Abstract
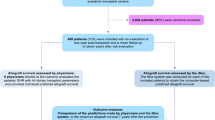
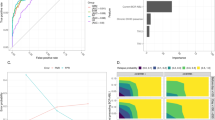
Allogeneic haematopoietic cell transplantation (alloHCT) has curative potential counterbalanced by its toxicity. Prognostic scores fail to include current era patients and alternative donors. We examined adult patients from the EBMT registry who underwent alloHCT between 2010 and 2019 for oncohaematological disease. Our primary objective was to develop a new prognostic score for overall mortality (OM), with a secondary objective of predicting non-relapse mortality (NRM) using the OM score. AI techniques were employed. The model for OM was trained, optimized, and validated using 70%, 15%, and 15% of the data set, respectively. The top models, “gradient boosting” for OM (AUC = 0.64) and “elasticnet” for NRM (AUC = 0.62), were selected. The analysis included 33,927 patients. In the final prognostic model, patients with the lowest score had a 2-year OM and NRM of 18 and 13%, respectively, while those with the highest score had a 2-year OM and NRM of 82 and 93%, respectively. The results were consistent in the subset of the haploidentical cohort (n = 4386). Our score effectively stratifies the risk of OM and NRM in the current era but do not significantly improve mortality prediction. Future prognostic scores can benefit from identifying biological or dynamic markers post alloHCT.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The study data belong to the EBMT and may be requested through previous authorization.
References
Cieri N, Maurer K, Wu CJ. 60 Years Young: The Evolving Role of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 2021;81:4373–84.
Snowden JA, Sánchez-Ortega I, Corbacioglu S, Basak GW, Chabannon C, de la Camara R, et al. Indications for haematopoietic cell transplantation for haematological diseases, solid tumours and immune disorders: current practice in Europe, 2022. Bone Marrow Transplant [Internet]. 2022 May [cited 2022 Jul 25]; Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41409-022-01691-w
Passweg JR, Baldomero H, Chabannon C, Basak GW, de la Cámara R, Corbacioglu S, et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation and cellular therapy survey of the EBMT: monitoring of activities and trends over 30 years. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2021;56:1651–64.
McDonald GB, Sandmaier BM, Mielcarek M, Sorror M, Pergam SA, Cheng GS, et al. Survival, Nonrelapse Mortality, and Relapse-Related Mortality After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: Comparing 2003–2007 Versus 2013–2017 Cohorts. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172:229.
Armand P, Kim HT, Logan BR, Wang Z, Alyea EP, Kalaycio ME, et al. Validation and refinement of the Disease Risk Index for allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2014;123:3664–71.
Papaemmanuil E, Gerstung M, Bullinger L, Gaidzik VI, Paschka P, Roberts ND, et al. Genomic Classification and Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl J Med. 2016;374:2209–21.
Della Porta MG, Gallì A, Bacigalupo A, Zibellini S, Bernardi M, Rizzo E, et al. Clinical Effects of Driver Somatic Mutations on the Outcomes of Patients With Myelodysplastic Syndromes Treated With Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation. JCO. 2016;34:3627–37.
Sorror ML, Maris MB, Storb R, Baron F, Sandmaier BM, Maloney DG, et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT)-specific comorbidity index: a new tool for risk assessment before allogeneic HCT. Blood. 2005;106:2912–9.
Gratwohl A. The EBMT risk score. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2012;47:749–56.
Sorror ML, Storb RF, Sandmaier BM, Maziarz RT, Pulsipher MA, Maris MB, et al. Comorbidity-Age Index: A Clinical Measure of Biologic Age Before Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. JCO. 2014;32:3249–56.
Barba P, Martino R, Pérez-Simón JA, Fernández-Avilés F, Castillo N, Piñana JL, et al. Combination of the Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Comorbidity Index and the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Score Allows a Better Stratification of High-Risk Patients Undergoing Reduced-Toxicity Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20:66–72.
Parimon T, Au DH, Martin PJ, Chien JW. A Risk Score for Mortality after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Ann Intern Med. 2006;144:407.
Luft T, Benner A, Terzer T, Jodele S, Dandoy CE, Storb R, et al. EASIX and mortality after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2020;55:553–61.
Shouval R, Labopin M, Bondi O, Mishan-Shamay H, Shimoni A, Ciceri F, et al. Prediction of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation Mortality 100 Days After Transplantation Using a Machine Learning Algorithm: A European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Acute Leukemia Working Party Retrospective Data Mining Study. JCO. 2015;33:3144–51.
Salas MQ, Atenafu EG, Bascom O, Wilson L, Lam W, Law AD, et al. Pilot prospective study of Frailty and Functionality in routine clinical assessment in allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2021;56:60–9.
Shouval R, Fein JA, Shouval A, Danylesko I, Shem-Tov N, Zlotnik M, et al. External validation and comparison of multiple prognostic scores in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood Adv. 2019;3:1881–90.
Bacigalupo A, Ballen K, Rizzo D, Giralt S, Lazarus H, Ho V, et al. Defining the Intensity of Conditioning Regimens: Working Definitions. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009;151628–33.
Penack O, Peczynski C, Mohty M, Yakoub-Agha I, de la Camara R, Glass B, et al. Association of pre-existing comorbidities with outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. A retrospective analysis from the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2022;57:183–90.
Iacobelli S, On behalf of the EBMT Statistical Committee. Suggestions on the use of statistical methodologies in studies of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2013;48:S1–37.
Domínguez-Almendros S, Benítez-Parejo N, Gonzalez-Ramirez AR. Logistic regression models. Allergologia et Immunopathologia. 2011;39:295–305.
Yamashita T, Yamashita K, Kamimura R. A Stepwise AIC Method for Variable Selection in Linear Regression. Commun Stat - Theory Methods. 2007;36:2395–403.
Cortes C, Vapnik V. Support-vector networks. Mach Learn. 1995;20:273–97.
Chen T, Guestrin C XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining [Internet]. San Francisco California USA: ACM; 2016 [cited 2023 Jul 14]. p. 785–94. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1145/2939672.2939785.
Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R Regularization Paths for Generalized Linear Models via Coordinate Descent. J Stat Soft [Internet]. 2010 [cited 2023 Jul 14];33. Available from: http://www.jstatsoft.org/v33/i01/.
R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2021. http://www.R-project.org/.
Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: Development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1987;40:373–83.
Sorror ML. How I assess comorbidities before hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood. 2013;121:2854–63.
Vaughn JE, Storer BE, Armand P, Raimondi R, Gibson C, Rambaldi A, et al. Design and Validation of an Augmented Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation-Comorbidity Index Comprising Pretransplant Ferritin, Albumin, and Platelet Count for Prediction of Outcomes after Allogeneic Transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015;21:1418–24.
Potdar R, Varadi G, Fein J, Labopin M, Nagler A, Shouval R. Prognostic Scoring Systems in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Where Do We Stand? Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017;23:1839–46.
Luznik L, O’Donnell PV, Symons HJ, Chen AR, Leffell MS, Zahurak M, et al. HLA-haploidentical bone marrow transplantation for hematologic malignancies using nonmyeloablative conditioning and high-dose, posttransplantation cyclophosphamide. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2008;14(Jun):641–50.
Holmes HM, Des Bordes JKA, Kebriaei P, Yennu S, Champlin RE, Giralt S, et al. Optimal screening for geriatric assessment in older allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation candidates. J Geriatr Oncol. 2014;5:422–30.
Peña M, Salas MQ, Mussetti A, Moreno-Gonzalez G, Bosch A, Patiño B, et al. Pretransplantation EASIX predicts intensive care unit admission in allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood Adv. 2021;5:3418–26.
Nitski O, Azhie A, Qazi-Arisar FA, Wang X, Ma S, Lilly L, et al. Long-term mortality risk stratification of liver transplant recipients: real-time application of deep learning algorithms on longitudinal data. Lancet Digital Health. 2021;3:e295–305.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MA, RSB, SA were responsible for the overall research questions and design of the study. RSB, MV, GJE performed the statistical analyses. MA, RSB wrote the original draft. PC, GJE, PE, KN, BD, PLR, KA, MA, SM, HRM, BM, SU, SH, FE, PU, RP, AE, CP, YAI, CC, CF, ST, AM, KC, MI, PO, SH, MM, GB, BG, PZ reviewed and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mussetti, A., Rius-Sansalvador, B., Moreno, V. et al. Artificial intelligence methods to estimate overall mortality and non-relapse mortality following allogeneic HCT in the modern era: an EBMT-TCWP study. Bone Marrow Transplant 59, 232–238 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-023-02147-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-023-02147-5