Figure 12 - Pharyngoglottal closure reflex: effect of pharyngeal water stimulation on myoelectrical activity.
From the following article
Reflex interaction of pharynx, esophagus, and airways
Reza Shaker
GI Motility online (2006)
doi:10.1038/gimo11

Example of the effect of pharyngeal water stimulation on myoelectrical activity of the interarytenoid (human equivalent), lateral cricoarytenoid, and cricopharyngeus muscles (CP). Whereas pharyngeal water injection resulted in contraction of the glottal adductor as well as CP muscles (A and B), swallows triggered by pharyngeal water injection resulted in contraction of glottal adductors and relaxation of the CP muscles (C and D). This relaxation, however, was followed by a postdeglutitive contraction. IA, interarytenoid muscle; LCA, lateral cricoarytenoid muscle; EMG, raw electromyographic activity; 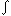 , integrated EMG activity. (Source: Shaker R, Medda BK, Ren J, Jaradeh S, Xie P, Lang IM. Pharyngoglottal closure reflex: identification and characterization in a feline model. Am J Physiol 1998;275:G521-G525 with permission from the American Physiological Association.)
, integrated EMG activity. (Source: Shaker R, Medda BK, Ren J, Jaradeh S, Xie P, Lang IM. Pharyngoglottal closure reflex: identification and characterization in a feline model. Am J Physiol 1998;275:G521-G525 with permission from the American Physiological Association.)
Powerpoint slides for teaching
If the slide opens in your browser, Select "File > Save as" to save it.
Download Power Point slide (716K)
