Abstract
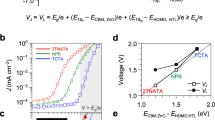
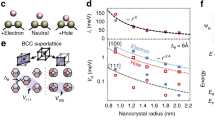
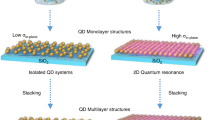
Inorganic nanocrystals are attractive materials for solar-cell applications. However, the performance of such devices is often limited by an insufficient alignment of energy levels in the nanocrystals. Here, we report that by attaching two different molecules to a single quantum dot or nanocrystal one can induce electric fields large enough to significantly alter the electronic and optoelectronic properties of the quantum dot. This electric field is created within the nanocrystals owing to a mixture of amine- and thiol-anchor-group ligands. Examining the steady state as well as temporal evolution of the optical properties and the nuclear magnetic resonances of the nanocrystals we found that the first excitonic peak shifts as a function of the capping-layer composition. We also demonstrate that the use of a mixed-ligand-induced electric field markedly enhances the charge generation efficiency in layer-by-layer CdSe-nanocrystal-based solar cells, thus improving the overall cell efficiency.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luther, J. M. et al. Schottky solar cells based on colloidal nanocrystal films. Nano Lett. 8, 3488–3492 (2008).
Tessler, N., Medvedev, V., Kazes, M., Kan, S. H. & Banin, U. Efficient near-infrared polymer nanocrystal light-emitting diodes. Science 295, 1506–1508 (2002).
Solomeshch, O. et al. Optoelectronic properties of polymer-nanocrystal composites active at near-infrared wavelengths. J. Appl. Phys. 98, 074310 (2005).
Leatherdale, C. A. et al. Photoconductivity in CdSe quantum dot solids. Phys. Rev. B 62, 2669–2680 (2000).
Bullen, C. & Mulvaney, P. The effects of chemisorption on the luminescence of CdSe quantum dots. Langmuir 22, 3007–3013 (2006).
Ginger, D. S. & Greenham, N. C. Charge injection and transport in films of CdSe nanocrystals. J. Appl. Phys. 87, 1361–1368 (2000).
Soreni-Harari, M. et al. Tuning energetic levels in nanocrystal quantum dots through surface manipulations. Nano Lett. 8, 678–684 (2008).
Talapin, D. V., Rogach, A. L., Kornowski, A., Haase, M. & Weller, H. Highly luminescent monodisperse CdSe and CdSe/ZnS nanocrystals synthesized in a hexadecylamine-trioctylphosphine oxide-trioctylphospine mixture. Nano Lett. 1, 207–211 (2001).
Munro, A. M., Zacher, B., Graham, A. & Armstrong, N. R. Photoemission spectroscopy of tethered CdSe nanocrystals: Shifts in ionization potential and local vacuum level as a function of nanocrystal capping ligand. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2, 863–869 (2010).
Shalom, M., Ruhle, S., Hod, I., Yahav, S. & Zaban, A. Energy level alignment in CdS quantum dot sensitized solar cells using molecular dipoles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 9876–9877 (2009).
Donakowski, M. D. et al. A quantitative description of the binding equilibria of para-substituted aniline ligands and CdSe quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 22526–22534 (2010).
Knowles, K. E., Tice, D. B., McArthur, E. A., Solomon, G. C. & Weiss, E. A. Chemical control of the photoluminescence of CdSe quantum dot-organic complexes with a series of para-substituted aniline ligands. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 1041–1050 (2010).
Empedocles, S. A. & Bawendi, M. G. Quantum-confined stark effect in single CdSe nanocrystallite quantum dots. Science 278, 2114–2117 (1997).
Rothenberg, E., Kazes, M., Shaviv, E. & Banin, U. Electric field induced switching of the fluorescence of single semiconductor quantum rods. Nano Lett. 5, 1581–1586 (2005).
Kuno, M., Lee, J. K., Dabbousi, B. O., Mikulec, F. V. & Bawendi, M. G. The band edge luminescence of surface modified CdSe nanocrystallites: Probing the luminescing state. J. Chem. Phys. 106, 9869–9882 (1997).
Yu, W. W., Qu, L. H., Guo, W. Z. & Peng, X. G. Experimental determination of the extinction coefficient of CdTe, CdSe, and CdS nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 15, 2854–2860 (2003).
Munro, A. M., Jen-La Plante, I., Ng, M. S. & Ginger, D. S. Quantitative study of the effects of surface ligand concentration on CdSe nanocrystal photoluminescence. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 6220–6227 (2007).
Talapin, D. V., Lee, J. S., Kovalenko, M. V. & Shevchenko, E. V. Prospects of colloidal nanocrystals for electronic and optoelectronic applications. Chem. Rev. 110, 389–458 (2010).
Nelson, J. The Physics of Solar Cells (Imperial College Press, 2003).
Gaunt, J. A., Knight, A. E., Windsor, S. A. & Chechik, V. Stability and quantum yield effects of small molecule additives on solutions of semiconductor nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 290, 437–443 (2005).
Li, R. F. et al. Amine-assisted facetted etching of CdSe nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 2524–2532 (2005).
Lovingood, D. D., Achey, R., Paravastu, A. K. & Strouse, G. F. Size- and site-dependent reconstruction in CdSe QDs evidenced by 77Se{1H} CP-MAS NMR spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 3344–3354 (2010).
Yin, Y. & Alivisatos, A. P. Colloidal nanocrystal synthesis and the organic–inorganic interface. Nature 437, 664–670 (2005).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to U. Banin and T. Mokari for discussions. We acknowledge partial support from the Ollendorff Minerva Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the work presented in this paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 806 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yaacobi-Gross, N., Soreni-Harari, M., Zimin, M. et al. Molecular control of quantum-dot internal electric field and its application to CdSe-based solar cells. Nature Mater 10, 974–979 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3133
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat3133
This article is cited by
-
Rational Design of Capping Ligands of Quantum Dots for Biosensing
Chemical Research in Chinese Universities (2024)
-
Interface polarization in heterovalent core–shell nanocrystals
Nature Materials (2022)
-
Roles of BiOCl(001) in face-to-faced BiOI(010)/BiOCl(001) heterojunction
Journal of Nanoparticle Research (2018)
-
Novel Hybrid Ligands for Passivating PbS Colloidal Quantum Dots to Enhance the Performance of Solar Cells
Nano-Micro Letters (2015)
-
Broadband energy transfer to sensitizing dyes by mobile quantum dot mediators in solar cells
Scientific Reports (2013)