Abstract
Objective An evidence-based review on the role of botulinum toxin type A (BoNTA) on diverse cosmetic applications of interest to dental practitioners and allied specialities. In this context, to identify the cosmetic treatments that have an evidence-based rationale against areas requiring further research, with a view to assess the safety and efficacy of BoNTA.
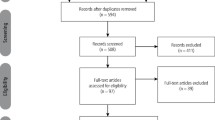
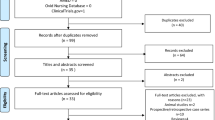
Data source and selection A comprehensive search was conducted using Cochrane Library of Systematic Reviews, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, and PubMed (Medline) electronic databases. Thirty-nine studies of variable quality were included. The Best Evidence Topics (BETs) Critical Appraisal Tool was used to facilitate the quality assessment of relevant studies.
Data extraction Based on current level II evidence, BoNTA was safe and effective to improve facial contour, reduce volume and thickness of bilateral hypertrophic masseter. Conservative doses using a combined approach of BoNTA and hyaluronic acid was recommended as a safe and effective treatment for perioral enhancement supported by level II evidence. There was limited evidence, not higher than level III, to support BoNTA effectiveness for gummy smile associated to perioral musculature hyperactivity, while jawline sculpting targeting the platysma muscle had lower level IV evidence up to this date.
Conclusion BoNTA has been widely used off-label for the investigated cosmetic orofacial conditions, with reports of 'good patient and practitioner satisfaction'. However, there is limited high-quality evidence to support the long-term safety and effectiveness of repetitive BoNTA injections. Additionally, no studies were found that provided a cost-effectiveness evaluation of BoNTA formulations against other current cosmetic interventions. Well-designed clinical trials, including long-term follow-up, would help to provide robust evidence-based recommendations for clinical practice, supporting BoNTA popularity, independently or in a combined approach.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carruthers A, Kane M A C, Flynn T C et al. The convergence of medicine and neurotoxins: a focus on botulinum toxin type A and its application in aesthetic medicine-a global, evidence-based botulinum toxin consensus education initiative: part I: botulinum toxin in clinical and cosmetic practice. Dermatol Surg 2013; 39: 493-509.
Samizadeh S, De Boulle K. Botulinum neurotoxin formulations: overcoming the confusion. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2018; 11: 273-287.
Lee K C, Pascal A B, Halepas S, Koch A. What Are the Most Commonly Reported Complications With Cosmetic Botulinum Toxin Type A Treatments? J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2020; DOI: 10.1016/j.joms.2020.02.016.
U.S. Food & Drug Administration. FDA Gives Update on Botulinum Toxin Safety Warnings; Established Names of Drugs Changed. 2009. Available at https://wayback.archive-it.org/7993/20170112032330/http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/2009/ucm175013.htm (accessed February 2020).
Walker T J, Dayan S H. Comparison and overview of currently available neurotoxins. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 2014; 7: 31-39.
The Aesthetic Society. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery National Databank Statistics for 2019. 2019. Available at https://www.surgery.org/media/statistics (accessed May 2020).
EU Clinical Trials Register. Clinical trials for Botulinum Toxin Type A. Available at https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/search?query=Botulinum+Toxin+Type+A (accessed February 2020).
Miller J, Clarkson E. Botulinum Toxin Type A: Review and Its Role in the Dental Office. Dent Clin North Am 2016; 60: 509-521.
Walker T W M, Gately F, Stagnell S, Kerai A, Mills C, Thomas S. Can UK undergraduate dental programmes provide training in non-surgical facial aesthetics? Br Dent J 2017; 222: 949-953.
Khan O A, Dunning J, Parvaiz A C, Agha R, Rosin D, Mackway-Jones K. Towards evidence-based medicine in surgical practice: best BETs. Int J Surg 2011; 9: 585-588.
Best BETs. Best Evidence Topics and Critical Appraisal. Available at https://bestbets.org/background/bets-and-cats.php (accessed April 2020).
Sundaram H, Signorini M, Liew S et al. Global Aesthetics Consensus: Botulinum Toxin Type A-Evidence-Based Review, Emerging Concepts, and Consensus Recommendations for Aesthetic Use, Including Updates on Complications. Plast Reconstr Surg 2016; DOI: 10.1097/01.prs.0000475758.63709.23.
Carruthers J, Carruthers A. A Multimodal Approach to Rejuvenation of the Lower Face. Dermatol Surg 2016; 42 Suppl 2: S89-S93.
Carruthers A, Carruthers J, Monheit G D, Davis P G, Tardie G. Multicentre, randomized, parallel-group study of the safety and effectiveness of onabotulinumtoxinA and hyaluronic acid dermal fillers (24-mg/ml smooth, cohesive gel) alone and in combination for lower facial rejuvenation. Dermatol Surg 2010; 36 Suppl 4: 2121-2134.
Cavallini M, Cirillo P, Fundarò S P et al. Safety of botulinum toxin A in aesthetic treatments: a systematic review of clinical studies. Dermatol Surg 2014; 40: 525-536.
OCEBM Levels of Evidence Working Group. The Oxford 2011 Levels of Evidence. Available at https://www.cebm.net/wp-content/uploads/2014/06/CEBM-Levels-of-Evidence-2.1.pdf (accessed April 2020).
Cochrane Training. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Available at https://training.cochrane.org/handbook/current (accessed August 2021).
Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev 2015; 4: 1.
Cheng J, Hsu S H, McGee J S. Botulinum Toxin Injections for Masseter Reduction in East Asians. Dermatol Surg 2019; 45: 566-572.
Park G, Choi Y-C, Bae J-H, Kim S-T. Does Botulinum Toxin Injection into Masseter Muscles Affect Subcutaneous Thickness? Aesthet Surg J 2018; 38: 192-198.
Shome D, Khare S, Kapoor R. Efficacy of Botulinum Toxin in Treating Asian Indian Patients with Masseter Hypertrophy: A 4-Year Follow-Up Study. Plast Reconstr Surg 2019; DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000005944.
Fedorowicz Z, van Zuuren E J, Schoones J. Botulinum toxin for masseter hypertrophy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2013; DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007510.pub3.
Yeh Y-T, Peng J-H, Peng H-L P. Literature review of the adverse events associated with botulinum toxin injection for the masseter muscle hypertrophy. J Cosmet Dermatol 2018; 17: 675-687.
Peng H-L P, Peng J-H. Complications of botulinum toxin injection for masseter hypertrophy: Incidence rate from 2036 treatments and summary of causes and preventions. J Cosmet Dermatol 2018; 17: 33-38.
Lee H-H, Kim S T, Lee K-J, Baik H-S. Effect of a second injection of botulinum toxin on lower facial contouring, as evaluated using 3-dimensional laser scanning. Dermatol Surg 2015; 41: 439-444.
Lee H-J, Kim S-J, Lee K-J, Yu H-S, Baik H-S. Repeated injections of botulinum toxin into the masseter muscle induce bony changes in human adults: A longitudinal study. Korean J Orthod 2017; 47: 222-228.
Wei J, Xu H, Dong J, Li Q, Dai C. Prolonging the duration of masseter muscle reduction by adjusting the masticatory movements after the treatment of masseter muscle hypertrophy with botulinum toxin type A injection. Dermatol Surg 2015; 41 Suppl 1: S101-S109.
Xie Y, Zhou J, Li H, Cheng C, Herrler T, Li Q. Classification of masseter hypertrophy for tailored botulinum toxin type A treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg 2014; DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000000371.
Cha Y R, Kim Y G, Kim J H, Kim S T. Effect of unilateral injection of botulinum toxin on lower facial asymmetry as evaluated using three-dimensional laser scanning. Dermatol Surg 2013; 39: 900-906.
Kim N-H, Park R-H, Park J-B. Botulinum toxin type A for the treatment of hypertrophy of the masseter muscle. Plast Reconstr Surg 2010; 125: 1693-1705.
Kim N-H, Chung J-H, Park R-H, Park J-B. The use of botulinum toxin type A in aesthetic mandibular contouring. Plast Reconstr Surg 2005; 115: 919-930.
Lee J H, Park J H, Lee S K et al. Efficacy and safety of incobotulinum toxin A in periocular rhytides and masseteric hypertrophy: side-by-side comparison with onabotulinum toxin A. J Dermatologue Treat 2014; 25: 326-330.
Wanitphakdeedecha R, Ungaksornpairote C, Kaewkes A, Sathaworawong A, Lektrakul N, Manuskiatti W. The efficacy of two formulations of botulinum toxin type A for masseter reduction: a split-face comparison study. J Dermatologue Treat 2017; 28: 443-446.
Lee D H, Jin S-P, Cho S et al. RimabotulinumtoxinB versus OnabotulinumtoxinA in the treatment of masseter hypertrophy: a 24-week double-blind randomized split-face study. Dermatology (Basel) 2013; 226: 227-232.
Park M Y, Ahn K Y, Jung D S. Botulinum toxin type A treatment for contouring of the lower face. Dermatol Surg 2003; 29: 477-483; discussion 483.
Choe S W, Cho W I, Lee C K, Seo S J. Effects of botulinum toxin type A on contouring of the lower face. Dermatol Surg 2005; 31: 502-508.
Kim H J, Yum K-W, Lee S-S, Heo M-S, Seo K. Effects of botulinum toxin type A on bilateral masseteric hypertrophy evaluated with computed tomographic measurement. Dermatol Surg 2003; 29: 484-489.
Lee S H, Wee S H, Kim H-J et al. Abobotulinum toxin A and onabotulinum toxin A for masseteric hypertrophy: a split-face study in 25 Korean patients. J Dermatologue Treat 2013; 24: 133-136.
Lee S J, Kang J M, Kim Y K, Park J, Kim D Y. Paradoxical bulging of muscle after injection of botulinum neurotoxin type A into hypertrophied masseter muscle. J Dermatol 2012; 39: 804-805.
To E W, Ahuja A T, Ho W S et al. A prospective study of the effect of botulinum toxin A on masseteric muscle hypertrophy with ultrasonographic and electromyographic measurement. Br J Plast Surg 2001; 54: 197-200.
Yu C-C, Chen P K-T, Chen Y-R. Botulinum toxin a for lower facial contouring: a prospective study. Aesthetic Plast Surg 2007; 31: 445-453.
Kadunc B V, Trindade D E, Almeida A R, Vanti A A, DI Chiacchio N. Botulinum toxin A adjunctive use in manual chemabrasion: controlled long-term study for treatment of upper perioral vertical wrinkles. Dermatol Surg 2007; 33: 1066-1072.
Cohen J L, Dayan S H, Cox S E, Yalamanchili R, Tardie G. OnabotulinumtoxinA dose-ranging study for hyperdynamic perioral lines. Dermatol Surg 2012; 38: 1497-1505.
Carruthers J, Carruthers A, Monheit G D, Davis P G. Multicentre, randomized, parallel-group study of onabotulinumtoxinA and hyaluronic acid dermal fillers (24-mg/ml smooth, cohesive gel) alone and in combination for lower facial rejuvenation: satisfaction and patient-reported outcomes. Dermatol Surg 2010; 36 Suppl 4: 2135-2145.
Hexsel D, Brum C, Porto M D et al. Full-face injections of variable total doses of abobotulinum toxin type A: A randomized, phase IV clinical trial of safety and efficacy. J Drugs Dermatol 2013; 12: 1356-1362.
Chang C S, Chang B L, Lanni M, Wilson A J, Beer J, Percec I. Perioral Rejuvenation: A Prospective, Quantitative Dynamic Three-Dimensional Analysis of a Dual Modality Treatment. Aesthet Surg J 2018; 38: 1225-1236.
Semchyshyn N, Sengelmann R D. Botulinum toxin A treatment of perioral rhytides. Dermatol Surg 2003; 29: 490-495.
de Maio M, Wu W T L, Goodman G J, Monheit G, Alliance for the Future of Aesthetics Consensus Committee. Facial Assessment and Injection Guide for Botulinum Toxin and Injectable Hyaluronic Acid Fillers: Focus on the Lower Face. Plast Reconstr Surg 2017; DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000003646.
Sundaram H, Liew S, Signorini M et al. Global Aesthetics Consensus: Hyaluronic Acid Fillers and Botulinum Toxin Type A-Recommendations for Combined Treatment and Optimizing Outcomes in Diverse Patient Populations. Plast Reconstr Surg 2016; 137: 1410-1423.
Bertossi D, Cavallini M, Cirillo P et al. Italian consensus report on the aesthetic use of onabotulinum toxin A. J Cosmet Dermatol 2018; 17: 719-730.
Qian W, Zhang Y-K, Lv W, Hou Y, Cao Q, Fan J-F. Application of Local Injection of Botulinum Toxin A in Cosmetic Patients with Congenital Drooping Mouth Corner. Aesthetic Plast Surg 2016; 40: 926-930.
Bae G Y, Na J-I, Park K-C, Cho S B. Nonsurgical correction of drooping mouth corners using monophasic hyaluronic acid and incobotulinumtoxin A. J Cosmet Dermatol 2020; 19: 338-345.
Jeong T-K. Mouth Corner Lift with Botulinum Toxin Type A, Hyaluronic Acid Filler. Plast Reconstr Surg 2020; DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000006605.
Nasr M W, Jabbour S F, Sidaoui J A, Haber R N, Kechichian E G. Botulinum Toxin for the Treatment of Excessive Gingival Display: A Systematic Review. Aesthet Surg J 2016; 36: 82-88.
Duruel O, Ataman-Duruel E T, Tözüm T F, Berker E. Ideal Dose and Injection Site for Gummy Smile Treatment with Botulinum Toxin-A: A Systematic Review and Introduction of a Case Study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2019; DOI: 10.11607/prd.3580.
Chagas T F, de Almeida N V, Lisboa C O et al. Duration of effectiveness of Botulinum toxin type A in excessive gingival display: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Braz Oral Res 2018; DOI: 10.1590/1807-3107bor-2018.vol32.0030.
Mazzuco R, Hexsel D. Gummy smile and botulinum toxin: a new approach based on the gingival exposure area. J Am Acad Dermatol 2010; 63: 1042-1051.
Polo M. Botulinum toxin type A (Botox) for the neuromuscular correction of excessive gingival display on smiling (gummy smile). Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2008; 133: 195-203.
Suber J S, Dinh T P, Prince M D, Smith P D. OnabotulinumtoxinA for the treatment of a 'gummy smile'. Aesthet Surg J 2014; 34: 432-437.
Sucupira E, Abramovitz A. A simplified method for smile enhancement: botulinum toxin injection for gummy smile. Plast Reconstr Surg 2012; 130: 726-728.
Somaiah M S, Muddaiah S, Shetty B P, Vijayananda K, Bhat M, Shetty P S. Effectiveness of botulinum toxin A, in unraveling gummy smile: A prospective clinical study. APOS Trends Orthod 2013; 3: 54-58.
Al-Fouzan A F, Mokeem L S, Al-Saqat R T, Alfalah M A, Alharbi M A, Al-Samary A E. Botulinum Toxin for the Treatment of Gummv Smile. J Contemp Dent Pract 2017; 18: 474-478.
Cengiz A F, Goymen M, Akcali C. Efficacy of botulinum toxin for treating a gummy smile. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 2020; 158: 50-58.
Gupta N, Kohli S. Evaluation of a Neurotoxin as an Adjunctive Treatment Modality for the Management of Gummy Smile. Indian Dermatol Online J 2019; 10: 560-563.
Aly L A, Hammouda N I. Botox as an adjunct to lip repositioning for the management of excessive gingival display in the presence of hypermobility of upper lip and vertical maxillary excess. Dent Res J (Isfahan) 2016; 13: 478-483.
Duruel O, Ataman-Duruel E T, Berker E, Tözüm T F. Treatment of Various Types of Gummy Smile With Botulinum Toxin-A. J Craniofac Surg 2019; 30: 876-878.
D'Emilio R, Rosati G. Full-face treatment with onabotulinumtoxinA: Results from a single-centre study. J Cosmet Dermatol 2020; 19: 809-816.
de Almeida A R T, Romiti A, Carruthers J D A. The Facial Platysma and Its Underappreciated Role in Lower Face Dynamics and Contour. Dermatol Surg 2017; 43: 1042-1049.
Zhou R, Fei Y, Sun L, Guo J, Zhou X, Zhang X. BTX-A Rejuvenation: Regional Botulinum Toxin-A Injection of the Platysma in Patients with Facial Sagging. Aesthetic Plast Surg 2019; 43: 1044-1053.
Awaida C J, Jabbour S F, Rayess Y A, El Khoury J S, Kechichian E G, Nasr M W. Evaluation of the Microbotox Technique: An Algorithmic Approach for Lower Face and Neck Rejuvenation and a Crossover Clinical Trial. Plast Reconstr Surg 2018; 142: 640-649.
Jabbour S F, Kechichian E G, Awaida C J, Tomb R R, Nasr M W. Botulinum Toxin for Neck Rejuvenation: Assessing Efficacy and Redefining Patient Selection. Plast Reconstr Surg 2017; DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000003429.
Wu W T L, Liew S, Chan H H et al. Consensus on Current Injectable Treatment Strategies in the Asian Face. Aesthetic Plast Surg 2016; 40: 202-214.
Wu W T L. Microbotox of the Lower Face and Neck: Evolution of a Personal Technique and Its Clinical Effects. Plast Reconstr Surg 2015; 136: 92S-100S.
White S, Ahmed B, Ondhia A. The effectiveness of Clostridium botulinum toxin A (Dysport, AbobotulinumtoxinA) in the management of temporomandibular dysfunction (TMD) and a small number of other maxillofacial conditions; an open cohort study. Oral Surg 2018; 11: 175-182.
Tsai C-Y, Shyr Y-M, Chiu W-C, Lee C-M. Bone changes in the mandible following botulinum neurotoxin injections. Eur J Orthod 2011; 33: 132-138.
Rafferty K L, Liu Z J, Ye W et al. Botulinum toxin in masticatory muscles: short-and long-term effects on muscle, bone, and craniofacial function in adult rabbits. Bone 2012; 50: 651-662.
Kün-Darbois J-D, Libouban H, Chappard D. Botulinum toxin in masticatory muscles of the adult rat induces bone loss at the condyle and alveolar regions of the mandible associated with a bone proliferation at a muscle enthesis. Bone 2015; 77: 75-82.
Raphael K G, Tadinada A, Bradshaw J M et al. Osteopenic consequences of botulinum toxin injections in the masticatory muscles: a pilot study. J Oral Rehabil 2014; 41: 555-563.
Balanta-Melo J, Toro-Ibacache V, Kupczik K, Buvinic S. Mandibular Bone Loss after Masticatory Muscles Intervention with Botulinum Toxin: An Approach from Basic Research to Clinical Findings. Toxins (Basel) 2019; 11: 84.
Trévidic P, Sykes J, Criollo-Lamilla G. Anatomy of the Lower Face and Botulinum Toxin Injections. Plast Reconstr Surg 2015; 136: 84S-91S.
Delpachitra S N, Sklavos A W, Dastaran M. Clinical uses of botulinum toxin A in smile aesthetic modification. Br Dent J 2018; 225: 502-506.
Choi Y-J, We Y-J, Lee H-J et al. Three-Dimensional Evaluation of the Depressor Anguli Oris and Depressor Labii Inferioris for Botulinum Toxin Injections [published online ahead of print]. Aesthet Surg J 2020; DOI: 10.1093/asj/sjaa083.
Tjan A H, Miller G D, The J G. Some esthetic factors in a smile. J Prosthet Dent 1984; 51: 24-28.
Polo M. Commentary on: Botulinum Toxin for the Treatment of Excessive Gingival Display: A Systematic Review. Aesthet Surg J 2016; 36: 89-92.
Hwang W-S, Hur M-S, Hu K-S et al. Surface anatomy of the lip elevator muscles for the treatment of gummy smile using botulinum toxin. Angle Orthod 2009; 79: 70-77.
Heitmiller K, Ring C, Saedi N. Facial Contouring with Neuromodulators. Adv Cosmet Surg 2020; 3: 99-107.
Bertucci V. Commentary on The Facial Platysma and Its Underappreciated Role in Lower Face Dynamics and Contour. Dermatol Surg 2017; 43: 1050-1052.
Liew S, Dart A. Nonsurgical reshaping of the lower face. Aesthet Surg J 2008; 28: 251-257.
Wu W T L. Botox facial slimming/facial sculpting: the role of botulinum toxin-A in the treatment of hypertrophic masseteric muscle and parotid enlargement to narrow the lower facial width. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am 2010; 18: 133-140.
Levy P M. Neurotoxins: Current Concepts in Cosmetic Use on the Face and Neck-Jawline Contouring/Platysma Bands/Necklace Lines. Plast Reconstr Surg 2015; 136: 80S-83S.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the help and assistance of the editors and reviewers of the Evidence-Based Dentistry journal for their support and review of the research that was undertaken. Thanks to Miss R. Al-Barazanchi for proofreading.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
INP is a dental practitioner working for the National Health Service primary care and currently a PhD resident at the University of Porto, Faculty of Dental Medicine. This study was based on INP master's degree dissertation in Aesthetic Medicine at the Queen Mary University of London. Both authors had full access to all the data in the work and the decision to submit for publication rested with the correspondent author. HH is a clinical senior lecturer at the Academic Plastic Surgery, Blizard Institute, Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry, Queen Mary University of London.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Neither author has any conflict of interests, nor financial or non-financial competing interest.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pereira, I., Hassan, H. Botulinum toxin A in dentistry and orofacial surgery: an evidence-based review - part 2: cosmetic applications. Evid Based Dent (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41432-022-0277-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41432-022-0277-4