Abstract
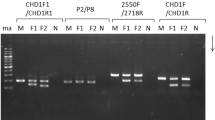
We have obtained the DNA sequence of a region from the bovine ZFY and ZFX loci and used it to design nested primers that, together with a previously described PstI polymorphism, were applied in a sensitive PCR assay to determine the sex of embryo biopsies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krlich, H.A., Gelfand, D. and Sninsky, J.J. 1991. Recent advances in polymerase chain reaction. Science 252: 1643–1651.
Bondioli, K.R., Ellis, S.B., Pryor, J.H., Williams, M.W. and Harpold, M.M. 1989. The use of male-specific chromosomal DNA fragments to determine the sex of bovine preimplantation embryos. Theriogenology 31: 95–104.
Herr, C.M., Matthaei, K.I., Petrzak, U. and Reed, K.C. 1990. A rapid Y-chromosome-detecting ovine embryo sexing assay. Theriogenology 33: 245.
Herr, C.M., Holt, N.A., Matthaei, K.I. and Reed, K.C. 1990. Sex of progeny from bovine embryos sexed with a rapid Y-chromosome-detecting assay. Theriogenoiogy 33: 247.
Bradbury, M.W., Isola, L.M. and Gordon, J.W. 1990. Enzymatic amplification of a Y chromosome repeat in a single blastomere allows identification of the sex of preimplantation mouse embryos. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87: 4053–4057.
Handyside, A.H., Kontogianni, E.H., Hardy, K. and Winston, R.M.L. 1990. Pregnancies from biopsied human preimplantation embryos sexed by Y-specific DNA amplification. Nature 344: 768–770.
Scheneider Gadicke, A., Beer-Romero, P., Brown, L.G., Nussbaum, R. and Page, D.C. 1989. ZFX has a gene structure similar to ZFY, the putative human sex determinant, and escapes X inactivation. Cell 57: 1247–1258.
Aasen, E. and Medrano, J.F. 1990. Amplification of the ZFY and ZFX genes for sex identification in humans, cattle, sheep and goats. Bio/Technology 8: 1279–1281.
Sarkar, G. and Sommer, S.S. 1990. Shedding light on PCR contamination. Nature 334: 27.
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E.F. and Sambrook, J. 1989. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, NY.
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S. and Coulson, A.R. 1977. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74: 5463–5467.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pollevick, G., Giambiagi, S., Mancardi, S. et al. Sex Determination of Bovine Embryos by Restriction Fragment Polymorphisms of PCR Amplified ZFX/ZFY Loci. Nat Biotechnol 10, 805–807 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0792-805
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0792-805