Abstract
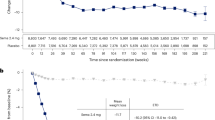
The antidiabetic effect of empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus has been explored in several trials. We performed this meta-analysis determining the effects of empagliflozin on blood pressure, uric acid, estimated glomerular filtration rate, blood lipids, blood glucose, and body weight in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. We searched three electronic databases (Pubmed, Web of Science, and Cochrane Central) for all published articles evaluating the effects of empagliflozin on blood glucose or blood pressure in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Total 5781 patients were included in 12 randomized controlled trials with a follow-up of 28 ± 22 weeks. Empagliflozin 10 or 25 mg reduced systolic and diastolic blood pressure, uric acid, hemoglobin A1c, fasting plasma glucose, and body weight in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (all p < 0.001). There were no differences for changes of estimated glomerular filtration rate between empagliflozin 10 or 25 mg and placebo in these patients (all p > 0.05). In conclusion, empagliflozin reduces systolic and diastolic blood pressure, uric acid, hemoglobin A1c, fasting plasma glucose, and body weight. These data suggest the beneficial effects of empagliflozin on these cardiovascular risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Plosker GL. Canagliflozin: a review of its use in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs. 2014;74:807–24.
Plosker GL. Dapagliflozin: a review of its use in patients with type 2 diabetes. Drugs. 2014;74:2191–209.
Majewski C, Bakris GL. Blood pressure reduction: an added benefit of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:429–30.
Rosenstock J, Jelaska A, Zeller C, Kim G, Broedl UC, Woerle HJ, et al. Impact of empagliflozin added on to basal insulin in type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on basal insulin: a 78-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015;17:936–48.
Tikkanen I, Narko K, Zeller C, Green A, Salsali A, Broedl UC, et al. Empagliflozin reduces blood pressure in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:420–8.
Häring HU, Merker L, Seewaldt-Becker E, Weimer M, Meinicke T, Woerle HJ, et al. Empagliflozin as add-on to metformin plus sulfonylurea in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 2013;36:3396–404.
Kovacs CS, Seshiah V, Swallow R, Jones R, Rattunde H, Woerle HJ, et al. Empagliflozin improves glycaemic and weight control as add-on therapy to pioglitazone or pioglitazone plus metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014;16:147–58.
Ross S, Thamer C, Cescutti J, Meinicke T, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin twice daily versus once daily in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin: a 16-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015;17:699–702.
Roden M, Merker L, Christiansen AV, Roux F, Salsali A, Kim G, et al. Safety, tolerability and effects on cardiometabolic risk factors of empagliflozin monotherapy in drug-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes: a double-blind extension of a Phase III randomized controlled trial. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015;14:154.
Häring HU, Merker L, Seewaldt-Becker E, Weimer M, Meinicke T, Broedl UC, et al. Empagliflozin as add-on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:1650–9.
Rosenstock J, Jelaska A, Frappin G, Salsali A, Kim G, Woerle HJ, et al. Improved glucose control with weight loss, lower insulin doses, and no increased hypoglycemia with empagliflozin added to titrated multiple daily injections of insulin in obese inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:1815–23.
Nishimura R, Tanaka Y, Koiwai K, Inoue K, Hach T, Salsali A, et al. Effect of empagliflozin monotherapy on postprandial glucose and 24-hour glucose variability in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 4-week study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015;14:11.
Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2117–28.
Fitchett D, Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Hantel S, Salsali A, et al. Heart failure outcomes with empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes at high cardiovascular risk: results of the EMPA-REG OUTCOME® trial. Eur Heart J. 2016;37:1526–34.
Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, von Eynatten M, Mattheus M, et al. Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:323–34.
Ingelfinger JR, Rosen CJ. Cardiovascular risk and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2178–9.
Rosenstock J, Seman LJ, Jelaska A, Hantel S, Pinnetti S, Hach T, et al. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin, a sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, as add-on to metformin in type 2 diabetes with mild hyperglycaemia. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013;15:1154–60.
Kadowaki T, Haneda M, Inagaki N, Terauchi Y, Taniguchi A, Koiwai K, et al. Empagliflozin monotherapy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II trial. Adv Ther. 2014;31:621–38.
Barnett AH, Mithal A, Manassie J, Jones R, Rattunde H, Woerle HJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin added to existing antidiabetes treatment in patients with type 2diabetes and chronic kidney disease: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014;2:369–84.
Cherney DZ, Perkins BA, Soleymanlou N, Xiao F, Zimpelmann J, Woerle HJ, et al. Sodium glucose cotransport-2 inhibition and intrarenal RAS activity in people with type 1 diabetes. Kidney Int. 2014;86:1057–8.
Zinman B, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, Wanner C, Fitchett D, Kohler S, et al. Empagliflozin and cerebrovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus at high cardiovascular risk. Stroke. 2017;48:1218–25.
Kaku K, Lee J, Mattheus M, Kaspers S, George J, Woerle HJ, et al. Empagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in asian patients with type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease- results from EMPA-REG OUTCOME®. Circ J. 2017;81:227–34.
Inzucchi SE, Zinman B, Fitchett D, Wanner C, Ferrannini E, Schumacher M, et al. How does empagliflozin reduce cardiovascular mortality? Insights from a mediation analysis of the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial. Diabetes Care. 2018;41:356–63.
Dentali F, Riva N, Crowther M, Turpie AG, Lip GY, Ageno W. Efficacy and safety of the novel oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. Circulation. 2012;126:2381–91.
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996;17:1–12.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in metaanalyses. BMJ. 2003;327:557–60.
Begg CB, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics. 1994;50:1088–101.
Oliva RV, Bakris GL. Blood pressure effects of sodium–glucose co-transport 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2014;8:330–9.
Sarafidis PA, Tsapas A. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:1092.
Mancia G, Cannon CP, Tikkanen I, Zeller C, Ley L, Woerle HJ, et al. Impact of empagliflozin on blood pressure in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension by background antihypertensive medication. Hypertension. 2016;68:1355–64.
Maliha G, Townsend RR. SGLT2 inhibitors: their potential reduction in blood pressure. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2015;9:48–53.
Mancia G, Grassi G, Borghi C. Hyperuricemia, urate deposition and the association with hypertension. Curr Med Res Opin. 2015;31(Suppl 2):15–19.
Saito Y, Nakayama T, Sugimoto K, Fujimoto Y, Kobayashi Y. Relation of lipid content of coronary plaque to level of serum uric acid. Am J Cardiol. 2015;116:1346–50.
Prasad M, Matteson EL, Herrmann J, Gulati R, Rihal CS, Lerman LO, et al. Uric acid is associated with inflammation, coronary microvascular dysfunction, and adverse outcomes in postmenopausal women. Hypertension. 2017;69:236–42.
Kanbay M, Jensen T, Solak Y, Le M, Roncal-Jimenez C, Rivard C, et al. Uric acid in metabolic syndrome: from an innocent bystander to a central player. Eur J Intern Med. 2016;29:3–8.
Yale JF, Bakris G, Cariou B, Yue D, David-Neto E, Xi L, et al. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin in subjects with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013;15:463–73.
Kohan DE, Fioretto P, Tang W, List JF. Long-term study of patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate renal impairment shows that dapagliflozin reduces weight and blood pressure but does not improve glycemic control. Kidney Int. 2014;85:962–71.
Cefalu WT, Leiter LA, Yoon KH, Arias P, Niskanen L, Xie J, et al. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin versus glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin (CANTATA-SU): 52 week results from a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2013;382:941–50.
Vallon V, Thomson SC. Targeting renal glucose reabsorption to treat hyperglycaemia: the pleiotropic effects of SGLT2 inhibition. Diabetologia. 2017;60:215–25.
Neeland IJ, McGuire DK, Chilton R, Crowe S, Lund SS, Woerle HJ, et al. Empagliflozin reduces body weight and indices of adipose distribution in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2016;13:119–26.
Imprialos K, Faselis C, Boutari C, Stavropoulos K, Athyros V, Karagiannis A, et al. SGLT-2 inhibitors and cardiovascular risk in diabetes mellitus: a comprehensive and critical review of the literature. Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23:1510–21.
Perrone-Filardi P, Avogaro A, Bonora E, Colivicchi F, Fioretto P, Maggioni AP, et al. Mechanisms linking empagliflozin to cardiovascular and renal protection. Int J Cardiol. 2017;241:450–6.
Scheen AJ. Effects of reducing blood pressure on cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes: focus on SGLT2 inhibitors and EMPA-REG OUTCOME. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2016;121:204–14.
Sattar N, McLaren J, Kristensen SL, Preiss D, McMurray JJ. SGLT2 Inhibition and cardiovascular events: why did EMPA-REG Outcomes surprise and what were the likely mechanisms? Diabetologia. 2016;59:1333–9.
Dalan R. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibition in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a review of large-scale cardiovascular outcome studies and possible mechanisms of benefit. Cardiol Rev. 2018;26:312–20.
Vettor R, Inzucchi SE, Fioretto P. The cardiovascular benefits of empagliflozin: SGLT2-dependent and -independent effects. Diabetologia. 2017;60:395–8.
Cavaiola TS, Pettus J. Cardiovascular effects of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2018;11:133–48.
Mudaliar S, Polidori D, Zambrowicz B, Henry RR. Sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibitors: effects on renal and intestinal glucose transport: from bench to bedside. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:2344–53.
Staels B. Cardiovascular protection by sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors: potential mechanisms. Am J Med. 2017;130(6S):S30–S39.
Lambers Heerspink HJ, de Zeeuw D, Wie L, Leslie B, List J. Dapagliflozin a glucose-regulating drug with diuretic properties in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013;15:853–62.
Sano M, Takei M, Shiraishi Y, Suzuki Y. Increased hematocrit during sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor therapy indicates recovery of tubulointerstitial function in diabetic kidneys. J Clin Med Res. 2016;8:844–7.
Paneni F, Lüscher TF. Cardiovascular protection in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: a review of clinical trial results across drug classes. Am J Cardiol. 2017;120(1S):S17–S27.
Muskiet MH, van Raalte DH, van Bommel EJ, Smits MM, Tonneijck L. Understanding EMPA-REG OUTCOME. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015;3:928–9.
Sano M. A new class of drugs for heart failure: SGLT2 inhibitors reduce sympathetic overactivity. J Cardiol. 2018;71:471–6.
Ceriello A, Genovese S, Mannucci E, Gronda E. Glucagon and heart in type 2 diabetes: new perspectives. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2016;15:123.
Jones BJ, Tan T, Bloom SR. Minireview: glucagon in stress and energy homeostasis. Endocrinology. 2012;153:1049–54.
Ferrannini E, Muscelli E, Frascerra S, Baldi S, Mari A, Heise T, et al. Metabolic response to sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition in type 2 diabetic patients. J Clin Invest. 2014;124:499–508.
Lahnwong S, Chattipakorn SC, Chattipakorn N. Potential mechanisms responsible for cardioprotective effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018;17:101.
Verma S, McMurray JJV. SGLT2 inhibitors and mechanisms of cardiovascular benefit: a state-of-the-art review. Diabetologia. 2018;61:2108–17.
Daniele G, Xiong J, Solis-Herrera C, Merovci A, Eldor R, Tripathy D, et al. Dapagliflozin enhances fat oxidation and ketone production in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2016;39:2036–41.
Jorgensen NB, Pedersen J, Vaag AA. EMPA-REG: glucose excretion and lipid mobilization - not storage - saves lives. J Diabetes Complicat. 2016;30:753.
Pham SV, Chilton RJ. EMPA-REG OUTCOME: the cardiologist’s point of view. Am J Cardiol. 2017;120(1S):S53–S58.
Tahara A, Kurosaki E, Yokono M, Yamajuku D, Kihara R, Hayashizaki Y, et al. Effects of SGLT2 selective inhibitor ipragliflozin on hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, hepatic steatosis, oxidative stress, inflammation, and obesity in type 2 diabetic mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;715:246–55.
Beckman JA, Creager MA, Libby P. Diabetes and atherosclerosis: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. JAMA. 2002;287:2570–81.
Shi X, Verma S, Yun J, Brand-Arzamendi K, Singh KK, Liu X, et al. Effect of empagliflozin on cardiac biomarkers in a zebrafish model of heart failure: clues to the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial? Mol Cell Biochem. 2017;433:97–102.
Packer M, Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Zannad F, et al. Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for the treatment of patients with heart failure: proposal of a novel mechanism of action. JAMA Cardiol. 2017;2:1025–9.
Baron KT, Macha S, Broedl UC, Nock V, Retlich S, Riggs M. Population pharmacokinetics and exposure-response (efficacy and safety/tolerability) of empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Ther. 2016;7:455–71.
Wilding J, Fernando K, Milne N, Evans M, Ali A, Bain S, et al. SGLT2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes management: key evidence and implications for clinical practice. Diabetes Ther. 2018;9:1757–73.
Barnett AH, Mithal A, Manassie J, et al. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin added to existing antidiabetes treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014;2:369–84.
Scheen AJ. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and clinical use of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2015;54:691–708.
Riggs MM, Seman LJ, Staab A, MacGregor TR, Gillespie W, Gastonguay MR, et al. Exposure-response modelling for empagliflozin, a sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, in patients with type 2 diabetes. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2014;78:1407–18.
Dardi I, Kouvatsos T, Jabbour SA. SGLT2 inhibitors. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016;101:27–39.
Macha S, Mattheus M, Halabi A, Pinnetti S, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety of empagliflozin, a sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, in subjects with renal impairment. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014;16:215–22.
Boehringer Ingelheim Limited. Empagliflozin: summary of product characteristics. 2018. https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/5441. AccessedApril 2018.
Sano M, Meguro S, Kawai T, Suzuki Y. Increased grip strength with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2. J Diabetes. 2016;8:736–7.
Bolinder J, Ljunggren Ö, Johansson L, Wilding J, Langkilde AM, Sjöström CD, et al. Dapagliflozin maintains glycaemic control while reducing weight and body fat mass over 2 years in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on metformin. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014;16:159–69.
Fujita Y, Inagaki N. Renal sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors as a novel therapeutic approach to treatment of type 2 diabetes: Clinical data and mechanism of action. J Diabetes Investig. 2014;5:265–75.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by funding from the First Affiliated Hospital, and College of Clinical Medicine of Henan University of Science and Technology, and Luoyang Central Hospital Affiliated to Zhengzhou University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, D., Liu, H. & Dong, P. Empagliflozin reduces blood pressure and uric acid in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hum Hypertens 33, 327–339 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-018-0134-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-018-0134-2
This article is cited by
-
Effects of empagliflozin on serum uric acid level of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta‐analysis
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome (2023)
-
Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on renal risk factors in patients with abnormal glucose metabolism: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (2023)
-
Management of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: from neurohormonal antagonists to empagliflozin
Heart Failure Reviews (2022)
-
The Pleiotropic Effects of Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors: Beyond the Glycemic Benefit
Diabetes Therapy (2019)
-
Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors on the Sympathetic Nervous System and Blood Pressure
Current Cardiology Reports (2019)