Abstract
Background
Surgical treatment of symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) has seen an evolution during the last decades. On one hand, en-bloc HoLEP emerged as a valid endoscopic treatment regardless prostate size. On the other hand, robot-assisted simple prostatectomy (RASP) has gained attention in larger prostates showing encouraging results. Herein, for the first time in the scientific scenario, we sought to compare the outcomes of RASP and en-bloc HoLEP cases after propensity-score matching (PSM) analysis.
Methods
We retrospectively queried our prospectively database of patients treated with HoLEP or RASP between 2017 and 2022 among two high-volume centers. PSM was applied based on the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) questionnaire, prostate volume and max-flow rate. All procedures were performed by a single surgeon per center. Outcomes were assessed at 1, 3, and 6-month postoperatively and therefore annually. Trifecta definition was used to assess “success” in surgical procedures and was defined as the contemporary presence of: a) no postoperative complications within the first postoperative month; b) 1-month postoperative Qmax >15 ml/s and c) no urinary incontinence at 3-month evaluation.
Results
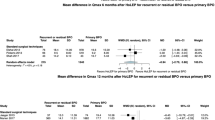
Overall, 48 HoLEP and 47 RASPs were matched. Operative time, hospitalization time (median 4 vs 5 days) and catheterization time (median 3 vs 2 day) were found to be shorter in the HoLEP group as compared to the counterpart (p < 0.05). Early postoperative complication rate was also lower in the HoLEP cohort (6.2% vs 12.6%; p = 0.03) as well as postoperative haemoglobine blood level drop (1.4 vs 2.4 g/dL; p = 0.03). On the other hand, postoperative antegrade ejaculation (55.3% vs 6.8%) 1-month max flow (median 28 vs 24 ml/sec) and continence rates (0% vs 20.8%) favored RASP (p < 0.05). Overall, Trifecta rate was similar in the two groups (76.1% vs 82.6%).
Conclusion
Both HoLEP and RASP are safe and effective treatments for symptomatic BPH. HoLEP demonstrated to have lower perioperative risks while is affecting by a higher probability of transient early UI. On the other hand, RASP is more effective in reducing postoperative ejaculatory dysfunction.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Dataset in which data have been collected and employed for the present study is available to the corresponding author.
References
Speakman MJ, Cornu JN, Gacci M, Gratzke C, Mamoulakis C, Herrmann TRW, et al. What Is the Required Certainty of Evidence for the Implementation of Novel Techniques for the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Obstruction? Eur Urol Focus. 2019;5:351–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euf.2019.05.014.
Cornu JN, Ahyai S, Bachmann A, de la Rosette J, Gilling P, Gratzke C, et al. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Functional Outcomes and Complications Following Transurethral Procedures for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Resulting from Benign Prostatic Obstruction: An Update. Eur Urol. 2015;67:1066–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2014.06.017.
Cornu JN, Gacci M, Hashim H, Herrmann TRW, Malde S, Netsch C, et al. Panel of the European Guideline on Non-Neurogenic Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) EAU Guidel Off 2023.
Merseburger AS, Herrmann TRW, Liatsikos E, Nagele U, Traxer O: EAU guidelines on Lasers and Technology. EAU Guidel Off 2020
Kuntz RM, Lehrich K, Ahyai SA. Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate versus Open Prostatectomy for Prostates Greater than 100 Grams: 5-Year Follow-Up Results of a Randomised Clinical Trial. Eur Urol. 2008;53:160–8.
Gilling PJ, Wilson LC, King CJ, Westenberg AM, Frampton CM, Fraundorfer MR. Long-term results of a randomized trial comparing holmium laser enucleation of the prostate and transurethral resection of the prostate: Results at 7 years. BJU Int. 2012;109:408–11.
Tuccio A, Sessa F, Campi R, Grosso AA, Viola L, Muto G, et al. En-bloc endoscopic enucleation of the prostate: a systematic review of the literature. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2020;72:292–312. https://doi.org/10.23736/S0393-2249.20.03706-6.
Goel MC. Re: Robotic simple prostatectomy R. Sotelo, R. Clavijo, O. Carmona, A. Garcia, E. Banda, M. Miranda and R. Fagin J Urol 2008; 179: 513-515. J Urol. 2008;180:1569–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2008.06.057.
Autorino R, Zargar H, Mariano MB, Sanchez-Salas R, Sotelo RJ, et al. Perioperative Outcomes of Robotic and Laparoscopic Simple Prostatectomy: A European-American Multi-institutional Analysis. Eur Urol. 2015;68:86–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2014.11.044
Sorokin I, Sundaram V, Singla N, Walker J, Margulis V, Roehrborn C, et al. Robot-Assisted Versus Open Simple Prostatectomy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Large Glands: A Propensity Score-Matched Comparison of Perioperative and Short-Term Outcomes. J Endourol. 2017;31:1164–9. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2017.0489.
Pandolfo SD, Del Giudice F, Chung BI, Manfredi C, De Sio M, Damiano R, et al. Robotic assisted simple prostatectomy versus other treatment modalities for large benign prostatic hyperplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of over 6500 cases. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-022-00616-4.
Vince R, Hampton LJ, Vartolomei MD, Shariat SF, Porpiglia F, Autorino R. Robotic assisted simple prostatectomy: recent advances. Curr Opin Urol. 2018;28:309–14. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOU.0000000000000499.
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien P-A. Classification of Surgical Complications: A New Proposal With Evaluation in a Cohort of 6336 Patients and Results of a Survey. Ann Surg. 2004;240:205–13.
Grosso AA, Di Maida F, Nardoni S, Salvi M, Giudici S, Lambertini L, et al. Patterns and Predictors of Optimal Surgical and Functional Outcomes after Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP): Introducing the Concept of “Trifecta”. World J Mens Health. 2023. https://doi.org/10.5534/wjmh.220042.
Tuccio A, Grosso AA, Sessa F, Salvi M, Tellini R, Cocci A, et al. En-Bloc Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate with Early Apical Release: Are We Ready for a New Paradigm? J Endourol. 2021;35:1675–83. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2020.1189.
Grosso AA, Di Maida F, Mari A, Nardoni S, Tuccio A, Minervini A. Holmium laser ablation of the prostate (HoLAP) with moses technology for the surgical treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Int Braz J Urol. 2022;48:200–1. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2021.0455.
Porpiglia F, Checcucci E, Amparore D, Niculescu G, Volpi G, Piramide F, et al. Urethral-sparing Robot-assisted Simple Prostatectomy: An Innovative Technique to Preserve Ejaculatory Function Overcoming the Limitation of the Standard Millin Approach. Eur Urol. 2021;80:222–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2020.09.028.
Autorino R, Amparore D, Loizzo D, Pandolfo SD, Checcucci E, Porpiglia F. Robot-assisted Simple Prostatectomy Is Better than Endoscopic Enucleation of the Prostate. Eur Urol Focus. 2022;8:368–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euf.2022.03.014.
Capogrosso P, Fallara G, Pozzi E, Schifano N, Candela L, Costa A, et al. Rates and predictors of postoperative complications after Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) at a high-volume center. Minerva Urol Nephrol. 2022;74:461–6. https://doi.org/10.23736/S2724-6051.21.04315-9.
Zhang MW, El Tayeb MM, Borofsky MS, Dauw CA, Wagner KR, Lowry PS, et al. Comparison of Perioperative Outcomes Between Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate and Robot-Assisted Simple Prostatectomy. J Endourol. 2017;31:847–50. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2017.0095.
Fuschi A, Al Salhi Y, Velotti G, Capone L, Martoccia A, Suraci PP, et al. Holmium laser enucleation of prostate versus minimally invasive simple prostatectomy for large volume (≥120 mL) prostate glands: a prospective multicenter randomized study. Minerva Urol Nephrol. 2021;73:638–48. https://doi.org/10.23736/S2724-6051.20.04043-6.
Di Maida F, Grosso AA, Tellini R, Nardoni S, Giudici S, Cadenar A, et al. Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) is safe and effective in patients with high comorbidity burden. Int Braz J Urol. 2023;49:341–50. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2022.0174.
Tuccio A, Grosso AA, Di Maida F, Mari A, Minervini A. Letter to the Editor regarding the article “The “Omega Sign”: a novel HoLEP technique that improves continence outcomes after enucleation”. World J Urol. 2022;40:1067–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-021-03667-9.
Grosso AA, Tuccio A, Salvi M, Paganelli D, Minervini A, Di Maida F. Re: Paolo Capogrosso, Eugenio Ventimiglia, Giuseppe Fallara, et al. Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate Is Associated with Complications and Sequelae Even in the Hands of an Experienced Surgeon Following Completion of the Learning Curve. Eur Urol Focus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euf.2023.03.018. In press. Eur Urol Focus. 2023;3:S2405-4569(23)00149-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euf.2023.05.013.
Tunc L, Yalcin S, Kaya E, Gazel E, Yılmaz S, Aybal HC, et al. The “Omega Sign”: a novel HoLEP technique that improves continence outcomes after enucleation. World J Urol. 2021;39:135–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-020-03152-9.
Lin YH, Chang SY, Tsao SH, Hou CP, Chen CL, Lin WC, et al. Anterior fibromuscular stroma-preserved endoscopic enucleation of the prostate: a precision anatomical approach. World J Urol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-022-04270-2.
Lee MS, Assmus MA, Ganesh M, Han J, Helon J, Mai Q, et al. An Outcomes Comparison Between Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate, Open Simple Prostatectomy, and Robotic Simple Prostatectomy for Large Gland Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy. Urology. 2023;173:180–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2022.12.018.
Shelton TM, Drake C, Vasquez R, Rivera M. Comparison of Contemporary Surgical Outcomes Between Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate and Robotic-Assisted Simple Prostatectomy. Curr Urol Rep. 2023;24:221–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-023-01146-9.
Brunckhorst O, Ahmed K, Nehikhare O, Marra G, Challacombe B, Popert R. Evaluation of the Learning Curve for Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate Using Multiple Outcome Measures. Urology. 2015;86:824–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2015.07.021.
Johnson B, Sorokin I, Singla N, Roehrborn C, Gahan JC. Determining the Learning Curve for Robot-Assisted Simple Prostatectomy in Surgeons Familiar with Robotic Surgery. J Endourol. 2018;32:865–70. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2018.0377.
Sokolakis I, Pyrgidis N, Russo GI, Sountoulides P, Hatzichristodoulou G. Preserving Ejaculation: A Guide Through the Landscape of Interventional and Surgical Options for Benign Prostatic Obstruction. Eur Urol Focus. 2022;8:380–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euf.2022.03.008.
Porto JG, Arbelaez MCS, Blachman-Braun R, Bhatia A, Bhatia S, Satyanarayana R, et al. Complications associated with minimally invasive surgical therapies (MIST) for surgical management of benign prostatic hyperplasia: a Manufacturer and User Facility Device Experience (MAUDE) database review. World J Urol. 2023;41:1975–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-023-04440-w.
Checcucci E, Veccia A, De Cillis S, Piramide F, Volpi G, Amparore D, et al. New Ultra-minimally Invasive Surgical Treatment for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Systematic Review and Analysis of Comparative Outcomes. Eur Urol Open Sci. 2021;33:28–41.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AAG: project development and manuscript writing. DA: manuscript writing, Data collection and analysis. FDiM: Data collection and analysis. SdeC: Data collection. AC: Data collection. MDiD: Data collection. GIR: Manuscript editing. SC: Data collection. AQ: Data collection. MS: Data collection. CF: Manuscript editing. Andrea Mari: Manuscript editing. FP: Project development and manuscript editing. Andrea Minervini: Project development and manuscript editing. AT: Project development and manuscript writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Informed consent
Informed consent Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. All the procedures were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research Committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Grosso, A.A., Amparore, D., Di Maida, F. et al. Comparison of perioperative and short-terms outcomes of en-bloc Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) and robot-assisted simple prostatectomy: a propensity-score matching analysis. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-023-00743-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-023-00743-6
This article is cited by
-
Influence of anterior fibromuscular stroma on incontinence outcomes in RASP and HoLEP: a critical analysis of Grosso et al.‘s findings
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases (2024)
-
Ejaculation sparing of classic and minimally invasive surgical treatments of LUTS/BPH
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases (2024)
-
Thulium fiber laser vs. holmium laser enucleation of the prostate: results of a prospective randomized non-inferiority trial
World Journal of Urology (2024)