Abstract
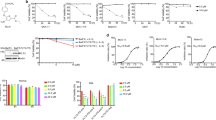
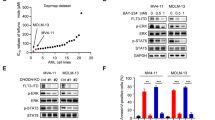
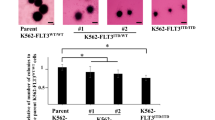
Treatment using Fms-like tyrosine kinase-3 (FLT3) inhibitors is a promising approach to overcome the dismal prognosis of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with activating FLT3 mutations. Current trials are combining FLT3 inhibitors with p53-activating conventional chemotherapy. The mechanisms of cytotoxicity of FLT3 inhibitors are poorly understood. We investigated the interaction of FLT3 and p53 pathways after their simultaneous blockade using the selective FLT3 inhibitor FI-700 and the MDM2 inhibitor Nutlin-3 in AML. We found that FI-700 immediately reduced antiapoptotic Mcl-1 levels and enhanced Nutlin-induced p53-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis in FLT3/internal tandem duplication cells through the Mcl-1/Noxa axis. FI-700 induced proteasome-mediated degradation of Mcl-1, resulting in the reduced ability of Mcl-1 to sequester proapoptotic Bim. Nutlin-3 induced Noxa, which displaced Bim from Mcl-1. The FI-700/Nutlin-3 combination profoundly activated Bax and induced apoptosis. Our findings suggest that FI-700 actively enhances p53 signaling toward mitochondrial apoptosis and that a combination strategy aimed at inhibiting FLT3 and activating p53 signaling could potentially be effective in AML.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Stirewalt DL, Radich JP . The role of FLT3 in haematopoietic malignancies. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 650–665.
Nakao M, Yokota S, Iwai T, Kaneko H, Horiike S, Kashima K et al. Internal tandem duplication of the flt3 gene found in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 1996; 10: 1911–1918.
Yamamoto Y, Kiyoi H, Nakano Y, Suzuki R, Kodera Y, Miyawaki S et al. Activating mutation of D835 within the activation loop of FLT3 in human hematologic malignancies. Blood 2001; 97: 2434–2439.
Yanada M, Matsuo K, Suzuki T, Kiyoi H, Naoe T . Prognostic significance of FLT3 internal tandem duplication and tyrosine kinase domain mutations for acute myeloid leukemia: a meta-analysis. Leukemia 2005; 19: 1345–1349.
Whitman SP, Ruppert AS, Radmacher MD, Mrózek K, Paschka P, Langer C et al. FLT3 D835/I836 mutations are associated with poor disease-free survival and a distinct gene-expression signature among younger adults with de novo cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia lacking FLT3 internal tandem duplications. Blood 2008; 111: 1552–1559.
Radomska HS, Bassères DS, Zheng R, Zhang P, Dayaram T, Yamamoto Y et al. Block of C/EBP alpha function by phosphorylation in acute myeloid leukemia with FLT3 activating mutations. J Exp Med 2006; 203: 371–381.
Mizuki M, Fenski R, Halfter H, Matsumura I, Schmidt R, Müller C et al. Flt3 mutations from patients with acute myeloid leukemia induce transformation of 32D cells mediated by the Ras and STAT5 pathways. Blood 2000; 96: 3907–3914.
Choudhary C, Brandts C, Schwable J, Tickenbrock L, Sargin B, Ueker A et al. Activation mechanisms of STAT5 by oncogenic Flt3-ITD. Blood 2007; 110: 370–374.
Shimamura A, Ballif BA, Richards SA, Blenis J . Rsk1 mediates a MEK-MAP kinase cell survival signal. Curr Biol 2000; 10: 127–135.
Rosa Santos SC, Dumon S, Mayeux P, Gisselbrecht S, Gouilleux F . Cooperation between STAT5 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in the IL-3-dependent survival of a bone marrow derived cell line. Oncogene 2000; 19: 1164–1172.
Warr MR, Shore GC . Unique biology of Mcl-1: therapeutic opportunities in cancer. Curr Mol Med 2008; 8: 138–147.
Aichberger KJ, Mayerhofer M, Krauth MT, Skvara H, Florian S, Sonneck K et al. Identification of mcl-1 as a BCR/ABL-dependent target in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML): evidence for cooperative antileukemic effects of imatinib and mcl-1 antisense oligonucleotides. Blood 2005; 105: 3303–3311.
Kuo ML, Chuang SE, Lin MT, Yang SY . The involvement of PI3-K/Akt-dependent up-regulation of Mcl-1 in the prevention of apoptosis of Hep3B cells by interleukin-6. Oncogene 2001; 20: 677–685.
Maurer U, Charvet C, Wagman AS, Dejardin E, Green DR . Glycogen synthase kinase-3 regulates mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization and apoptosis by destabilization of MCL-1. Mol Cell 2006; 21: 749–760.
Kiyoi H, Shiotsu Y, Ozeki K, Yamaji S, Kosugi H, Umehara H et al. A novel FLT3 inhibitor FI-700 selectively suppresses the growth of leukemia cells with FLT3 mutations. Clin Cancer Res 2007; 13: 4575–4582.
Weisberg E, Roesel J, Bold G, Furet P, Jiang J, Cools J et al. Anti-leukemic effects of the novel, mutant FLT3 inhibitor, NVP-AST487: effects on PKC412-sensitive and -resistant FLT3-expressing cells. Blood 2008; 112: 5161–5170.
Zhang W, Konopleva M, Shi YX, McQueen T, Harris D, Ling X et al. Mutant FLT3: a direct target of sorafenib in acute myelogenous leukemia. J Natl Cancer Inst 2008; 100: 184–198.
Smith BD, Levis M, Beran M, Giles F, Kantarjian H, Berg K et al. Single-agent CEP-701, a novel FLT3 inhibitor, shows biologic and clinical activity in patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2004; 103: 3669–3676.
Stone RM, DeAngelo DJ, Klimek V, Galinsky I, Estey E, Nimer SD et al. Patients with acute myeloid leukemia and an activating mutation in FLT3 respond to a small-molecule FLT3 tyrosine kinase inhibitor, PKC412. Blood 2005; 105: 54–60.
Fiedler W, Serve H, Döhner H, Schwittay M, Ottmann OG, O'Farrell AM et al. A phase 1 study of SU11248 in the treatment of patients with refractory or resistant acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or not amenable to conventional therapy for the disease. Blood 2005; 105: 986–993.
DeAngelo DJ, Stone RM, Heaney ML, Nimer SD, Paquette RL, Klisovic RB et al. Phase 1 clinical results with tandutinib (MLN518), a novel FLT3 antagonist, in patients with acute myelogenous leukemia or high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome: safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics. Blood 2006; 108: 3674–3681.
Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B, Harris CC . p53 mutations in human cancers. Science 1991; 253: 49–53.
Kojima K, Konopleva M, Samudio IJ, Shikami M, Cabreira-Hansen M, McQueen T et al. MDM2 antagonists induce p53-dependent apoptosis in AML: implications for leukemia therapy. Blood 2005; 106: 3150–3159.
Michael D, Oren M . The p53-Mdm2 module and the ubiquitin system. Semin Cancer Biol 2003; 13: 49–58.
Vassilev LT, Vu BT, Graves B, Carvajal D, Podlaski F, Filipovic Z et al. In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of MDM2. Science 2004; 303: 844–848.
Chipuk JE, Green DR . Dissecting p53-dependent apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 2006; 13: 994–1002.
Mihara M, Erster S, Zaika A, Petrenko O, Chittenden T, Pancoska P et al. p53 has a direct apoptogenic role at the mitochondria. Mol Cell 2003; 11: 577–590.
Quentmeier H, Reinhardt J, Zaborski M, Drexler HG . FLT3 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia cell lines. Leukemia 2003; 17: 120–124.
Levis M, Murphy KM, Pham R, Kim KT, Stine A, Li L et al. Internal tandem duplications of the FLT3 gene are present in leukemia stem cells. Blood 2005; 106: 673–680.
Petitjean A, Mathe E, Kato S, Ishioka C, Tavtigian SV, Hainaut P et al. Impact of mutant p53 functional properties on TP53 mutation patterns and tumor phenotype: lessons from recent developments in the IARC TP53 database. Hum Mutat 2007; 28: 622–629.
Kojima K, Konopleva M, Tsao T, Nakakuma H, Andreeff M . Concomitant inhibition of Mdm2-p53 interaction and Aurora kinases activates the p53-dependent postmitotic checkpoints and synergistically induces p53-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis along with reduced endoreduplication in acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood 2008; 112: 2886–2895.
Oltersdorf T, Elmore SW, Shoemaker AR, Armstrong RC, Augeri DJ, Belli BA et al. An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces regression of solid tumours. Nature 2005; 435: 677–681.
Kohl TM, Hellinger C, Ahmed F, Buske C, Hiddemann W, Bohlander SK et al. BH3 mimetic ABT-737 neutralizes resistance to FLT3 inhibitor treatment mediated by FLT3-independent expression of BCL2 in primary AML blasts. Leukemia 2007; 21: 1763–1772.
Heidel FH, Schulze-Bergkamen H, Vick B, Lipka DB, Mirea FK, Urbanik T et al. The role of Mcl-1 expression and phosphorylation in resistance to chemotherapy and kinase inhibitors in FLT3-ITD-positive acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Blood 2008; 112: 88 (abstract 220).
Czabotar PE, Lee EF, van Delft MF, Day CL, Smith BJ, Huang DC et al. Structural insights into the degradation of Mcl-1 induced by BH3 domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 6217–6222.
Saddler C, Ouillette P, Kujawski L, Shangary S, Talpaz M, Kaminski M et al. Comprehensive biomarker and genomic analysis identifies p53 status as the major determinant of response to MDM2 inhibitors in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2008; 111: 1584–1593.
Breitenbuecher F, Markova B, Kasper S, Carius B, Stauder T, Bohmer FD et al. A novel molecular mechanism of primary resistance to FLT3-kinase inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2009; 113: 4063–4073.
Han J, Goldstein LA, Hou W, Rabinowich H . Functional linkage between NOXA and Bim in mitochondrial apoptotic events. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 16223–16231.
Certo M, Del Gaizo Moore V, Nishino M, Wei G, Korsmeyer S, Armstrong SA et al. Mitochondria primed by death signals determine cellular addiction to antiapoptotic BCL-2 family members. Cancer Cell 2006; 9: 351–365.
Zhong Q, Gao W, Du F, Wang X . Mule/ARF-BP1, a BH3-only E3 ubiquitin ligase, catalyzes the polyubiquitination of Mcl-1 and regulates apoptosis. Cell 2005; 121: 1085–1095.
Oltersdorf T, Elmore SW, Shoemaker AR, Armstrong RC, Augeri DJ, Belli BA et al. An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces regression of solid tumours. Nature 2005; 435: 677–681.
van Delft MF, Wei AH, Mason KD, Vandenberg CJ, Chen L, Czabotar PE et al. The BH3 mimetic ABT-737 targets selective Bcl-2 proteins and efficiently induces apoptosis via Bak/Bax if Mcl-1 is neutralized. Cancer Cell 2006; 10: 389–399.
Konopleva M, Contractor R, Tsao T, Samudio I, Ruvolo PP, Kitada S et al. Mechanisms of apoptosis sensitivity and resistance to the BH3 mimetic ABT-737 in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 2006; 10: 375–388.
Stone RM, DeAngelo DJ, Klimek V, Galinsky I, Estey E, Nimer SD et al. Patients with acute myeloid leukemia and an activating mutation in FLT3 respond to a small-molecule FLT3 tyrosine kinase inhibitor, PKC412. Blood 2005; 105: 54–60.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Maria Soengas, Department of Dermatology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, for providing lentivirus encoding Noxa-specific shRNA. KK was supported, in part, by grants from the Yasuda Medical Foundation and the Japan Leukemia Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kojima, K., Konopleva, M., Tsao, T. et al. Selective FLT3 inhibitor FI-700 neutralizes Mcl-1 and enhances p53-mediated apoptosis in AML cells with activating mutations of FLT3 through Mcl-1/Noxa axis. Leukemia 24, 33–43 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2009.212
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2009.212
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Imipridone ONC212 activates orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR132 and integrated stress response in acute myeloid leukemia
Leukemia (2019)
-
The novel BMI-1 inhibitor PTC596 downregulates MCL-1 and induces p53-independent mitochondrial apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia progenitor cells
Blood Cancer Journal (2017)
-
Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Current Treatment Options in Oncology (2017)
-
Targeting p53 by small molecules in hematological malignancies
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2013)
-
FLT3 inhibition: a moving and evolving target in acute myeloid leukaemia
Leukemia (2013)