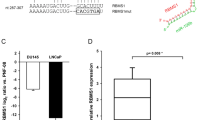
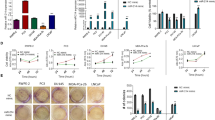
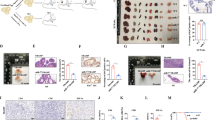
Abstract
Prostate cancer is one of the most significant cancers of men all over the world. The microRNAs (miRNAs) possess crucial functions in pathogenesis of the disease and its gain of androgen independency. The miRNAs are small, approximately 18–24 nucleotides, non-coding, endogenously synthesized RNAs that regulate gene expression post-transcriptionally. They are found in viruses, plants, and animal cells. The miRNAs have critical functions in gene expression and their dysregulation may cause tumor formation and progression of several diseases. Here, we have reviewed the most current literature to elucidate the function of miRNAs in human prostate cancer. We believe that this will help investigators not only working in prostate cancer, but also studying the miRNAs in other diseases to delineate the functions of miRNAs implicated in human prostate cancer development and progression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sullivan CS, Grundhoff A, Tevethia S, Treisman R, Pipas JM, Ganem D . Expression and function of microRNAs in viruses great and small. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 2006; 71: 351–356.
Mallory AC, Vaucheret H . Functions of microRNAs and related small RNAs in plants. Nat Genet 2006; 38 (Suppl): S31–S36.
Stefani G, Slack FJ . Small non-coding RNAs in animal development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008; 9: 219–230.
Griffiths-Jones S, Saini HK, van Dongen S, Enright AJ . miRBase: tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 2008; 36: D154–D158.
Griffiths-Jones S, Grocock RJ, van Dongen S, Bateman A, Enright AJ . miRBase: microRNA sequences, targets and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res 2006; 34: D140–D144.
Griffiths-Jones S . The microRNA registry. Nucleic Acids Res 2004; 32: D109–D111.
Bartel DP . MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function (reprinted from Cell, vol 116, pg 281–297, 2004). Cell 2007; 131: 11–29.
Wu LG, Fan JH, Belasco JG . MicroRNAs direct rapid deadenylation of mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 4034–4039.
Selbach M, Schwanhausser B, Thierfelder N, Fang Z, Khanin R, Rajewsky N . Widespread changes in protein synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature 2008; 455: 58–63.
Porkka KP, Pfeiffer MJ, Waltering KK, Vessella RL, Tammela TLJ, Visakorpi T . MicroRNA expression profiling in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 6130–6135.
Ambs S, Prueitt RL, Yi M, Hudson RS, Howe TM, Petrocca F et al. Genomic profiling of MicroRNA and messenger RNA reveals deregulated MicroRNA expression in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 6162–6170.
Musiyenko A, Bitko V, Barik S . Ectopic expression of miR-126*, an intronic product of the vascular endothelial EGF-like 7 gene, regulates prostein translation and invasiveness of prostate cancer LNCaP cells. J Mol Med 2008; 86: 313–322.
Saito Y, Friedman JM, Chihara Y, Egger G, Chuang JC, Liang G . Epigenetic therapy upregulates the tumor suppressor microRNA-126 and its host gene EGFL7 in human cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009; 379: 726–731.
Chiosea S, Jelezcova E, Chandran U, Acquafondata M, McHale T, Sobol RW et al. Up-regulation of dicer, a component of the MicroRNA machinery, in prostate adenocarcinoma. Am J Pathol 2006; 169: 1812–1820.
Sun RP, Fu XP, Li Y, Xie Y, Mao YM . Global gene expression analysis reveals reduced abundance of putative microRNA targets in human prostate tumours. BMC Genomics 2009; 93: 10.
Shi XB, Tepper CG, White RW . MicroRNAs and prostate cancer. J Cell Mol Med 2008; 12: 1456–1465.
Tong AW, Fulgham P, Jay C, Chen P, Khalil I, Liu S et al. MicroRNA profile analysis of human prostate cancers. Cancer Gene Ther 2009; 16: 206–216.
Ozen M, Creighton CJ, Ozdemir M, Ittmann M . Widespread deregulation of microRNA expression in human prostate cancer. Oncogene 2008; 27: 1788–1793.
Lu Z, Liu M, Stribinskis V, Klinge CM, Ramos KS, Colburn NH et al. MicroRNA-21 promotes cell transformation by targeting the programmed cell death 4 gene. Oncogene 2008; 27: 4373–4379.
He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT, Hernando-Monge E, Mu D, Goodson S et al. A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature 2005; 435: 828–833.
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 2257–2261.
Sylvestre Y, De Guire V, Querido E, Mukhopadhyay UK, Bourdeau V, Major F et al. An E2F/miR-20a autoregulatory feedback loop. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 2135–2143.
Xiao CC, Srinivasan L, Calado DP, Patterson HC, Zhang BC, Wang J et al. Lymphoproliferative disease and autoimmunity in mice with increased miR-17-92 expression in lymphocytes. Nat Immunol 2008; 9: 405–414.
Ventura A, Young AG, Winslow MM, Lintault L, Meissner A, Erkeland SJ et al. Targeted deletion reveals essential and overlapping functions of the miR-17 similar to 92 family of miRNA clusters. Cell 2008; 132: 875–886.
Shi XB, Xue L, Yang J, Ma AH, Zhao J, Xu M et al. An androgen-regulated miRNA suppresses Bak1 expression and induces androgen-independent growth of prostate cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 19983–19988.
Lee YS, Kim HK, Chung S, Kim KS, Dutta A . Depletion of human micro-RNA miR-125b reveals that it is critical for the proliferation of differentiated cells but not for the down-regulation of putative targets during differentiation. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 16635–16641.
Scott GK, Goga A, Bhaumik D, Berger CE, Sullivan CS, Benz CC . Coordinate suppression of ERBB2 and ERBB3 by enforced expression of micro-RNA miR-125a or miR-125b. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 1479–1486.
Craft N, Shostak Y, Carey M, Sawyers CL . A mechanism for hormone-independent prostate cancer through modulation of androgen receptor signaling by the HER-2/neu tyrosine kinase. Nat Med 1999; 5: 280–285.
Li T, Li D, Sha J, Sun P, Huang Y . MicroRNA-21 directly targets MARCKS and promotes apoptosis resistance and invasion in prostate cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009; 383: 280–285.
Zhu SM, Wu HL, Wu FT, Nie DT, Sheng SJ, Mo YY . MicroRNA-21 targets tumor suppressor genes in invasion and metastasis. Cell Res 2008; 18: 350–359.
Galardi S, Mercatelli N, Giorda E, Massalini S, Frajese GV, Ciafre SA et al. miR-221 and miR-222 expression affects the proliferation potential of human prostate carcinoma cell lines by targeting p27(Kip1)*. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 23716–23724.
Mercatelli N, Coppola V, Bonci D, Miele F, Costantini A, Guadagnoli M et al. The inhibition of the highly expressed miR-221 and miR-222 impairs the growth of prostate carcinoma xenografts in mice. PLoS One 2008; 3: e4029.
Sun T, Wang Q, Balk S, Brown M, Lee GS, Kantoff P . The role of microRNA-221 and microRNA-222 in androgen-independent prostate cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 3356–3363.
Hu L, Ibrahim S, Liu C, Skaar J, Pagano M, Karpatkin S . Thrombin induces tumor cell cycle activation and spontaneous growth by down-regulation of p27Kip1, in association with the up-regulation of Skp2 and MiR-222. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 3374–3381.
Calin GA, Ferracin M, Cimmino A, Di Leva G, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE et al. A MicroRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 1793–1801.
Bonci D, Coppola V, Musumeci M, Addario A, Giuffrida R, Memeo L et al. The miR-15a-miR-16-1 cluster controls prostate cancer by targeting multiple oncogenic activities. Nat Med 2008; 14: 1271–1277.
Aqeilan RI, Calin GA, Groce CM . miR-15a and miR 16-1 in cancer: discovery, function and future perspectives. Cell Death Differ 2010; 17: 215–220; advanced online publication.
Michael MZ, O’Connor SM, Pellekaan NGV, Young GP, James RJ . Reduced accumulation of specific MicroRNAs in colorectal neoplasia. Mol Cancer Res 2003; 1: 882–891.
Akao Y, Nakagawa Y, Naoe T . MicroRNAs 143 and 145 are possible common onco-microRNAs in human cancers. Oncol Rep 2006; 16: 845–850.
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S et al. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 7065–7070.
La Rocca G, Badin M, Shi B, Xu SQ, deAngelis T, Sepp-Lorenzinoi L et al. Mechanism of growth inhibition by MicroRNA 145: the role of the IGF-I receptor signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol 2009; 220: 485–491.
Shi B, Sepp-Lorenzino L, Prisco M, Linsley P, deAngelis T, Baserga R . Micro RNA 145 targets the insulin receptor substrate-1 and inhibits the growth of colon cancer cells. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 32582–32590.
Wang S, Bian C, Yang Z, Bo Y, Li J, Zeng L et al. miR-145 inhibits breast cancer cell growth through RTKN. Int J Oncol 2009; 34: 1461–1466.
Liu X, Sempere LF, Galimberti F, Freemantle SJ, Black C, Dragnev KH et al. Uncovering growth-suppressive MicroRNAs in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 1177–1183.
Cho WC, Chow AS, Au JS . Restoration of tumour suppressor hsa-miR-145 inhibits cancer cell growth in lung adenocarcinoma patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation. Eur J Cancer 2009; 45: 2197–2206.
Wang L, Tang H, Thayanithy V, Subramanian S, Oberg AL, Cunningham JM et al. Gene networks and microRNAs implicated in aggressive prostate cancer. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 9490–9497.
Lin SL, Chiang A, Chang D, Ying SY . Loss of mir-146a function in hormone-refractory prostate cancer. RNA 2008; 14: 417–424.
Fujita Y, Kojima K, Hamada N, Ohhashi R, Akao Y, Nozawa Y et al. Effects of miR-34a on cell growth and chemoresistance in prostate cancer PC3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2008; 377: 114–119.
Lodygin D, Tarasov V, Epanchintsev A, Berking C, Knyazeva T, Korner H et al. Inactivation of miR-34a by aberrant CpG methylation in multiple types of cancer. Cell Cycle 2008; 7: 2591–2600.
Jung-Hynes B, Ahmad N . Role of p53 in the anti-proliferative effects of Sirt1 inhibition in prostate cancer cells. Cell Cycle 2009; 8: 1478–1483.
Rokhlin OW, Scheinker VS, Taghiyev AF, Bumcrot D, Glover RA, Cohen MB . MicroRNA-34 mediates AR-dependent p53-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 2008; 7: 1288–1296.
Sachdeva M, Zhu S, Wu F, Wu H, Walia V, Kumar S et al. p53 represses c-Myc through induction of the tumor suppressor miR-145. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 3207–3212.
Suzuki HI, Yamagata K, Sugimoto K, Iwamoto T, Kato S, Miyazono K . Modulation of microRNA processing by p53. Nature 2009; 460: 529–533.
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, Byrom M, Jarvis R, Cheng A et al. RAS is regulated by the let-7 MicroRNA family. Cell 2005; 120: 635–647.
Tong AW, Nemunaitis J . Modulation of miRNA activity in human cancer: a new paradigm for cancer gene therapy? Cancer Gene Ther 2008; 15: 341–355.
Noonan EJ, Place RF, Pookot D, Basak S, Whitson JM, Hirata H et al. miR-449a targets HDAC-1 and induces growth arrest in prostate cancer. Oncogene 2009; 28: 1714–1724.
Gandellini P, Folini M, Longoni N, Pennati M, Binda M, Colecchia M et al. miR-205 exerts tumor-suppressive functions in human prostate through down-regulation of protein kinase Cepsilon. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 2287–2295.
Kong D, Li Y, Wang Z, Banerjee S, Ahmad A, Kim HR et al. The MiR-200 regulates PDGF-D mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition, adhesion and invasion of prostate cancer cells. Stem Cells 2009; 27: 1712–1721.
Varambally S, Cao Q, Mani RS, Shankar S, Wang X, Ateeq B et al. Genomic loss of microRNA-101 leads to overexpression of histone methyltransferase EZH2 in cancer. Science 2008; 322: 1695–1699.
Sampson VB, Rong NH, Han J, Yang Q, Aris V, Soteropoulos P et al. MicroRNA let-7a down-regulates MYC and reverts MYC-induced growth in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 9762–9770.
Peng Y, Laser J, Shi G, Mittal K, Melamed J, Lee P et al. Antiproliferative effects by Let-7 repression of high-mobility group A2 in uterine leiomyoma. Mol Cancer Res 2008; 6: 663–673.
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005; 435: 834–838.
Liang H, Li WH . MicroRNA regulation of human protein-protein interaction network. RNA—A Publication of the RNA Society 2007; 13: 1402–1408.
Cui QH, Yu ZB, Pan YL, Purisima EO, Wang E . MicroRNAs preferentially target the genes with high transcriptional regulation complexity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2007; 352: 733–738.
Ke XS, Qu Y, Rostad K, Li WC, Lin B, Halvorsen OJ et al. Genome-wide profiling of histone h3 lysine 4 and lysine 27 trimethylation reveals an epigenetic signature in prostate carcinogenesis. PLoS One 2009; 4: e4687.
Saito Y, Liang G, Egger G, Friedman JM, Chuang JC, Coetzee GA et al. Specific activation of microRNA-127 with downregulation of the proto-oncogene BCL6 by chromatin-modifying drugs in human cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2006; 9: 435–443.
Thomson JM, Newman M, Parker JS, Morin-Kensicki EM, Wright T, Hammond SM . Extensive post-transcriptional regulation of microRNAs and its implications for cancer. Genes Dev 2006; 20: 2202–2207.
Xu N, Papagiannakopoulos T, Pan G, Thomson JA, Kosik KS . MicroRNA-145 regulates OCT4, SOX2, and KLF4 and represses pluripotency in human embryonic stem cells. Cell 2009; 137: 647–658.
Scharer CD, McCabe CD, Ali-Seyed M, Berger MF, Bulyk ML, Moreno CS . Genome-wide promoter analysis of the SOX4 transcriptional network in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 709–717.
Andersen CL, Christensen LL, Thorsen K, Schepeler T, Sorensen FB, Verspaget HW et al. Dysregulation of the transcription factors SOX4, CBFB and SMARCC1 correlates with outcome of colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 2009; 100: 511–523.
Medina PP, Castillo SD, Blanco S, Sanz-Garcia M, Largo C, Alvarez S et al. The SRY-HMG box gene, SOX4, is a target of gene amplification at chromosome 6p in lung cancer. Hum Mol Genet 2009; 18: 1343–1352.
Prueitt RL, Yi M, Hudson RS, Wallace TA, Howe TM, Yfantis HG et al. Expression of microRNAs and protein-coding genes associated with perineural invasion in prostate cancer. Prostate 2008; 68: 1152–1164.
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 10513–10518.
Hanson EK, Lubenow H, Ballantyne J . Identification of forensically relevant body fluids using a panel of differentially expressed microRNAs. Anal Biochem 2009; 387: 303–314.
DeVere White RW, Vinall RL, Tepper CG, Shi XB . MicroRNAs and their potential for translation in prostate cancer. Urol Oncol 2009; 27: 307–311.
Huang Q, Gumireddy K, Schrier M, le Sage C, Nagel R, Nair S et al. The microRNAs miR-373 and miR-520c promote tumour invasion and metastasis. Nat Cell Biol 2008; 10: 202–210.
Negrini M, Calin GA . Breast cancer metastasis: a microRNA story. Breast Cancer Res 2008; 10: 203.
Gao P, Tchernyshyov I, Chang TC, Lee YS, Kita K, Ochi T et al. c-Myc suppression of miR-23a/b enhances mitochondrial glutaminase expression and glutamine metabolism. Nature 2009; 458: 762–765.
Dangi-Garimella S, Yun J, Eves EM, Newman M, Erkeland SJ, Hammond SM et al. Raf kinase inhibitory protein suppresses a metastasis signalling cascade involving LIN28 and let-7. EMBO J 2009; 28: 347–358.
Leite KR, Sousa-Canavez JM, Reis ST, Tomiyama AH, Camara-Lopes LH, Sanudo A et al. Change in expression of miR-let7c, miR-100, and miR-218 from high grade localized prostate cancer to metastasis. Urol Oncol 2009, doi:10.1016/J.urolonc.2009.02.002.
Korpal M, Kang Y . The emerging role of miR-200 family of microRNAs in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer metastasis. RNA Biol 2008; 5: 115–119.
Ma L, Liu J, Shen J, Liu L, Wu J, Li W et al. Expression of miR-122 mediated by adenoviral vector induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther 2010; 9: 554–561.
Okada H, Kohanbash G, Lotze MT . MicroRNAs in immune regulation-opportunities for cancer immunotherapy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2010, doi:10.1016/J.biocel.2010.02.002.
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Shimizu M et al. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 13944–13949.
Dews M, Homayouni A, Yu D, Murphy D, Sevignani C, Wentzel E et al. Augmentation of tumor angiogenesis by a Myc-activated microRNA cluster. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 1060–1065.
Wang Q, Li YC, Wang J, Kong J, Qi Y, Quigg RJ et al. miR-17-92 cluster accelerates adipocyte differentiation by negatively regulating tumor-suppressor Rb2/p130. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 2889–2894.
Fontana L, Fiori ME, Albini S, Cifaldi L, Giovinazzi S, Forloni M et al. Antagomir-17-5p abolishes the growth of therapy-resistant neuroblastoma through p21 and BIM. PLoS One 2008; 3: e2236.
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal K, Jacob ST, Patel T . MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology 2007; 133: 647–658.
Zhu S, Si ML, Wu H, Mo YY . MicroRNA-21 targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 14328–14336.
Wong CF, Tellam RL . MicroRNA-26a targets the histone methyltransferase enhancer of Zeste homolog 2 during myogenesis. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 9836–9843.
Luzi E, Marini F, Sala SC, Tognarini I, Galli G, Brandi ML . Osteogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells is modulated by the miR-26a targeting of the SMAD1 transcription factor. J Bone Miner Res 2008; 23: 287–295.
Royuela M, Arenas MI, Bethencourt FR, Sanchez-Chapado M, Fraile B, Paniagua R . Immunoexpressions of p21, Rb, mcl-1 and bad gene products in normal, hyperplastic and carcinomatous human prostates. Eur Cytokine Netw 2001; 12: 654–663.
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G et al. The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol 2008; 10: 593–601.
Fornari F, Gramantieri L, Ferracin M, Veronese A, Sabbioni S, Calin GA et al. MiR-221 controls CDKN1C/p57 and CDKN1B/p27 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2008; 27: 5651–5661.
Schaefer A, Jung M, Mollenkopf HJ, Wagner I, Stephan C, Jentzmik F et al. Diagnostic and prognostic implications of microRNA profiling in prostate carcinoma. Int J Cancer 2010; 126: 1166–1176.
Jiang J, Lee EJ, Gusev Y, Schmittgen TD . Real-time expression profiling of microRNA precursors in human cancer cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res 2005; 33: 5394–5403.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by a grant (108S051) from The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sevli, S., Uzumcu, A., Solak, M. et al. The function of microRNAs, small but potent molecules, in human prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 13, 208–217 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2010.21
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2010.21
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Protein network-based Lasso regression model for the construction of disease-miRNA functional interactions
EURASIP Journal on Bioinformatics and Systems Biology (2013)
-
MicroRNA profiling in lymphocytes and serum of tyrosinemia type-I patients
Molecular Biology Reports (2013)
-
miR-17-5p targets the p300/CBP-associated factor and modulates androgen receptor transcriptional activity in cultured prostate cancer cells
BMC Cancer (2012)
-
MicroRNAs as putative mediators of treatment response in prostate cancer
Nature Reviews Urology (2012)