Abstract
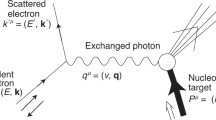
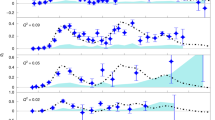
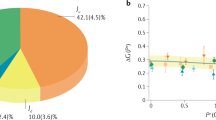
Understanding the nucleon spin structure in the regime where the strong interaction becomes truly strong poses a challenge to both experiment and theory. At energy scales below the nucleon mass of about 1 GeV, the intense interaction among the quarks and gluons inside the nucleon makes them highly correlated. Their coherent behaviour causes the emergence of effective degrees of freedom, requiring the application of non-perturbative techniques such as chiral effective field theory1. Here we present measurements of the neutron’s generalized spin polarizabilities that quantify the neutron’s spin precession under electromagnetic fields at very low energy-momentum transfer squared down to 0.035 GeV2. In this regime, chiral effective field theory calculations2,3,4 are expected to be applicable. Our data, however, show a strong discrepancy with these predictions, presenting a challenge to the current description of the neutron’s spin properties.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All experimental data that support the findings of this study are provided in the Supplementary Information or are available from J.P.C. (jpchen@jlab.org), A.D. (deurpam@jlab.org), C.P. (cpeng@jlab.org) or V.S. (vasulk@jlab.org) upon request.
Code availability
The computer codes that support the plots within this paper and the findings of this study are available from J.P.C. (jpchen@jlab.org), A.D. (deurpam@jlab.org), C.P. (cpeng@jlab.org) or V.S. (vasulk@jlab.org) upon request.
Change history
03 March 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-022-01569-0
References
Bernard, V., Kaiser, N. & Meissner, U.-G. Chiral dynamics in nucleons and nuclei. Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 4, 193–346 (1995).
Bernard, V., Epelbaum, E., Krebs, H. & Meissner, U.-G. New insights into the spin structure of the nucleon. Phys. Rev. D 87, 054032 (2013).
Lensky, V., Alarcón, J. M. & Pascalutsa, V. Moments of nucleon structure functions at next-to-leading order in baryon chiral perturbation theory. Phys. Rev. C 90, 055202 (2014).
Alarcón, J. M., Hagelstein, F., Lensky, V. & Pascalutsa, V. Forward doubly-virtual Compton scattering off the nucleon in chiral perturbation theory. II. Spin polarizabilities and moments of polarized structure functions. Phys. Rev. D 102, 114026 (2020).
Deur, A., Brodsky, S. J. & de Téramond, G. F. The QCD running coupling. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 90, 1–74 (2016).
Deur, A., Brodsky, S. J. & de Téramond, G. F. The spin structure of the nucleon. Rep. Prog. Phys. 82, 076201 (2019).
Gell-Mann, M., Goldberger, M. L. & Thirring, W. E. Use of causality conditions in quantum theory. Phys. Rev. 95, 1612–1627 (1954).
Guichon, P. A. M., Liu, G. Q. & Thomas, A. W. Virtual Compton scattering and generalized polarizabilities of the proton. Nucl. Phys. A 591, 606–638 (1995).
Hand, L. N. Experimental investigation of pion electroproduction. Phys. Rev. 129, 1834–1846 (1963).
Chen, J.-P. Moments of spin structure functions: sum rules and polarizabilities. Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 19, 1893–1921 (2010).
Amarian, M. et al. Measurement of the generalized forward spin polarizabilities of the neutron. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 152301 (2004).
Bernard, V., Hemmert, T. R. & Meissner, U.-G. Spin structure of the nucleon at low-energies. Phys. Rev. D 67, 076008 (2003).
Kao, C. W., Spitzenberg, T. & Vanderhaeghen, M. Burkhardt-Cottingham sum rule and forward spin polarizabilities in heavy baryon chiral perturbation theory. Phys. Rev. D 67, 016001 (2003).
Hagelstein, F., Miskimen, R. & Pascalutsa, V. Nucleon polarizabilities: from Compton scattering to hydrogen atom. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 88, 29–97 (2016).
Alcorn, J. et al. Basic instrumentation for Hall A at Jefferson Lab. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 522, 294–346 (2004).
Sulkosky, V. et al. Measurement of the 3He spin-structure functions and of neutron (3He) spin-dependent sum rules at 0.035 ≤ Q2 ≤ 0.24 GeV2. Phys. Lett. B 805, 135428 (2020).
Garibaldi, F. et al. High-resolution hypernuclear spectroscopy at Jefferson Lab, Hall A. Phys. Rev. C 99, 054309 (2019).
Ciofi degli Atti, C. & Scopetta, S. On the extraction of the neutron spin structure functions and the Gerasimov–Drell–Hearn integral from \({}^{3}\overrightarrow{{\rm{He}}}(\overrightarrow{e},{e}^{\prime})X\) data. Phys. Lett. B 404, 223–229 (1997).
Deltuva, A., Fonseca, A. C. & Sauer, P. U. Momentum-space treatment of Coulomb interaction in three-nucleon reactions with two protons. Phys. Rev. C 71, 054005 (2005).
Golak, J. et al. Proton polarizations in polarized 3He studied with the 3He (e, e-prime p) d and 3He (polarized-e, e-prime p) pn processes. Phys. Rev. C 72, 054005 (2005).
Drechsel, D., Hanstein, O., Kamalov, S. S. & Tiator, L. A unitary isobar model for pion photo- and electroproduction on the proton up to 1 GeV. Nucl. Phys. A 645, 145–174 (1999).
Guler, N. et al. Precise determination of the deuteron spin structure at low to moderate Q2 with CLAS and extraction of the neutron contribution. Phys. Rev. C 92, 055201 (2015).
Schwinger, J. S. Source theory viewpoints in deep inelastic scattering. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 72, 1–5 (1975).
Adhikari, K. P. et al. Measurement of the Q2 dependence of the deuteron spin structure function g1 and its moments at low Q2 with CLAS. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 062501 (2018).
Bass, S. D., Skurzok, M. & Moskal, P. Updating spin-dependent Regge intercepts. Phys. Rev. C 98, 025209 (2018).
Gerasimov, S. B. A sum rule for magnetic moments and the damping of the nucleon magnetic moment in nuclei. Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 2, 430–433 (1966).
Drell, S. D. & Hearn, A. C. Exact sum rule for nucleon magnetic moments. Phys. Rev. Lett. 16, 908–911 (1966).
Helbing, K. The Gerasimov–Drell–Hearn sum rule. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 57, 405–469 (2006).
Chambers, A. J. et al. Nucleon structure functions from operator product expansion on the lattice. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 242001 (2017).
Burkhardt, H. & Cottingham, W. N. Sum rules for forward virtual Compton scattering. Ann. Phys. 56, 453–463 (1970).
Ye, Z., Arrington, J., Hill, R. J. & Lee, G. Proton and neutron electromagnetic form factors and uncertainties. Phys. Lett. B 777, 8–15 (2018).
Acknowledgements
All authors are members of The Jefferson Lab E97-110 Collaboration. We acknowledge the outstanding support of the Jefferson Lab Hall A technical staff and the Physics and Accelerator Divisions that made this work possible. We thank A. Deltuva, J. Golak, F. Hagelstein, H. Krebs, V. Lensky, U.-G. Meißner, V. Pascalutsa, G. Salmè, S. Scopetta and M. Vanderhaeghen for useful discussions and for sharing their calculations. We are grateful to V. Pascalutsa and M. Vanderhaeghen for suggesting a comparison of the data to the Schwinger relation. This material is based upon work supported by the United States Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Nuclear Physics under contract DE-AC05-06OR23177 and by the United States National Science Foundation under grant PHY-0099557.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The members of the Jefferson Lab E97-110 Collaboration constructed and operated the experimental equipment used in this experiment. All authors contributed to the data collection, experiment design and commissioning, data processing, data analysis or Monte Carlo simulations. The following authors especially contributed to the main data analysis: J.P.C., A.D., C.P. and V.S.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Peer review information Nature Physics thanks Mohammad Ahmed, Jan Friedrich and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Tables 1–4.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sulkosky, V., Peng, C., Chen, Jp. et al. Measurement of the generalized spin polarizabilities of the neutron in the low-Q2 region. Nat. Phys. 17, 687–692 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-021-01245-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-021-01245-9
This article is cited by
-
Ground State Quantum Vortex Proton Model
Foundations of Physics (2023)
-
Testing the theory of the strong force by measuring proton spin polarizabilities
Nature Physics (2022)
-
Measured proton electromagnetic structure deviates from theoretical predictions
Nature (2022)
-
Proton spin structure and generalized polarizabilities in the strong quantum chromodynamics regime
Nature Physics (2022)
-
Nucleon spins surprise
Nature Physics (2021)