A rewritable platform for subwavelength optical components is demonstrated by combining surface phonon–polaritons, sustained in a polar dielectric layer, with the switching functionality provided by a phase-change material.
- Isabelle Staude
- & Carsten Rockstuhl
-
Article |
 Reversible optical switching of highly confined phonon–polaritons with an ultrathin phase-change material
Reversible optical switching of highly confined phonon–polaritons with an ultrathin phase-change material
Optically rewritable surface phonon–polariton resonators are demonstrated in a system combining phase-change materials that can reversibly switch between amorphous and crystalline phases, with polar crystals that support surface phonon–polaritons.
- Peining Li
- , Xiaosheng Yang
- & Thomas Taubner
-
Article |
 Exploring the origin of high optical absorption in conjugated polymers
Exploring the origin of high optical absorption in conjugated polymers
The photocurrent generated in organic photodetectors and solar cells can be enhanced by increasing light absorption in the active layer. It is now shown that an extended persistence length can increase the oscillator strength of conjugated polymers.
- Michelle S. Vezie
- , Sheridan Few
- & Jenny Nelson
-
News & Views |
 Hovering solar cells
Hovering solar cells
Ultrathin, flexible and lightweight perovskite solar cells with improved stability in air can now power model airplanes for several hours.
- Michele Sessolo
- & Henk J. Bolink
-
Article |
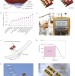 Flexible high power-per-weight perovskite solar cells with chromium oxide–metal contacts for improved stability in air
Flexible high power-per-weight perovskite solar cells with chromium oxide–metal contacts for improved stability in air
The use of a chromium oxide interlayer separating the perovskite film from the metal contacts improves the stability of perovskite solar cells in air. Deposited on thin plastic foils, these ultralight devices power model airplanes and dirigibles.
- Martin Kaltenbrunner
- , Getachew Adam
- & Siegfried Bauer
-
News & Views |
 Framing upconversion materials
Framing upconversion materials
Solid-state organic materials that convert low-power visible light into higher-energy radiation have been synthesized using metal–organic frameworks. This approach could be used to make polymers that increase the efficiency of photovoltaic devices.
- Yoan C. Simon
- & Christoph Weder
-
-
News & Views |
 Perovskite cells charge forward
Perovskite cells charge forward
Now that certified energy conversion efficiencies for perovskite solar cells are above 20%, researchers are exploring other critical areas, such as understanding device hysteresis and film growth, as well as the replacement of lead and the development of tandem cell stacks. Cell stability remains a crucial issue.
- Martin A. Green
- & Thomas Bein
-
-
News & Views |
 Energy transfer is speeded up in 2D
Energy transfer is speeded up in 2D
When efficient energy transfer under high carrier densities is required, two-dimensional nanoplatelets are the material of choice, combining an exceptional suppression of nonlinear fluorescence quenching with ultrafast transfer capabilities.
- Iwan Moreels
-
News & Views |
 Switchable photovoltaics
Switchable photovoltaics
The migration of ions under the effect of an external electric field locally modifies the doping of organometal halide perovskite films. This is used to reversibly switch the photocurrent direction in very simple photovoltaic architectures.
- Nam-Gyu Park
-
News & Views |
 Bringing dark states to light
Bringing dark states to light
Semiconducting quantum dots have been used to harvest triplet excitons produced through singlet fission in organic semiconductors. These hybrid organic–inorganic materials may boost the efficiency of solar cells.
- Christopher J. Bardeen
-
Article |
 Energy harvesting of non-emissive triplet excitons in tetracene by emissive PbS nanocrystals
Energy harvesting of non-emissive triplet excitons in tetracene by emissive PbS nanocrystals
Lead sulphide colloidal nanocrystals are now used to harvest non-emissive triplet excitons generated in a tetracene layer. Depending on the length of the ligands capping the nanocrystals, exciton transfer efficiency as high as 90% can be achieved.
- Nicholas J. Thompson
- , Mark W. B. Wilson
- & Marc A. Baldo
-
Letter |
 Redox shuttle mechanism enhances photocatalytic H2 generation on Ni-decorated CdS nanorods
Redox shuttle mechanism enhances photocatalytic H2 generation on Ni-decorated CdS nanorods
Photocatalytic efficiency can be limited by slow transfer of photoexcited holes and high charge recombination rates. Using a hydroxyl anion–radical redox couple leads to enhanced photocatalytic H2 generation on Ni-decorated CdS nanorods.
- Thomas Simon
- , Nicolas Bouchonville
- & Jochen Feldmann
-
Letter |
 Printing-based assembly of quadruple-junction four-terminal microscale solar cells and their use in high-efficiency modules
Printing-based assembly of quadruple-junction four-terminal microscale solar cells and their use in high-efficiency modules
A strategy to overcome the maximum theoretical efficiency limit of single-junction solar cells is to realize stacked, multi-junction cells that are used under highly concentrated light. Now, a printing-based, scalable approach for the assembly of multi-junction solar cells in concentrator photovoltaic modules that reach a high power conversion efficiency is reported.
- Xing Sheng
- , Christopher A. Bower
- & John A. Rogers
-
News & Views |
 Electric fields line up graphene oxide
Electric fields line up graphene oxide
The macroscopic alignment of dilute dispersions of graphene oxide can be controlled, with extremely large optical sensitivity, through the application of weak electric fields.
- Ju Young Kim
- & Sang Ouk Kim
-
Correspondence |
Reply to 'On the thermodynamics of light trapping in solar cells'
- Harry A. Atwater
- & Albert Polman
-
News & Views |
 An adaptive junction
An adaptive junction
The energetic and kinetic behaviours of water-oxidation catalysts deposited on semiconductor electrodes are probed in situ, elucidating the junction formed between them, and transforming the design principles of the catalysts.
- Thomas W. Hamann
-
Article |
 Efficient charge generation by relaxed charge-transfer states at organic interfaces
Efficient charge generation by relaxed charge-transfer states at organic interfaces
The efficiency of organic blends used for photovoltaic applications depends on their ability to convert photoexcited charges into free holes and electrons. It is now demonstrated that the lowermost energetic states formed at the donor/acceptor interface can reach conversion efficiencies close to 100%, and therefore do not behave as traps for charge carriers.
- Koen Vandewal
- , Steve Albrecht
- & Alberto Salleo
-
-
-
Article |
 H2 evolution at Si-based metal–insulator–semiconductor photoelectrodes enhanced by inversion channel charge collection and H spillover
H2 evolution at Si-based metal–insulator–semiconductor photoelectrodes enhanced by inversion channel charge collection and H spillover
Photoelectrochemical water-splitting is a promising route for the renewable production of hydrogen, but trade-offs between photoelectrode stability and efficiency remain problematic. A metal–oxide–semiconductor photoelectrode architecture demonstrates stable and efficient water splitting using narrow-bandgap semiconductors. Substantial improvement in the performance of Si-based photocathodes is achieved by combining a high-quality SiO2 layer and bilayer metal catalysts.
- Daniel V. Esposito
- , Igor Levin
- & A. Alec Talin
-
-
News & Views |
 Some like it hot
Some like it hot
Excitation of organic donor–acceptor systems with high-energy light can produce hot charge-transfer states that are delocalized across the heterojunction and readily dissociate. Two studies now reveal the dynamics of this process and pave the way towards unravelling the details of the molecular landscape that favours fast photocarrier generation.
- Carlos Silva
-
Letter |
 Hot exciton dissociation in polymer solar cells
Hot exciton dissociation in polymer solar cells
The standard picture of organic photovoltaics predicts that excitons, which are created under light irradiation, thermalize before dissociation into free electrons and holes. Experimental results and calculations on a low-bandgap polymer–fullerene blend now illustrate the dynamics of hot charge-transfer states and their contribution to charge generation in bulk heterojunctions.
- G. Grancini
- , M. Maiuri
- & G. Lanzani
-
Article |
 Hot charge-transfer excitons set the time limit for charge separation at donor/acceptor interfaces in organic photovoltaics
Hot charge-transfer excitons set the time limit for charge separation at donor/acceptor interfaces in organic photovoltaics
Photocurrent generation in organic solar cells relies on the dissociation of excitons into free electrons and holes at donor/acceptor heterointerfaces. Femtosecond spectroscopy and non-adiabatic simulations on the phthalocyanine–fullerene model system now reveal the relaxation dynamics of hot charge-transfer excitons in this process.
- Askat E. Jailaubekov
- , Adam P. Willard
- & X-Y. Zhu
-
Letter |
 Tightly bound trions in monolayer MoS2
Tightly bound trions in monolayer MoS2
The appealing electronic properties of the monolayer semiconductor molybdenum disulphide make it a candidate material for electronic devices. The observation of tightly bound trions in this system—which have no analogue in conventional semiconductors—opens up possibilities for controlling these quasiparticles in future optoelectronic applications.
- Kin Fai Mak
- , Keliang He
- & Jie Shan
-
Article |
 Tailored exciton diffusion in organic photovoltaic cells for enhanced power conversion efficiency
Tailored exciton diffusion in organic photovoltaic cells for enhanced power conversion efficiency
Photoconversion in organic photovoltaic cells, which relies on charge generation at donor/acceptor interfaces, is limited by short exciton-diffusion-lengths. Diluting an electron donor into a wide-energy-gap host material has now led to an ~50% increase in exciton diffusion length and enhanced power conversion efficiencies in planar heterojunction cells compared with optimized devices with an undiluted donor layer.
- S. Matthew Menke
- , Wade A. Luhman
- & Russell J. Holmes
-
Correspondence |
 Progress towards an all-renewable electricity supply
Progress towards an all-renewable electricity supply
- Keith Barnham
- , Kaspar Knorr
- & Massimo Mazzer
-
Review Article |
 From metamaterials to metadevices
From metamaterials to metadevices
Metamaterials are man-made structures that allow optical properties to be shaped on length scales far smaller than the wavelength of light. Although metamaterials were initially considered mainly for static applications, this Review summarizes efforts towards an active functionality that enables a much broader range of photonic device applications.
- Nikolay I. Zheludev
- & Yuri S. Kivshar
-
Letter |
 Nanometre optical coatings based on strong interference effects in highly absorbing media
Nanometre optical coatings based on strong interference effects in highly absorbing media
Optical coatings usually consist of many multilayers of thin films to achieve the desired properties. A new approach using interference effects between an absorbing dielectric film and a metallic substrate now enables ultrathin optical coatings that could also find applications as thin solar cells or photodetectors.
- Mikhail A. Kats
- , Romain Blanchard
- & Federico Capasso
-
-
Letter |
 Blue-phase templated fabrication of three-dimensional nanostructures for photonic applications
Blue-phase templated fabrication of three-dimensional nanostructures for photonic applications
Liquid-crystalline order can be templated in a material by refilling a photopolymerized liquid-crystal cast with the material after the non-polymerized portion has been washed out. This approach has now been used to template, in achiral liquid crystals, chiral three-dimensional blue phases with unprecedented thermal stability that are suitable for narrowband mirrorless lasing and switchable electro-optic devices.
- F. Castles
- , F. V. Day
- & H. J. Coles
-
Correspondence |
A photoferroelectric material is more than the sum of its parts
- J. Kreisel
- , M. Alexe
- & P. A. Thomas
-
Editorial |
 Solar energy's path towards competitiveness
Solar energy's path towards competitiveness
Progress in photovoltaic technology could soon mean grid parity for solar electricity. In this issue we highlight scientific as well as science-policy strategies aimed towards achieving this goal.
-
Commentary |
 Photonic design principles for ultrahigh-efficiency photovoltaics
Photonic design principles for ultrahigh-efficiency photovoltaics
For decades, solar-cell efficiencies have remained below the thermodynamic limits. However, new approaches to light management that systematically minimize thermodynamic losses will enable ultrahigh efficiencies previously considered impossible.
- Albert Polman
- & Harry A. Atwater
-
Letter |
 Collective osmotic shock in ordered materials
Collective osmotic shock in ordered materials
Vesicles can rupture as a result of an imbalance in osmotic pressure between their inside and the exterior. Such an ‘osmotic shock’ has now been multiplexed in a coordinated fashion within an ordered material in which a minor component swells and ruptures, thus leading to a porous bicontinuous structure. Such perforated ordered materials may find applications in photonics, optoelectronics and nanofiltration.
- Paul Zavala-Rivera
- , Kevin Channon
- & Hernan Miguez
-
Letter |
 Solution-processed small-molecule solar cells with 6.7% efficiency
Solution-processed small-molecule solar cells with 6.7% efficiency
Polymer-based bulk-heterojunction solar cells have shown some of the highest photoconversion efficiencies in organic photovoltaics, but polymer polydispersity impacts their performance. A small-molecule donor is now reported that enables the fabrication of bulk-heterojunction devices with low acceptor content and photoconversion efficiencies of up to 6.7%.
- Yanming Sun
- , Gregory C. Welch
- & Alan J. Heeger
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Adaptive optics
- Astronomical optics
- Atmospheric optics
- Displays
- Fibre optics and optical communications
- Integrated optics
- Laser material processing
- Microwave photonics
- Mid-infrared photonics
- Optical data storage
- Optical sensors
- Optoelectronic devices and components
- Solar energy and photovoltaic technology

 The revolution of silicon photonics
The revolution of silicon photonics Trapped in a flat dispersion
Trapped in a flat dispersion