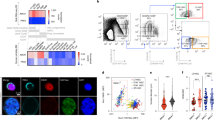
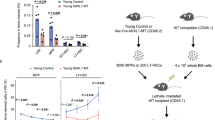
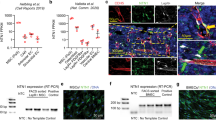
Abstract
Although DNA mutation drives stem cell aging, how mutation-accumulated stem cells obtain clonal advantage during aging remains poorly understood. Here, using a mouse model of irradiation-induced premature aging and middle-aged mice, we show that DNA mutation accumulation in hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) during aging upregulates their surface expression of major histocompatibility complex class II (MHCII). MHCII upregulation increases the chance for recognition by bone marrow (BM)-resident regulatory T cells (Tregs), resulting in their clonal expansion and accumulation in the HSC niche. On the basis of the establishment of connexin 43 (Cx43)-mediated gap junctions, BM Tregs transfer cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) to aged HSCs to diminish apoptotic priming and promote their survival via activation of protein kinase A (PKA) signaling. Importantly, targeting the HSC–Treg interaction or depleting Tregs effectively prevents the premature/physiological aging of HSCs. These findings show that aged HSCs use an active self-protective mechanism by entrapping local Tregs to construct a prosurvival niche and obtain a clonal advantage.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Transcriptome, TCR-seq, and WES datasets generated in this study are available in the GEO database (GSE211007, GSE211136, GSE211203, GSE211205, GSE211206) and in the Sequence Read Archive (PRJNA866671, PRJNA866602, PRJNA866684). Published datasets (GSE156807, GSE20366, GSE69408, GSE104379, GSE175604) were reanalyzed in this paper with the authors’ permission.
References
Yousefzadeh MJ, Flores RR, Zhu Y, Schmiechen ZC, Brooks RW, Trussoni CE, et al. An aged immune system drives senescence and ageing of solid organs. Nature.2021;594:100–5.
Bogeska R, Mikecin A-M, Kaschutnig P, Fawaz M, Büchler-Schäff M, Le D, et al. Inflammatory exposure drives long-lived impairment of hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal activity and accelerated aging. Cell Stem Cell. 2022;29:1273–84.e8.
Jeon OH, Mehdipour M, Gil T-H, Kang M, Aguirre NW, Robinson ZR, et al. Systemic induction of senescence in young mice after single heterochronic blood exchange. Nat Metab. 2022;4:995–1006.
Kovtonyuk LV, Caiado F, Garcia-Martin S, Manz E-M, Helbling P, Takizawa H, et al. IL-1 mediates microbiome-induced inflammaging of hematopoietic stem cells in mice. Blood. 2022;139:44–58.
Schumacher B, Pothof J, Vijg J, Hoeijmakers JHJ. The central role of DNA damage in the ageing process. Nature. 2021;592:695–703.
Cagan A, Baez-Ortega A, Brzozowska N, Abascal F, Coorens THH, Sanders MA, et al. Somatic mutation rates scale with lifespan across mammals. Nature. 2022;604:517–24.
Brengdahl MI, Kimber CM, Elias P, Thompson J, Friberg U. Deleterious mutations show increasing negative effects with age in Drosophila melanogaster. BMC Biol. 2020;18:128.
Garaycoechea JI, Crossan GP, Langevin F, Mulderrig L, Louzada S, Yang F, et al. Alcohol and endogenous aldehydes damage chromosomes and mutate stem cells. Nature. 2018;553:171–7.
Batsivari A, Haltalli MLR, Passaro D, Pospori C, Lo Celso C, Bonnet D. Dynamic responses of the haematopoietic stem cell niche to diverse stresses. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22:7–17.
Ya-Hsuan H, Simón M-F. Microenvironmental contributions to hematopoietic stem cell aging. Haematologica. 2020;105:38–46.
Mitchell E, Spencer Chapman M, Williams N, Dawson KJ, Mende N, Calderbank EF, et al. Clonal dynamics of haematopoiesis across the human lifespan. Nature. 2022;606:343–50.
Fabre MA, de Almeida JG, Fiorillo E, Mitchell E, Damaskou A, Rak J, et al. The longitudinal dynamics and natural history of clonal haematopoiesis. Nature. 2022;606:335–42.
Naik S, Larsen SB, Cowley CJ, Fuchs E. Two to Tango: dialog between immunity and stem cells in health and disease. Cell. 2018;175:908–20.
Frisch BJ, Hoffman CM, Latchney SE, LaMere MW, Myers J, Ashton J, et al. Aged marrow macrophages expand platelet-biased hematopoietic stem cells via Interleukin1B. JCI Insight. 2019;5:e124213.
Pioli PD, Casero D, Montecino-Rodriguez E, Morrison SL, Dorshkind K. Plasma cells are obligate effectors of enhanced myelopoiesis in aging bone marrow. Immunity. 2019;51:351–66.e6.
Riether C. Regulation of hematopoietic and leukemia stem cells by regulatory T cells. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1049301.
Hirata Y, Furuhashi K, Ishii H, Li HW, Pinho S, Ding L, et al. CD150high bone marrow tregs maintain hematopoietic stem cell quiescence and immune privilege via adenosine. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;22:445–53.e5.
Yuichi H, Miwako K, Simon CR, Joji F. CD150high CD4 T cells and CD150high regulatory T cells regulate hematopoietic stem cell quiescence via CD73. Haematologica. 2019;104:1136–42.
Fujisaki J, Wu J, Carlson AL, Silberstein L, Putheti P, Larocca R, et al. In vivo imaging of Treg cells providing immune privilege to the haematopoietic stem-cell niche. Nature. 2011;474:216–9.
Ito M, Komai K, Mise-Omata S, Iizuka-Koga M, Noguchi Y, Kondo T, et al. Brain regulatory T cells suppress astrogliosis and potentiate neurological recovery. Nature. 2019;565:246–50.
Kolodin D, van Panhuys N, Li C, Magnuson Angela M, Cipolletta D, Miller Christine M, et al. Antigen- and cytokine-driven accumulation of regulatory T cells in visceral adipose tissue of lean mice. Cell Metab. 2015;21:543–57.
Camacho V, Matkins VR, Patel SB, Lever JM, Yang Z, Ying L, et al. Bone marrow Tregs mediate stromal cell function and support hematopoiesis via IL-10. JCI Insight. 2020;5:e135681.
Wilkinson AC, Ishida R, Nakauchi H, Yamazaki S. Long-term ex vivo expansion of mouse hematopoietic stem cells. Nat Protoc. 2020;15:628–48.
Gutierrez-Martinez P, Hogdal L, Nagai M, Kruta M, Singh R, Sarosiek K, et al. Diminished apoptotic priming and ATM signalling confer a survival advantage onto aged haematopoietic stem cells in response to DNA damage. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20:413–21.
Chang J, Wang Y, Shao L, Laberge R-M, Demaria M, Campisi J, et al. Clearance of senescent cells by ABT263 rejuvenates aged hematopoietic stem cells in mice. Nat Med. 2016;22:78–83.
Dou Z, Ghosh K, Vizioli MG, Zhu J, Sen P, Wangensteen KJ, et al. Cytoplasmic chromatin triggers inflammation in senescence and cancer. Nature. 2017;550:402–6.
Sun X, Cao B, Naval-Sanchez M, Pham T, Sun YBY, Williams B, et al. Nicotinamide riboside attenuates age-associated metabolic and functional changes in hematopoietic stem cells. Nat Commun. 2021;12:2665.
Flohr Svendsen A, Yang D, Kim K, Lazare S, Skinder N, Zwart E, et al. A comprehensive transcriptome signature of murine hematopoietic stem cell aging. Blood. 2021;138:439–51.
Crippa S, Bernardo ME. Mesenchymal stromal cells: role in the BM niche and in the support of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. HemaSphere. 2018;2:e151.
Chougnet CA, Tripathi P, Lages CS, Raynor J, Sholl A, Fink P, et al. A major role for Bim in regulatory T Cell homeostasis. J Immunol. 2011;186:156–63.
Reiko I, Laura PH, Susan MG, Jie L, Andrew S, Junko K, et al. Late effects of exposure to ionizing radiation and age on human thymus morphology and function. Radiat Res. 2017;187:589–98.
Feuerer M, Hill JA, Kretschmer K, von Boehmer H, Mathis D, Benoist C. Genomic definition of multiple ex vivo regulatory T cell subphenotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:5919–24.
Muñoz-Rojas AR, Mathis D. Tissue regulatory T cells: regulatory chameleons. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021;21:597–611.
Hernández-Malmierca P, Vonficht D, Schnell A, Uckelmann HJ, Bollhagen A, Mahmoud MAA, et al. Antigen presentation safeguards the integrity of the hematopoietic stem cell pool. Cell Stem Cell. 2022;29:760–75.e10.
Hinterbrandner M, Rubino V, Stoll C, Forster S, Schnüriger N, Radpour R, et al. Tnfrsf4-expressing regulatory T cells promote immune escape of chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells. JCI Insight. 2021;6:e151797.
Kim JM, Rasmussen JP, Rudensky AY. Regulatory T cells prevent catastrophic autoimmunity throughout the lifespan of mice. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:191–7.
Nyström SN, Bourges D, Garry S, Ross EM, van Driel IR, Gleeson PA. Transient Treg-cell depletion in adult mice results in persistent self-reactive CD4 + T-cell responses. Eur J Immunol. 2014;44:3621–31.
Radpour R, Riether C, Simillion C, Höpner S, Bruggmann R, Ochsenbein AF. CD8 + T cells expand stem and progenitor cells in favorable but not adverse risk acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2019;33:2379–92.
Schürch Christian M, Riether C, Ochsenbein, Adrian F. Cytotoxic CD8 + T cells stimulate hematopoietic progenitors by promoting cytokine release from bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2014;14:460–72.
Riether C, Gschwend T, Huguenin AL, Schürch CM, Ochsenbein AF. Blocking programmed cell death 1 in combination with adoptive cytotoxic T-cell transfer eradicates chronic myelogenous leukemia stem cells. Leukemia. 2015;29:1781–5.
Schürch C, Riether C, Amrein MA, Ochsenbein AF. Cytotoxic T cells induce proliferation of chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells by secreting interferon-γ. J Exp Med. 2013;210:605–21.
Beyaz S, Chung C, Mou H, Bauer-Rowe KE, Xifaras ME, Ergin I, et al. Dietary suppression of MHC class II expression in intestinal epithelial cells enhances intestinal tumorigenesis. Cell Stem Cell. 2021;28:1922–35.e5.
Li J, Williams MJ, Park HJ, Bastos HP, Wang X, Prins D, et al. STAT1 is essential for HSC function and maintains MHCIIhi stem cells that resist myeloablation and neoplastic expansion. Blood. 2022;140:1592–606.
Jardim DL, Goodman A, de Melo Gagliato D, Kurzrock R. The challenges of tumor mutational burden as an immunotherapy biomarker. Cancer Cell. 2021;39:154–73.
He K, Wan T, Wang D, Hu J, Zhou T, Tao W, et al. Gasdermin D licenses MHCII induction to maintain food tolerance in small intestine. Cell. 2023;186:3033–48.e20.
Ley TJ, Miller C, Ding L, Raphael BJ, Mungall AJ, Robertson A, et al. Genomic and epigenomic landscapes of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:2059–74.
Nowak J, Wozniak J, Mendek-Czajkowska E, Dlugokecka A, Mika-Witkowska R, Rogatko-Koros M, et al. Potential link between MHC-self-peptide presentation and hematopoiesis; the analysis of HLA-DR expression in CD34-positive cells and self-peptide presentation repertoires of MHC molecules associated with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013;65:321–33.
Mendoza-Naranjo A, Bouma G, Pereda C, Ramírez M, Webb KF, Tittarelli A, et al. Functional gap junctions accumulate at the immunological synapse and contribute to T cell activation. J Immunol. 2011;187:3121.
Singh AK, Cancelas JA. Gap junctions in the bone marrow lympho-hematopoietic stem cell niche, leukemia progression, and chemoresistance. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:796.
Klein M, Bopp T. Cyclic AMP represents a crucial component of Treg cell-mediated immune regulation. Front Immunol. 2016;7:315.
Negrotto S, Pacienza N, D’Atri LP, Pozner RG, Malaver E, Torres O, et al. Activation of cyclic AMP pathway prevents CD34+ cell apoptosis. Exp Hematol. 2006;34:1420–8.
Rundberg Nilsson A, Soneji S, Adolfsson S, Bryder D, Pronk CJ. Human and murine hematopoietic stem cell aging is associated with functional impairments and intrinsic megakaryocytic/erythroid bias. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0158369.
Luo Y, Xu C, Wang B, Niu Q, Su X, Bai Y, et al. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis reveals disparate effector differentiation pathways in human Treg compartment. Nat. Commun. 2021;12:3913.
Adelman ER, Huang H-T, Roisman A, Olsson A, Colaprico A, Qin T, et al. Aging human hematopoietic stem cells manifest profound epigenetic reprogramming of enhancers that may predispose to leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2019;9:1080–101.
Tirosh A, Tuncman G, Calay ES, Rathaus M, Ron I, Tirosh A, et al. Intercellular transmission of hepatic ER stress in obesity disrupts systemic metabolism. Cell Metab. 2021;33:319–33.e6.
Lumniczky K, Candéias SM, Gaipl US, Frey B. Editorial: Radiation and thE Immune System: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. Front Immunol. 2018;8:1933.
Persa E, Balogh A, Sáfrány G, Lumniczky K. The effect of ionizing radiation on regulatory T cells in health and disease. Cancer Lett. 2015;368:252–61.
Biton M, Haber AL, Rogel N, Burgin G, Beyaz S, Schnell A, et al. T helper cell cytokines modulate intestinal stem cell renewal and differentiation. Cell. 2018;175:1307–20.e22.
Agudo J, Park ES, Rose SA, Alibo E, Sweeney R, Dhainaut M, et al. Quiescent tissue stem cells evade immune surveillance. Immunity. 2018;48:271–85.e5.
Madsen L, Labrecque N, Engberg J, Dierich A, Svejgaard A, Benoist C, et al. Mice lacking all conventional MHC class II genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:10338–43.
Kuribayashi W, Oshima M, Itokawa N, Koide S, Nakajima-Takagi Y, Yamashita M, et al. Limited rejuvenation of aged hematopoietic stem cells in young bone marrow niche. J Exp Med. 2020;218:e20192283.
Cao X, Wu X, Frassica D, Yu B, Pang L, Xian L, et al. Irradiation induces bone injury by damaging bone marrow microenvironment for stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:1609–14.
Liu C, Liao W, Chen J, Yu K, Wu Y, Zhang S, et al. Cholesterol confers ferroptosis resistance onto myeloid-biased hematopoietic stem cells and prevents irradiation-induced myelosuppression. Redox Biol. 2023;62:102661.
Pietras Eric M, Reynaud D, Kang Y-A, Carlin D, Calero-Nieto Fernando J, Leavitt, et al. Functionally distinct subsets of lineage-biased multipotent progenitors control blood production in normal and regenerative conditions. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;17:35–46.
He H, Xu P, Zhang X, Liao M, Dong Q, Cong T, et al. Aging-induced IL27Ra signaling impairs hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. 2020;136:183–98.
Yamamoto R, Wilkinson AC, Ooehara J, Lan X, Lai C-Y, Nakauchi Y, et al. Large-scale clonal analysis resolves aging of the mouse hematopoietic stem cell compartment. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;22:600–7.e4.
Bayik D, Lathia JD. Cancer stem cell–immune cell crosstalk in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2021;21:526–36.
Schumacher TN, Schreiber RD. Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy. Science. 2015;348:69–74.
Riether C, Schürch CM, Ochsenbein AF. Regulation of hematopoietic and leukemic stem cells by the immune system. Cell Death Differ. 2015;22:187–98.
Visconte V, Maciejewski JP. Clonal dynamics of hematopoietic stem cell compartment in aplastic anemia. Semin Hematol. 2022;59:47–53.
Chen J, Kao Y-R, Sun D, Todorova TI, Reynolds D, Narayanagari S-R, et al. Myelodysplastic syndrome progression to acute myeloid leukemia at the stem cell level. Nat Med. 2019;25:103–10.
Acknowledgements
We thank Liting Wang for technical assistance with immunofluorescence. This study was supported by the Key Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81930090), the National Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of China (No. 81725019), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 82273571, 32171104, U22A20279, 81874256, and 81872556), Chongqing Natural Science Foundation (2023NSCQ-JQX0076).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WL, CL, and KY designed and performed experiments, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript. JC, YW, SZ, and KY contributed to flow cytometric analysis and animal experiments. LW and LR contributed to mouse model creation and animal experiments. MC and FC contributed to the ex vivo experiments and data analysis. YX and SW contributed to bioinformatics analysis and assisted with writing the manuscript. FW, QZ, and JZ contributed to the experimental design and data interpretation. LY, CD, and JW conceived and supervised the study, interpreted the data, and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, W., Liu, C., Yang, K. et al. Aged hematopoietic stem cells entrap regulatory T cells to create a prosurvival microenvironment. Cell Mol Immunol 20, 1216–1231 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-023-01072-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-023-01072-3
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Megakaryocytic IGF1 coordinates activation and ferroptosis to safeguard hematopoietic stem cell regeneration after radiation injury
Cell Communication and Signaling (2024)