Abstract
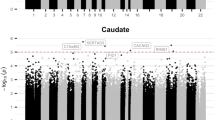
Despite advances in identifying rare and common genetic variants conferring risk for ADHD, the lack of a transcriptomic understanding of cortico-striatal brain circuitry has stymied a molecular mechanistic understanding of this disorder. To address this gap, we mapped the transcriptome of the caudate nucleus and anterior cingulate cortex in post-mortem tissue from 60 individuals with and without ADHD. Significant differential expression of genes was found in the anterior cingulate cortex and, to a lesser extent, the caudate. Significant downregulation emerged of neurotransmitter gene pathways, particularly glutamatergic, in keeping with models that implicate these neurotransmitters in ADHD. Consistent with the genetic overlap between mental disorders, correlations were found between the cortico-striatal transcriptomic changes seen in ADHD and those seen in other neurodevelopmental and mood disorders. This transcriptomic evidence points to cortico-striatal neurotransmitter anomalies in the pathogenesis of ADHD, consistent with current models of the disorder.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are being deposited in NIMH Data Archive under Collection 3151, experiment 2056 (https://nda.nih.gov/edit_collection.html?id=3151), with the https://doi.org/10.15154/1527972.
Code availability
Code used for analyses and figures is deposited here: https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/505945767, with the https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6798439.
References
Faraone SV, Larsson H. Genetics of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Mol Psychiatry. 2019;24:562–75.
Demontis D, Walters RK, Martin J, Mattheisen M, Als TD, Agerbo E, et al. Discovery of the first genome-wide significant risk loci for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Nat Genet. 2019;51:63–75.
Harich B, van der Voet M, Klein M, Čížek P, Fenckova M, Schenck A, et al. From rare copy number variants to biological processes in ADHD. Am J Psychiatry. 2020;177:855–66.
Qi X, Wang S, Zhang L, Liu L, Wen Y, Ma M, et al. An integrative analysis of transcriptome-wide association study and mRNA expression profile identified candidate genes for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2019;282:112639.
Liao C, Laporte AD, Spiegelman D, Akçimen F, Joober R, Dion PA, et al. Transcriptome-wide association study of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder identifies associated genes and phenotypes. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1–7.
McCaffrey TA, St Laurent G, Shtokalo D, Antonets D, Vyatkin Y, Jones D, et al. Biomarker discovery in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: RNA sequencing of whole blood in discordant twin and case-controlled cohorts. BMC Med Genomics. 2020;13:1–17.
Lorenzo G, Braun J, Muñoz G, Casarejos MJ, Bazán E, Jimenez-Escrig A. RNA-Seq blood transcriptome profiling in familial attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Psychiatry Res. 2018;270:544–6.
Mortimer N, Sánchez-Mora C, Rovira P, Vilar-Ribó L, Richarte V, Corrales M, et al. Transcriptome profiling in adult attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020;41:160–6.
Hoogman M, Muetzel R, Guimaraes JP, Shumskaya E, Mennes M, Zwiers MP, et al. Brain imaging of the cortex in ADHD: a coordinated analysis of large-scale clinical and population-based samples. Am J Psychiatry. 2019;176:531–42.
Hoogman M, Buitelaar JK, Faraone SV, Shaw P, Franke B. Subcortical brain volume differences in participants with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adults–Authors’ reply. Lancet Psychiatry. 2017;4:440–1.
Hart H, Radua J, Nakao T, Mataix-Cols D, Rubia K. Meta-analysis of functional magnetic resonance imaging studies of inhibition and attention in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: exploring task-specific, stimulant medication, and age effects, ADHD functional MR imaging studies meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2013;70:185–98.
Fusar-Poli P, Rubia K, Rossi G, Sartori G, Balottin U. Striatal dopamine transporter alterations in ADHD: pathophysiology or adaptation to psychostimulants? a meta-analysis. Am J Psychiatry. 2012;169:264–72.
Volkow ND, Wang G-J, Kollins SH, Wigal TL, Newcorn JH, Telang F, et al. Evaluating dopamine reward pathway in ADHD: clinical implications.[Erratum appears in JAMA. 2009 Oct 7;302(13):1420]. JAMA. 2009;302:1084–91.
Elia J, Glessner JT, Wang K, Takahashi N, Shtir CJ, Hadley D, et al. Genome-wide copy number variation study associates metabotropic glutamate receptor gene networks with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Nat Genet. 2012;44:78–84.
Halperin JM, Schulz KP. Revisiting the role of the prefrontal cortex in the pathophysiology of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Psychol Bull. 2006;132:560.
Shaw P, Sudre G. Adolescent attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: understanding teenage symptom trajectories. Biol Psychiatry. 2021;89:152–61.
Schulz KP, Li X, Clerkin SM, Fan J, Berwid OG, Newcorn JH, et al. Prefrontal and parietal correlates of cognitive control related to the adult outcome of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder diagnosed in childhood. Cortex. 2017;90:1–11.
Demontis D, Walters RK, Martin J, Mattheisen M, Als TD, Agerbo E, et al. Discovery of the first genome-wide significant risk loci for ADHD. bioRxiv. 2017.
Serretti A, Fabbri C. Shared genetics among major psychiatric disorders. Lancet. 2013;381:1339–41.
Opel N, Goltermann J, Hermesdorf M, Berger K, Baune BT, Dannlowski U. Cross-disorder analysis of brain structural abnormalities in six major psychiatric disorders: a secondary analysis of mega-and meta-analytical findings from the ENIGMA consortium. Biol Psychiatry. 2020;88:678–86.
Abramovitch A, Short T, Schweiger A. The C factor: cognitive dysfunction as a transdiagnostic dimension in psychopathology. Clin Psychol Rev. 2021;86:102007.
Hartley SW, Mullikin JC. QoRTs: a comprehensive toolset for quality control and data processing of RNA-Seq experiments. BMC Bioinforma. 2015;16:224.
Chen Y, Lun AT, Smyth GK. From reads to genes to pathways: differential expression analysis of RNA-Seq experiments using Rsubread and the edgeR quasi-likelihood pipeline. F1000Res. 2016;5:1438.
Bourgon R, Gentleman R, Huber W. Independent filtering increases detection power for high-throughput experiments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010;107:9546–51.
Kaiser HF. The application of electronic computers to factor analysis. Educ Psychol Meas. 1960;20:141–51.
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014;15:1–21.
Genomes Project C, Auton A, Brooks LD, Durbin RM, Garrison EP, Kang HM, et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature. 2015;526:68–74.
de Leeuw CA, Mooij JM, Heskes T, Posthuma D. MAGMA: generalized gene-set analysis of GWAS data. PLoS Comput Biol. 2015;11:e1004219.
Grove J, Ripke S, Als TD, Mattheisen M, Walters RK, Won H, et al. Identification of common genetic risk variants for autism spectrum disorder. Nat Genet. 2019;51:431–44.
Howard DM, Adams MJ, Clarke TK, Hafferty JD, Gibson J, Shirali M, et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis of depression identifies 102 independent variants and highlights the importance of the prefrontal brain regions. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22:343–52.
Wray NR, Ripke S, Mattheisen M, Trzaskowski M, Byrne EM, Abdellaoui A, et al. Genome-wide association analyses identify 44 risk variants and refine the genetic architecture of major depression. Nat Genet. 2018;50:668–81.
Stahl EA, Breen G, Forstner AJ, McQuillin A, Ripke S, Trubetskoy V, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 30 loci associated with bipolar disorder. Nat Genet. 2019;51:793–803.
Ripke S, Walters JT, O’Donovan MC, Consortium TSWGoPG. Mapping genomic loci prioritises genes and implicates synaptic biology in schizophrenia. medRxiv. 2020.
Yu D, Sul JH, Tsetsos F, Nawaz MS, Huang AY, Zelaya I, et al. Interrogating the genetic determinants of Tourette’s syndrome and other Tic disorders through genome-wide association studies. Am J Psychiatry. 2019;176:217–27.
International Obsessive Compulsive Disorder Foundation Genetics Collaborative, Studies OCDCGA. Revealing the complex genetic architecture of obsessive-compulsive disorder using meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23:1181–8.
Nievergelt CM, Maihofer AX, Klengel T, Atkinson EG, Chen CY, Choi KW, et al. International meta-analysis of PTSD genome-wide association studies identifies sex- and ancestry-specific genetic risk loci. Nat Commun. 2019;10:4558.
Kweon K, Shin ES, Park KJ, Lee JK, Joo Y, Kim HW. Genome-wide analysis reveals four novel loci for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in Korean youths. Soa Chongsonyon Chongsin Uihak. 2018;29:62–72.
Wang KS, Liu X, Zhang Q, Pan Y, Aragam N, Zeng M. A meta-analysis of two genome-wide association studies identifies 3 new loci for alcohol dependence. J Psychiatr Res. 2011;45:1419–25.
Zuo L, Gelernter J, Zhang CK, Zhao H, Lu L, Kranzler HR, et al. Genome-wide association study of alcohol dependence implicates KIAA0040 on chromosome 1q. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012;37:557–66.
Zuo L, Tan Y, Zhang X, Wang X, Krystal J, Tabakoff B, et al. A new genomewide association meta-analysis of alcohol dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2015;39:1388–95.
Sprooten E, Fleming KM, Thomson PA, Bastin ME, Whalley HC, Hall J, et al. White matter integrity as an intermediate phenotype: exploratory genome-wide association analysis in individuals at high risk of bipolar disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2013;206:223–31.
Kichaev G, Bhatia G, Loh PR, Gazal S, Burch K, Freund MK, et al. Leveraging polygenic functional enrichment to improve GWAS power. Am J Hum Genet. 2019;104:65–75.
van der Meer D, Frei O, Kaufmann T, Shadrin AA, Devor A, Smeland OB, et al. Understanding the genetic determinants of the brain with MOSTest. Nat Commun. 2020;11:3512.
Davies G, Lam M, Harris SE, Trampush JW, Luciano M, Hill WD, et al. Study of 300,486 individuals identifies 148 independent genetic loci influencing general cognitive function. Nat Commun. 2018;9:2098.
Lemarchant S, Pruvost M, Montaner J, Emery E, Vivien D, Kanninen K, et al. ADAMTS proteoglycanases in the physiological and pathological central nervous system. J Neuroinflammation. 2013;10:133.
Qiu Z, Yang J, Deng G, Li D, Zhang S. Angiopoietin-like 4 promotes angiogenesis and neurogenesis in a mouse model of acute ischemic stroke. Brain Res Bull. 2021;168:156–64.
Cicvaric A, Sachernegg HM, Stojanovic T, Symmank D, Smani T, Moeslinger T, et al. Podoplanin gene disruption in mice promotes in vivo neural progenitor cells proliferation, selectively impairs dentate gyrus synaptic depression and induces anxiety-like behaviors. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:561.
Mahajan GJ, Vallender EJ, Garrett MR, Challagundla L, Overholser JC, Jurjus G, et al. Altered neuro-inflammatory gene expression in hippocampus in major depressive disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2018;82:177–86.
Elkjaer ML, Frisch T, Reynolds R, Kacprowski T, Burton M, Kruse TA, et al. Unique RNA signature of different lesion types in the brain white matter in progressive multiple sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019;7:58.
Supek F, Bosnjak M, Skunca N, Smuc T. REVIGO summarizes and visualizes long lists of gene ontology terms. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e21800.
Zhang H, Zhou H, Lencz T, Farrer LA, Kranzler HR, Gelernter J. Genome-wide association study of cognitive flexibility assessed by the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2018;177:511–9.
de la Fuente J, Davies G, Grotzinger AD, Tucker-Drob EM, Deary IJ. A general dimension of genetic sharing across diverse cognitive traits inferred from molecular data. Nat Hum Behav. 2021;5:49–58.
Haber S, Knutson B. The reward circuit: linking primate anatomy and human imaging. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009;35:4–26.
Akutagava‐Martins GC, Salatino‐Oliveira A, Genro JP, Contini V, Polanczyk G, Zeni C, et al. Glutamatergic copy number variants and their role in attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Am J Med Genet Part B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2014;165:502–9.
Elia J, Ungal G, Kao C, Ambrosini A, De Jesus-Rosario N, Larsen L, et al. Fasoracetam in adolescents with ADHD and glutamatergic gene network variants disrupting mGluR neurotransmitter signaling. Nat Commun. 2018;9:1–9.
Zhang Q, Huang X, Chen XZ, Li SY, Yao T, Wu J. Association of gene variations in ionotropic glutamate receptor and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in the Chinese population: a two-stage case–control study. J Atten Disord. 2021;25:1362–73.
Gilbert D, Isaacs K, Augusta M, Macneil L, Mostofsky S. Motor cortex inhibition: a marker of ADHD behavior and motor development in children. Neurology. 2011;76:615–21.
Puts NA, Ryan M, Oeltzschner G, Horska A, Edden RA, Mahone EM. Reduced striatal GABA in unmedicated children with ADHD at 7T. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging. 2020;301:111082.
Calabresi P, Pisani A, Centonze D, Bernardi G. Synaptic plasticity and physiological interactions between dopamine and glutamate in the striatum. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1997;21:519–23.
Taylor H, Campbell J, Nobes CD. Ephs and ephrins. Curr Biol. 2017;27:R90–5.
Szekely E, Sudre GP, Sharp W, Leibenluft E, Shaw P. Defining the neural substrate of the adult outcome of childhood ADHD: a multimodal neuroimaging study of response inhibition. Am J Psychiatry. 2017;174:867–76.
Clerkin SM, Schulz KP, Berwid OG, Fan J, Newcorn JH, Tang CY, et al. Thalamo-cortical activation and connectivity during response preparation in adults with persistent and remitted ADHD. Am J Psychiatry. 2013;170:1011–9.
Nabavi S, Fox R, Proulx CD, Lin JY, Tsien RY, Malinow R. Engineering a memory with LTD and LTP. Nature. 2014;511:348–52.
Arrubla J, Farrher E, Strippelmann J, Tse DH, Grinberg F, Shah NJ, et al. Microstructural and functional correlates of glutamate concentration in the posterior cingulate cortex. J Neurosci Res. 2017;95:1796–808.
Gandal MJ, Haney JR, Parikshak NN, Leppa V, Ramaswami G, Hartl C, et al. Shared molecular neuropathology across major psychiatric disorders parallels polygenic overlap. Science. 2018;359:693–7.
Akula N, Marenco S, Johnson K, Feng N, Zhu K, Schulmann A, et al. Deep transcriptome sequencing of subgenual anterior cingulate cortex reveals cross-diagnostic and diagnosis-specific RNA expression changes in major psychiatric disorders. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021;46:1364–72.
Benjamin KJM, Feltrin AS, Barbosa AR, Jaffe AE, Collado-Torres L, Burke EE, et al. Genetic and environmental regulation of caudate nucleus transcriptome: insight into schizophrenia risk and the dopamine system. medRxiv 2020.11.18.20230540; https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.11.18.20230540.
Pacifico R, Davis R. Transcriptome sequencing implicates dorsal striatum-specific gene network, immune response and energy metabolism pathways in bipolar disorder. Mol Psychiatry. 2017;22:441–9.
Piantadosi SC, McClain LL, Klei L, Wang J, Chamberlain BL, Springer SA, et al. Transcriptome alterations are enriched for synapse-associated genes in the striatum of subjects with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Transl Psychiatry. 2021;11:171.
Wright C, Shin JH, Rajpurohit A, Deep-Soboslay A, Collado-Torres L, Brandon NJ, et al. Altered expression of histamine signaling genes in autism spectrum disorder. Transl Psychiatry. 2017;7:e1126.
Parikshak NN, Swarup V, Belgard TG, Irimia M, Ramaswami G, Gandal MJ, et al. Genome-wide changes in lncRNA, splicing, and regional gene expression patterns in autism. Nature. 2016;540:423–7.
Acknowledgements
The study was funded by the intramural programs of the NIMH and NHGRI: ZIC MH002903-15 to SM, ZIA HG200378-10 to PS, and ZIA HG000140 to ADB. We acknowledge the Pittsburgh and Maryland sites within the NIH funded Neurobiobank for the provision of tissues. We acknowledge Bhaskar Kolachana at the Human Brain Collection Core for preparing DNA for genotyping, Chandrasekharappa Settara and Frank Donovan at the Genomics Core for genotyping, and the NIH Intramural Sequencing Center. This work utilized the computational resources of the NIH HPC Biowulf cluster (http://hpc.nih.gov).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Contribution of each author to the manuscript: Study concept and design: GS, PS and SM. Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: all authors. Drafting of the manuscript: GS and PS. Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: all authors. Statistical analysis: GS. Administrative, technical, or material support: GGS, WS, BJ, QX, PKA and LE. Study supervision: PS and SM. Obtained funding: PS, SM and ADB.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sudre, G., Gildea, D.E., Shastri, G.G. et al. Mapping the cortico-striatal transcriptome in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Mol Psychiatry 28, 792–800 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-022-01844-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-022-01844-9
This article is cited by
-
Cortico-striatal differences in the epigenome in attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder
Translational Psychiatry (2024)
-
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder
Nature Reviews Disease Primers (2024)
-
The effects of methylphenidate and atomoxetine on Drosophila brain at single-cell resolution and potential drug repurposing for ADHD treatment
Molecular Psychiatry (2024)