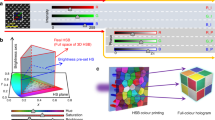
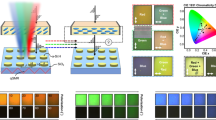
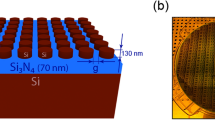
Abstract
The growing interest to develop modern digital displays and colour printing has driven the advancement of colouration technologies with remarkable speed. In particular, metasurface-based structural colouration shows a remarkable high colour saturation, wide gamut palette, chiaroscuro presentation and polarization tunability. However, previous approaches cannot simultaneously achieve all these features. Here, we design and experimentally demonstrate a surface-relief plasmonic metasurface consisting of shallow nanoapertures that enable the independent manipulation of colour hue, saturation and brightness by individually varying the geometric dimensions and orientation of the nanoapertures. We fabricate microscale artworks using a reusable template-stripping technique that features photorealistic and stereoscopic impressions. In addition, through the meticulous arrangement of differently oriented nanoapertures, kaleidoscopic information states can be decrypted by particular combinations of incident and reflected polarized light.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its Supplementary Information files. All the relevant data are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Kristensen, A. et al. Plasmonic colour generation. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2, 16088 (2016).
Song, M. et al. Colors with plasmonic nanostructures: a full-spectrum review. Appl. Phys. Rev. 6, 041308 (2019).
Barnes, W. L., Dereux, A. & Ebbesen, T. W. Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424, 824–830 (2003).
Luo, X., Tsai, D., Gu, M. & Hong, M. Extraordinary optical fields in nanostructures: from sub-diffraction-limited optics to sensing and energy conversion. Chem. Soc. Rev. 48, 2458–2494 (2019).
Li, Y., van de Groep, J., Talin, A. A. & Brongersma, M. L. Dynamic tuning of gap plasmon resonances using a solid-state electrochromic device. Nano Lett. 19, 7988–7995 (2019).
Chowdhury, S. N. et al. Lithography-free plasmonic color printing with femtosecond laser on semicontinuous silver films. ACS Photon. 8, 521–530 (2020).
Huang, Y.-W. et al. Aluminum plasmonic multicolor meta-hologram. Nano Lett. 15, 3122–3127 (2015).
Ellenbogen, T., Seo, K. & Crozier, K. B. Chromatic plasmonic polarizers for active visible color filtering and polarimetry. Nano Lett. 12, 1026–1031 (2012).
Neubrech, F., Duan, X. & Liu, N. Dynamic plasmonic color generation enabled by functional materials. Sci. Adv. 6, eabc2709 (2020).
Duan, X., Kamin, S. & Liu, N. Dynamic plasmonic colour display. Nat. Commun. 8, 14606 (2017).
Zhu, X., Vannahme, C., Højlund-Nielsen, E., Mortensen, N. A. & Kristensen, A. Plasmonic colour laser printing. Nat. Nanotechnol. 11, 325–329 (2016).
Xue, J. et al. Perturbative countersurveillance metaoptics with compound nanosieves. Light Sci. Appl. 8, 101 (2019).
Yang, Z., Ji, C., Cui, Q. & Guo, L. J. High-purity hybrid structural colors by enhancing optical absorption of organic dyes in resonant cavity. Adv. Opt. Mater. 8, 2000317 (2020).
Clausen, J. S. et al. Plasmonic metasurfaces for coloration of plastic consumer products. Nano Lett. 14, 4499–4504 (2014).
Esposito, M. et al. Symmetry breaking in oligomer surface plasmon lattice resonances. Nano Lett. 19, 1922–1930 (2019).
Joo, W.-J. et al. Metasurface-driven OLED displays beyond 10,000 pixels per inch. Science 370, 459–463 (2020).
Kumar, K. et al. Printing colour at the optical diffraction limit. Nat. Nanotechnol. 7, 557–561 (2012).
Xu, T., Wu, Y.-K., Luo, X. & Guo, L. J. Plasmonic nanoresonators for high-resolution colour filtering and spectral imaging. Nat. Commun. 1, 59 (2010).
Wang, H. et al. Full color generation using silver tandem nanodisks. ACS Nano 11, 4419–4427 (2017).
Rezaei, S. D. et al. Wide-gamut plasmonic color palettes with constant subwavelength resolution. ACS Nano 13, 3580–3588 (2019).
Roberts, A. S., Pors, A., Albrektsen, O. & Bozhevolnyi, S. I. Subwavelength plasmonic color printing protected for ambient use. Nano Lett. 14, 783–787 (2014).
Goh, X. M. et al. Three-dimensional plasmonic stereoscopic prints in full colour. Nat. Commun. 5, 5361 (2014).
Tan, S. J. et al. Plasmonic color palettes for photorealistic printing with aluminum nanostructures. Nano Lett. 14, 4023–4029 (2014).
Shaltout, A. M., Kim, J., Boltasseva, A., Shalaev, V. M. & Kildishev, A. V. Ultrathin and multicolour optical cavities with embedded metasurfaces. Nat. Commun. 9, 2673 (2018).
Hail, C. U., Schnoering, G., Damak, M., Poulikakos, D. & Eghlidi, H. A plasmonic painter’s method of color mixing for a continuous red–green–blue palette. ACS Nano 14, 1783–1791 (2020).
Lee, J. S. et al. Ultrahigh resolution and color gamut with scattering-reducing transmissive pixels. Nat. Commun. 10, 4782 (2019).
Wu, Y.-K., Hollowell, A. E., Zhang, C. & Guo, L. J. Angle-insensitive structural colours based on metallic nanocavities and coloured pixels beyond the diffraction limit. Sci. Rep. 3, 1194 (2013).
Proust, J., Bedu, F., Gallas, B., Ozerov, I. & Bonod, N. All-dielectric colored metasurfaces with silicon Mie resonators. ACS Nano 10, 7761–7767 (2016).
Li, Q., Wu, T., van de Groep, J., Lalanne, P. & Brongersma, M. L. Structural color from a coupled nanowire pair beyond the bonding and antibonding model. Optica 8, 464–470 (2021).
Dong, Z. et al. Printing beyond sRGB color gamut by mimicking silicon nanostructures in free-space. Nano Lett. 17, 7620–7628 (2017).
Sun, S. et al. All-dielectric full-color printing with TiO2 metasurfaces. ACS Nano 11, 4445–4452 (2017).
Tittl, A. et al. Imaging-based molecular barcoding with pixelated dielectric metasurfaces. Science 360, 1105 (2018).
Huo, P. et al. Photorealistic full-color nanopainting enabled by a low-loss metasurface. Optica 7, 1171 (2020).
Koshelev, K. & Kivshar, Y. Dielectric resonant metaphotonics. ACS Photon. 8, 102–112 (2021).
Bao, Y. et al. Coherent pixel design of metasurfaces for multidimensional optical control of multiple printing-image switching and encoding. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28, 1805306 (2018).
Zhou, J. et al. Visualizing Mie resonances in low-index dielectric nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 253902 (2018).
Yang, W. et al. All-dielectric metasurface for high-performance structural color. Nat. Commun. 11, 1864 (2020).
Yang, B. et al. Ultrahighly saturated structural colors enhanced by multipolar-modulated metasurfaces. Nano Lett. 19, 4221–4228 (2019).
Yang, J. H. et al. Structural colors enabled by lattice resonance on silicon nitride metasurfaces. ACS Nano 14, 5678–5685 (2020).
Bao, Y. et al. Full-colour nanoprint-hologram synchronous metasurface with arbitrary hue–saturation–brightness control. Light Sci. Appl. 8, 95 (2019).
Jiang, M. et al. Patterned resist on flat silver achieving saturated plasmonic colors with sub-20-nm spectral linewidth. Mater. Today 35, 99–105 (2020).
Johnson, P. B. & Christy, R. W. Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys. Rev. B 6, 4370–4379 (1972).
Wu, S. et al. Enhanced rotation of the polarization of a light beam transmitted through a silver film with an array of perforated s-shaped holes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 207401 (2013).
Kelf, T. A. et al. Localized and delocalized plasmons in metallic nanovoids. Phys. Rev. B 74, 245415 (2006).
Viguerie, L., Walter, P., Laval, E., Mottin, B. & Sole, V. A. Revealing the sfumato technique of Leonardo da Vinci by X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49, 6125–6128 (2010).
Kudyshev, Z. A., Kildishev, A. V., Shalaev, V. M. & Boltasseva, A. Machine-learning-assisted metasurface design for high-efficiency thermal emitter optimization. Appl. Phys. Rev. 7, 021407 (2020).
Ma, W. et al. Deep learning for the design of photonic structures. Nat. Photon. 15, 77–90 (2021).
Wiecha, P. R., Lecestre, A., Mallet, N. & Larrieu, G. Pushing the limits of optical information storage using deep learning. Nat. Nanotechnol. 14, 237–244 (2019).
Dong, Z. et al. Schrödinger’s red pixel by quasi-bound-states-in-the-continuum. Sci. Adv. 8, eabm4512 (2022).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge support from the Key Research and Development Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2017YFA0303700 to Y.L. and T.X.), National Natural Science Foundation of China (62005117 to M.S.), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20220068 to T.X. and BK20212004 to Y.L.) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (to T.X.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.S. and T.X. conceived the idea. M.S. performed all the numerical simulations and imaging experiments. L.F. fabricated all the samples. P.H., M.L. and C.H. provided help with the fabrication and experiments. F.Y., Y.L. and T.X. supervised the project. All the authors discussed results and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Nanotechnology thanks Jay Guo, Joel Yang and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary discussion, Figs. 1–11 and Supplementary Table 1.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, M., Feng, L., Huo, P. et al. Versatile full-colour nanopainting enabled by a pixelated plasmonic metasurface. Nat. Nanotechnol. 18, 71–78 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-022-01256-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-022-01256-4
This article is cited by
-
A water-soluble label for food products prevents packaging waste and counterfeiting
Nature Food (2024)
-
Single-step fabrication of liquid gallium nanoparticles via capillary interaction for dynamic structural colours
Nature Nanotechnology (2024)
-
Switchable unidirectional emissions from hydrogel gratings with integrated carbon quantum dots
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Tailoring high-refractive-index nanocomposites for manufacturing of ultraviolet metasurfaces
Microsystems & Nanoengineering (2024)
-
Cost-Effective and Environmentally Friendly Mass Manufacturing of Optical Metasurfaces Towards Practical Applications and Commercialization
International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology (2024)