Abstract
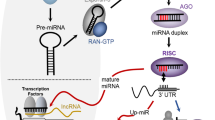
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding RNAs that control the expression of around 60% of the human protein-coding genes. In the past decade, deregulation of miRNAs (by expression and/or function) has been associated with the pathogenesis, progression and prognosis of different diseases, including leukemia. The number of discovered genes encoding miRNAs has risen exponentially in this period, but the numbers of miRNA-target genes discovered and validated lag far behind. Scientists have gained more in-depth knowledge of the basic mechanism of action of miRNAs, but the main challenge still remaining is the identification of direct targets of these important ‘micro-players’, to understand how they fine-tune so many biological processes in both healthy and diseased tissue. Many technologies have been developed in the past few years, some with more potential than others, but all with their own pros and cons. Here, we review the most common and most potent computational and experimental approaches for miRNA-target gene discovery and discuss how the hunting of targets is challenging but possible by taking the experimental limitations in consideration and choosing the correct cellular context for identifying relevant target genes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee RL, Feinbaum RC, Ambros V . The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993; 75: 843–854.
Wightman B, Ha I, Ruvkun G . Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell 1993; 75: 855–862.
Lai EC, Posakony JW . Regulation of Drosophila neurogenesis by RNA:RNA duplexes? Cell 1998; 93: 1103–1104.
Moss EG, Lee RC, Ambros V . The cold shock domain protein LIN-28 controls developmental timing in C. elegans and is regulated bythlin4 RNA. Cell 1997; 88: 637–646.
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T . Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science 2001; 294: 853–858.
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, Bartel DP . Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res 2009; 19: 92–105.
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Shimizu M et al. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 13944–13949.
Mott JL, Kobayashi S, Bronk SF, Gores GJ . Mir-29 regulates Mcl-1 protein expression and apoptosis. Oncogene 2007; 26: 6133–6140.
Lal A, Navarro F, Maher CA, Maliszewski LE, Yan N, O’Day E et al. MiR-24 inhibits cell proliferation by targeting E2F2, MYC, and other cell-cycle genes via binding to "seedless" 3'UTR microRNA recognition elements. Mol Cell 2009; 35: 610–625.
Lerner ML, undgren J, Akhoondi S, Jahn A, Ng HF, Moqadam FA et al. miRNA-27a controls FBW7/hCDC4-dependent cyclin E degradation and cell cycle progression. Cell Cycle 2011; 10: 2172–2183.
Belver L, Papavasiliou FN, Ramiro AR . MicroRNA control of lymphocyte differentiation and function. Curr Opin Immunol. 2011; 23: 368–373.
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 2257–2261.
Volinia S, Galasso M, Costinean S, Tagliavini L, Gamberoni G, Drusco A et al. Reprogramming of miRNA networks in cancer and leukemia. Genome Res 2010; 20: 589–599.
Chang TC, Mendell JT . microRNAs in vertebrate physiology and human disease. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 2007; 8: 215–239.
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 15524–15529.
Garzon R, Liu S, Fabbri M, Liu Z, Heaphy CE, Callegari E et al. MicroRNA-29b induces global DNA hypomethylation and tumor suppressor gene reexpression in acute myeloid leukemia by targeting directly DNMT3A and 3B and indirectly DNMT1. Blood. 2009; 113: 6411–6418.
Schotte D, LangeTurenhout EA, Stumpel DJ, Stam RW, BuijsGladdines JG, Meijerink JP et al. Expression of miR-196b is not exclusively MLL-driven but is especially linked to activation of HOXA genes in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2010; 95: 1675–1682.
Rainer J, Ploner C, Jesacher S, Ploner A, Eduardoff M, Mansha M et al. Glucocorticoid-regulated microRNAs and mirtrons in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2009; 23: 746–752.
Schotte D, De Menezes RX, Moqadam FA, Khankahdani LM, Lange-Turenhout E, Chen C et al. MicroRNA characterize genetic diversity and drug resistance in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2011; 96: 703–711.
Gefen N, Binder V, Zaliova M, Linka Y, Morrow M, Novosel A et al. Hsa-mir-125b-2 is highly expressed in childhood ETV6/RUNX1 (TEL/AML1) leukemias and confers survival advantage to growth inhibitory signals independent of p53. Leukemia 2010; 24: 89–96.
Ventura A, Young AG, Winslow MM, Lintault L, Meissner A, Erkeland SJ et al. Targeted deletion reveals essential and overlapping functions of the miR-17 through 92 family of miRNA clusters. Cell 2008; 132: 875–886.
Xiao C, Calado DP, Galler G, Thai TH, Patterson HC, Wang J et al. MiR-150 controls B cell differentiation by targeting the transcription factor c-Myb. Cell 2007; 131: 146–159.
Tsang WP, Kwok TT . Let-7a microRNA suppresses therapeutics-induced cancer cell death by targeting caspase-3. Apoptosis 2008; 13: 1215–1222.
Liang Y, Ridzon D, Wong L, Chen C . Characterization of microRNA expression profiles in normal human tissues. BMC Genomics 2007; 8: 166.
Siomi H, Siomi MC . Posttranscriptional regulation of microRNA biogenesis in animals. Mol Cell 2010; 38: 323–332.
Croce CM . Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 2009; 10: 704–714.
Kedde M, Strasser MJ, Boldajipour B, Oude Vrielink JA, Slanchev K, le Sage C et al. RNA-binding protein Dnd1 inhibits microRNA access to target mRNA. Cell. 2007; 131: 1273–1286.
Davis BN, Hilyard AC, Lagna G, Hata ASMAD . proteins control DROSHA-mediated microRNA maturation. Nature 2008; 454: 56–61.
Schotte D, Moqadam FA, Lange-Turenhout EA, Chen C, van Ijcken WF, Pieters R et al. Discovery of new microRNAs by small RNAome deep sequencing in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2011; 25: 1389–1399.
Barbarotto E, Schmittgen TD, Calin S . MicroRNAs and cancer: profile, profile, profile. Int J Cancer 2008; 122: 969–977.
Orom UA, Lund AH . Experimental identification of microRNA targets. Gene 2010; 451: 1–5.
Thomas M, Lieberman J, Lal A . Desperately seeking microRNA targets. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2010; 17: 1169–1174.
Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Burge CB . Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell. 2003; 115: 787–798.
Bartel DP . MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009; 136: 215–233.
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP . Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 2005; 120: 15–20.
Grimson A, Farh KK, Johnston WK, Garrett-Engele P, Lim LP, Bartel DP . MicroRNA targeting specificity in mammals: determinants beyond seed pairing. Mol Cell 2007; 27: 91–105.
Moretti F, Thermann R, Hentze MW . Mechanism of translational regulation by miR-2 from sites in the 5′ untranslated region or the open reading frame. RNA 2010; 16s: 2493–2502.
Forman JJ, Coller HA . The code within the code: microRNAs target coding regions. Cell Cycle 2010; 9: 1533–1541.
Wei J, Gao W, Zhu CJ, Liu YQ, Mei Z, Cheng T et al. Identification of plasma microRNA-21 as a biomarker for early detection and chemosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer. Chin J Cancer 2011; 30: 407–414.
Shin C, Nam JW, Farh KK, Chiang HR, Shkumatava A, Bartel DP . Expanding the microRNA targeting code: functional sites with centered pairing. Mol Cell 2010; 38: 789–802.
Didiano D, Hobert O . Perfect seed pairing is not a generally reliable predictor for miRNA-target interactions. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2006; 13: 849–851.
Chi SW, Hannon GJ, Darnell RB . An alternative mode of microRNA target recognition. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2012; 19: 321–327.
Li Y, Zhang M, Chen H, Dong Z, Ganapathy V, Thangaraju M et al. Ratio of miR-196s to HOXC8 messenger RNA correlates with breast cancer cell migration and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2010; 70: 7894–7904.
Wu S, Huang S, Ding J, Zhao Y, Liang L, Liu T et al. Multiple microRNAs modulate p21Cip1/Waf1 expression by directly targeting its 3′ untranslated region. Oncogene 2010; 29: 2302–2308.
Qiu X, Friedman JM, Liang G . Creating a flexible multiple microRNA expression vector by linking precursor microRNAs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2011; 411: 276–280.
Andachi Y . A novel biochemical method to identify target genes of individual microRNAs: identification of a new Caenorhabditis elegans let-7 target. RNA 2008; 14: 2440–2451.
Baek D, Villen J, Shin C, Camargo FD, Gygi SP, Bartel DP . The impact of microRNAs on protein output. Nature 2008; 455: 64–71.
Bracken CP, Gregory PA, Kolesnikoff N, Bert AG, Wang J, Shannon MF et al. A double-negative feedback loop between ZEB1-SIP1 and the microRNA-200 family regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 7846–7854.
Arvey A, Larsson E, Sander C, Leslie CS, Marks DS . Target mRNA abundance dilutes microRNA and siRNA activity. Mol Syst Biol 2010; 6: 363.
Meister G, Landthaler M, Dorsett Y, Tuschl T . Sequence-specific inhibition of microRNA- and siRNA-induced RNA silencing. RNA 2004; 10: 544–550.
Ebert MS, Sharp PA . MicroRNA sponges: progress and possibilities. RNA 2010; 16: 2043–2050.
Yang Y, Chaerkady R, Kandasamy K, Huang TC, Selvan LD, Dwivedi SB et al. Identifying targets of miR-143 using a SILAC-based proteomic approach. Mol Biosyst 2010; 6: 1873–1882.
Wang F, Wang XS, Yang GH, Zhai PF, Xiao Z, Xia LY et al. miR-29a and miR-142-3p downregulation and diagnostic implication in human acute myeloid leukemia. Mol Biol Rep 2012; 39: 2713–2722.
Beitzinger M, Meister G . Experimental identification of microRNA targets by immunoprecipitation of argonaute protein complexes. Methods Mol Biol 2011; 732: 153–167.
Beitzinger M, Peters L, Zhu JY, Kremmer E, Meister G . Identification of human microRNA targets from isolated argonaute protein complexes. RNA Biol 2007; 4: 76–84.
Moussay E, Wang K, Cho JH, van Moer K, Pierson S, Paggetti J et al. MicroRNA as biomarkers and regulators in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011; 108: 6573–6578.
Bianchi F, Nicassio F, Marzi M, Belloni E, Dall'olio V, Bernard L et al. A serum circulating miRNA diagnostic test to identify asymptomatic high-risk individuals with early stage lung cancer. EMBO Mol Med 2011; 3: 495–503.
Thomson DW, Bracken CP, Goodall GJ . Experimental strategies for microRNA target identification. Nucleic Acids Res 2011; 39: 6845–6853.
Brase JC, Johannes M, Schlomm T, Falth M, Haese A, Steuber T et al. Circulating miRNAs are correlated with tumor progression in prostate cancer. Int J Cancer 2011; 128: 608–616.
Mostert B, Sieuwerts AM, Martens JW, Sleijfer S . Diagnostic applications of cell-free and circulating tumor cell-associated miRNAs in cancer patients. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 2011; 11: 259–275.
Balakrishnan I, Yang X, Torok-Storb B, Hesselberth J, Pillai MM High throughput sequencing following cross-linked immune precipitation (HITS-CLIP) of argonaute (AGO) identifies mir-9 as a regulator of MMP2 in the marrow microenvironment (ME) 53rd ASH Annual Meeting and Exposition, San Diego, CA, USA; 10–13 December 2011.
Hafner M, Landthaler M, Burger L, Khorshid M, Hausser J, Berninger P et al. Transcriptome-wide identification of RNA-binding protein and microRNA target sites by PAR-CLIP. Cell 2010; 141: 129–141.
Skalsky RL, Corcoran DL, Gottwein E, Frank CL, Kang D, Hafner M et al. The viral and cellular microRNA targetome in lymphoblastoid cell lines. PLoS Pathog 2012; 8: 1002484.
Orom UA, Lund AH . Isolation of microRNA targets using biotinylated synthetic microRNAs. Methods 2007; 43: 162–165.
Li S, Zhu J, Fu H, Wan J, Hu Z, Liu S et al. Hepato-specific microRNA-122 facilitates accumulation of newly synthesized miRNA through regulating PRKRA. Nucleic Acids Res 2012; 40: 884–891.
Lal A, Thomas MP, Altschuler G, Navarro F, O'Day E, Li XL et al. Capture of microRNA-bound mRNAs identifies the tumor suppressor miR-34a as a regulator of growth factor signaling. PLoS Genet 2011; 7: 1002363.
Schetter AJ, Harris CC . Plasma microRNAs: a potential biomarker for colorectal cancer? Gut 2009; 58: 1318–1319.
Hsu RJ, Tsai HJ . Performing the Labeled microRNA pull-down (LAMP) assay system: an experimental approach for high-throughput identification of microRNA-target mRNAs. Methods Mol Biol 2011; 764: 241–247.
German MA, Luo S, Schroth G, Meyers BC, Green PJ . Construction of Parallel Analysis of RNA Ends (PARE) libraries for the study of cleaved miRNA targets and the RNA degradome. Nat Protoc 2009; 4: 356–362.
Heneghan HM, Miller N, Lowery AJ, Sweeney KJ, Newell J, Kerin MJ . Circulating microRNAs as novel minimally invasive biomarkers for breast cancer. Ann Surg 2010; 251: 499–505.
Samanta AK, Chakraborty SN, Wang Y, Schlette E, Reddy EP, Arlinghaus RB . Destabilization of Bcr-Abl/Jak2 Network by a Jak2/Abl Kinase Inhibitor ON044580 Overcomes Drug Resistance in Blast Crisis Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML). Genes Cancer 2010; 1: 346–359.
Guo H, Ingolia NT, Weissman JS, Bartel DP . Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA levels. Nature 2010; 466: 835–840.
Zenz T, Mohr J, Eldering E, Kater AP, Buhler A, Kienle D et al. miR-34a as part of the resistance network in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2009; 113: 3801–3808.
Petri A, Lindow M, Kauppinen S . MicroRNA silencing in primates: towards development of novel therapeutics. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 393–395.
Selbach M, Schwanhausser B, Thierfelder N, Fang Z, Khanin R, Rajewsky N . Widespread changes in protein synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature 2008; 455: 58–63.
Vinther J, Hedegaard MM, Gardner PP, Andersen JS, Arctander P . Identification of miRNA targets with stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture. Nucleic Acids Res 2006; 34: 107.
Ma L, Reinhardt F, Pan E, Soutschek J, Bhat B, Marcusson EG et al. Therapeutic silencing of miR-10b inhibits metastasis in a mouse mammary tumor model. Nat Biotechnol 2010; 28: 341–347.
Lossner C, Meier J, Warnken U, Rogers MA, Lichter P, Pscherer A et al. Quantitative proteomics identify novel miR-155 target proteins. PLoS One 2011; 6: 22146.
Yan GR, Xu SH, Tan ZL, Liu L, He QY . Global identification of miR-373-regulated genes in breast cancer by quantitative proteomics. Proteomics 2011; 11: 912–920.
Mercatelli N, Coppola V, Bonci D, Miele F, Costantini A, Guadagnoli M et al. The inhibition of the highly expressed miR-221 and miR-222 impairs the growth of prostate carcinoma xenografts in mice. PLoS One 2008; 3: 4029.
Bonnardot L, Bardet E, Steichen O, Cassagnau E, Piot B, Salam AP et al. Prognostic factors for T1-T2 squamous cell carcinomas of the mobile tongue: A retrospective cohort study. Head Neck 2011; 33: 928–934.
Nicolas FE . Experimental validation of microRNA targets using a luciferase reporter system. Methods Mol Biol 2011; 732: 139–152.
Yamagata K, Fujiyama S, Ito S, Ueda T, Murata T, Naitou M et al. Maturation of microRNA is hormonally regulated by a nuclear receptor. Mol Cell 2009; 36: 340–347.
Maru DM, Singh RR, Hannah C, Albarracin CT, Li YX, Abraham R et al. MicroRNA-196a is a potential marker of progression during Barrett's metaplasia-dysplasia-invasive adenocarcinoma sequence in esophagus. Am J Pathol 2009; 174: 1940–1948.
Iliopoulos D, Malizos KN, Oikonomou P, Tsezou A . Integrative microRNA and proteomic approaches identify novel osteoarthritis genes and their collaborative metabolic and inflammatory networks. PLoS One 2008; 3: 3740.
Nymark P, Guled M, Borze I, Faisal A, Lahti L, Salmenkivi K et al. Integrative analysis of microRNA, mRNA and aCGH data reveals asbestos- and histology-related changes in lung cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2011; 50: 585–597.
Sandberg R, Neilson JR, Sarma A, Sharp PA, Burge CB . Proliferating cells express mRNAs with shortened 3′ untranslated regions and fewer microRNA target sites. Science 2008; 320: 1643–1647.
Mayr C, Bartel DP . Widespread shortening of 3'UTRs by alternative cleavage and polyadenylation activates oncogenes in cancer cells. Cell 2009; 138: 673–684.
Yan LX, Wu QN, Zhang Y, Li YY, Liao DZ, Hou JH et al. Knockdown of miR-21 in human breast cancer cell lines inhibits proliferation, in vitro migration and in vivo tumor growth. Breast Cancer Res 2011; 13: 2.
Ujifuku K, Mitsutake N, Takakura S, Matsuse M, Saenko V, Suzuki K et al. miR-195, miR-455-3p and miR-10a(*) are implicated in acquired temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Cancer Lett 2010; 296: 241–248.
Elmen J, Lindow M, Schutz S, Lawrence M, Petri A, Obad S et al. LNA-mediated microRNA silencing in non-human primates. Nature 2008; 452: 896–899.
Wang F, Fu XD, Zhou Y, Zhang Y . Down-regulation of the cyclin E1 oncogene expression by microRNA-16-1 induces cell cycle arrest in human cancer cells. BMB Rep 2009; 42: 725–730.
Nakamachi Y, Kawano S, Takenokuchi M, Nishimura K, Sakai Y, Chin T et al. MicroRNA-124a is a key regulator of proliferation and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 secretion in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2009; 60: 1294–1304.
Suomi S, Taipaleenmaki H, Seppanen A, Ripatti T, Vaananen K, Hentunen T et al. MicroRNAs regulate osteogenesis and chondrogenesis of mouse bone marrow stromal cells. Gene Regul Syst Bio 2008; 2: 177–191.
Scherr M, Venturini L, Battmer K, Schaller-Schoenitz M, Schaefer D, Dallmann I et al. Lentivirus-mediated antagomir expression for specific inhibition of miRNA function. Nucleic Acids Res 2007; 35: 149.
Bhaumik D, Scott GK, Schokrpur S, Patil CK, Orjalo AV, Rodier F et al. MicroRNAs miR-146a/b negatively modulate the senescence-associated inflammatory mediators IL-6 and IL-8. Aging (Albany NY) 2009; 1: 402–411.
Curtale G, Citarella F, Carissimi C, Goldoni M, Carucci N, Fulci V et al. An emerging player in the adaptive immune response: microRNA-146a is a modulator of IL-2 expression and activation-induced cell death in T lymphocytes. Blood 2010; 115: 265–273.
Sorrentino A, Liu CG, Addario A, Peschle C, Scambia G, Ferlini C . Role of microRNAs in drug-resistant ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol 2008; 111: 478–486.
Xia HF, He TZ, Liu CM, Cui Y, Song PP, Jin XH et al. MiR-125b expression affects the proliferation and apoptosis of human glioma cells by targeting Bmf. Cell Physiol Biochem 2009; 23: 347–358.
Kong W, He L, Coppola M, Guo J, Esposito NN, Coppola D et al. MicroRNA-155 regulates cell survival, growth, and chemosensitivity by targeting FOXO3a in breast cancer. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 17869–17879.
Shatseva T, Lee DY, Deng Z, Yang BB . MicroRNA miR-199a-3p regulates cell proliferation and survival by targeting caveolin-2. J Cell Sci 2011; 124: 2826–2836.
Zhao Y, Samal E, Srivastava D . Serum response factor regulates a muscle-specific microRNA that targets Hand2 during cardiogenesis. Nature 2005; 436: 214–220.
Chen JF, Mandel EM, Thomson JM, Wu Q, Callis TE, Hammond SM et al. The role of microRNA-1 and microRNA-133 in skeletal muscle proliferation and differentiation. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 228–233.
Boutz PL, Chawla G, Stoilov P, Black DL . MicroRNAs regulate the expression of the alternative splicing factor nPTB during muscle development. Genes Dev 2007; 21: 71–84.
Naguibneva I, Ameyar-Zazoua M, Polesskaya A, Ait-Si-Ali S, Groisman R, Souidi M et al. The microRNA miR-181 targets the homeobox protein Hox-A11 during mammalian myoblast differentiation. Nat Cell Biol 2006; 8: 278–284.
Esau C, Kang X, Peralta E, Hanson E, Marcusson EG, Ravichandran LV et al. MicroRNA-143 regulates adipocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 52361–52365.
Wang C, Yao N, Lu CL, Li D, Ma X . Mouse microRNA-124 regulates the expression of Hes1 in P19 cells. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 2010; 2: 127–132.
Wayman GA, Davare M, Ando H, Fortin D, Varlamova O, Cheng HY et al. An activity-regulated microRNA controls dendritic plasticity by down-regulating p250GAP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 9093–9098.
Schratt GM, Tuebing F, Nigh EA, Kane CG, Sabatini ME, Kiebler M et al. A brain-specific microRNA regulates dendritic spine development. Nature 2006; 439: 283–289.
Fukuda Y, Kawasaki H, Taira K . Exploration of human miRNA target genes in neuronal differentiation. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser (Oxf) 2005; 49: 341–342.
Rapicavoli NA, Blackshaw S . New meaning in the message: noncoding RNAs and their role in retinal development. Dev Dyn 2009; 238: 2103–2114.
Akkina S, Becker BN . MicroRNAs in kidney function and disease. Transl Res 2011; 157: 236–240.
Calin GA, Cimmino A, Fabbri M, Ferracin M, Wojcik SE, Shimizu M et al. MiR-15a and miR-16-1 cluster functions in human leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 5166–5171.
Lu J, Guo S, Ebert BL, Zhang H, Peng X, Bosco J et al. MicroRNA-mediated control of cell fate in megakaryocyte-erythrocyte progenitors. Dev Cell 2008; 14: 843–853.
Fontana L, Pelosi E, Greco P, Racanicchi S, Testa U, Liuzzi F et al. MicroRNAs 17-5p-20a-106a control monocytopoiesis through AML1 targeting and M-CSF receptor upregulation. Nat Cell Biol 2007; 9: 775–787.
Fazi F, Rosa A, Fatica A, Gelmetti V, De Marchis ML, Nervi C et al. A minicircuitry comprised of microRNA-223 and transcription factors NFI-A and C/EBPalpha regulates human granulopoiesis. Cell. 2005; 123: 819–831.
Yuan JY, Wang F, Yu J, Yang GH, Liu XL, Zhang JW . MicroRNA-223 reversibly regulates erythroid and megakaryocytic differentiation of K562 cells. J Cell Mol Med 2009; 13: 4551–4559.
Chen Y, Gorski DH . Regulation of angiogenesis through a microRNA (miR-130a) that down-regulates antiangiogenic homeobox genes GAX and HOXA5. Blood 2008; 111: 1217–1226.
Hua Z, Lv Q, Ye W, Wong CK, Cai G, Gu D et al. MiRNA-directed regulation of VEGF and other angiogenic factors under hypoxia. PLoS One 2006; 1: 116.
Felli N, Fontana L, Pelosi E, Botta R, Bonci D, Facchiano F et al. MicroRNAs 221 and 222 inhibit normal erythropoiesis and erythroleukemic cell growth via kit receptor down-modulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 18081–18086.
Felli N, Pedini F, Romania P, Biffoni M, Morsilli O, Castelli G et al. MicroRNA 223-dependent expression of LMO2 regulates normal erythropoiesis. Haematologica 2009; 94: 479–486.
Garzon R, Pichiorri F, Palumbo T, Iuliano R, Cimmino A, Aqeilan R et al. MicroRNA fingerprints during human megakaryocytopoiesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 5078–5083.
Labbaye C, Spinello I, Quaranta MT, Pelosi E, Pasquini L, Petrucci E et al. A three-step pathway comprising PLZF/miR-146a/CXCR4 controls megakaryopoiesis. Nat Cell Biol 2008; 10: 788–801.
Romania P, Lulli V, Pelosi E, Biffoni M, Peschle C, Marziali G, Micro RNA . 155 modulates megakaryopoiesis at progenitor and precursor level by targeting Ets-1 and Meis1 transcription factors. Br J Haematol 2008; 143: 570–580.
Garcia DM, Baek D, Shin C, Bell GW, Grimson A, Bartel DP . Weak seed-pairing stability and high target-site abundance decrease the proficiency of lsy-6 and other microRNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2011; 18: 1139–1146.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research (NWO-Vidi Grant, MLdB), the Quality of Life Foundation (MLdB/RP) and the Pediatric Oncology Foundation Rotterdam, KOCR (MLdB/RP). We would like to kindly acknowledge the careful reading and editing by Dr Patricia Garrido Castro.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akbari Moqadam, F., Pieters, R. & den Boer, M. The hunting of targets: challenge in miRNA research. Leukemia 27, 16–23 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.179
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.179
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Expression study of microRNA cluster on chromosome 19 (C19MC) in tumor tissue and serum of breast cancer patient
Molecular Biology Reports (2023)
-
Circular RNA circCSPP1 knockdown attenuates doxorubicin resistance and suppresses tumor progression of colorectal cancer via miR-944/FZD7 axis
Cancer Cell International (2021)
-
Selective activation of miRNAs of the primate-specific chromosome 19 miRNA cluster (C19MC) in cancer and stem cells and possible contribution to regulation of apoptosis
Journal of Biomedical Science (2017)
-
MicroRNA-196a2 Biomarker and Targetome Network Analysis in Solid Tumors
Molecular Diagnosis & Therapy (2016)
-
Integrative computational in-depth analysis of dysregulated miRNA-mRNA interactions in drug-resistant pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells: an attempt to obtain new potential gene-miRNA pathways involved in response to treatment
Tumor Biology (2016)