Abstract
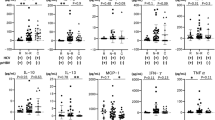
Chronicity of hepatitis B (CHB) infection is characterized by a weak immune response to the virus. Entecavir (ETV) and adefovir dipivoxil (ADV) are effective in suppressing hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication. However, the underlying immune mechanism in the antiviral response of patients treated with nucleoside or nucleotide analogs is not clearly understood. In this study, regulatory T cells (Tregs) and intracellular cytokines, including IL-2, interferon (IFN)-γ, tumor-necrosis factor (TNF)-α and IL-4, were measured prior to and at 12, 24, 36 and 48 weeks after treatment with ETV or ADV. The cytokines were increased from 24 to 48 weeks after treatment. Higher levels of Th1 cytokines were observed with ETV (n=29) versus ADV (n=28) treatment. By contrast, the numbers of Tregs in both groups were decreased. The altered cytokine profile and cellular component was accompanied by a decrease in HBV DNA levels in both groups, which may contribute to their therapeutic effect in CHB infection. Our findings suggest that the antiviral effect of the drugs may be attributed not only to their direct effect on virus suppression but also to their immunoregulatory capabilities.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
WHO. Hepatitis B. Geneva: WHO, 2008.
Bertoletti A, Gehring AJ . The immune response during hepatitis B virus infection. J Gen Virol 2006; 87: 1439–1449.
Huang CF, Lin SS, Ho YC, Chen FL, Yang CC . The immune response induced by hepatitis B virus principal antigens. Cell Mol Immunol 2006; 3: 97–106.
Billerbeck E, Bottler T, Thimme R . Regulatory T cells in viral hepatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13: 4858–4864.
Milich DR, Schodel F, Hughes JL, Jones JE, Peterson DL . The hepatitis B virus core and e antigens elicit different Th cell subsets: antigen structure can affect Th cell phenotype. J Virol 1997; 71: 2192–2201.
Ridge JP, Fuchs EJ, Matzinger P . Neonatal tolerance revisited: turning on newborn T cells with dendritic cells. Science 1996; 271: 1723–1726.
Chisari FV . Cytotoxic T cells and viral hepatitis. J Clin Invest 1997; 99: 1472–1477.
Stoop JN, van der Molen RG, Kuipers EJ, Kusters JG, Janssen HL . Inhibition of viral replication reduces regulatory T cells and enhances the antiviral immune response in chronic hepatitis B. Virology 2007; 361: 141–148.
Chang TT, Gish RG, de MR, Gadano A, Sollano J, Chao YC et al. A comparison of entecavir and lamivudine for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 2006; 354: 1001–1010.
Lai CL, Shouval D, Lok AS, Chang TT, Cheinquer H, Goodman Z et al. Entecavir versus lamivudine for patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 2006; 354: 1011–1020.
Cooksley H, Chokshi S, Maayan Y, Wedemeyer H, Andreone P, Gilson R et al. Hepatitis B virus e antigen loss during adefovir dipivoxil therapy is associated with enhanced virus-specific CD4+ T-cell reactivity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2008; 52: 312–320.
Sherman M, Yurdaydin C, Simsek H, Silva M, Liaw YF, Rustgi VK et al. Entecavir therapy for lamivudine-refractory chronic hepatitis B: improved virologic, biochemical, and serology outcomes through 96 weeks. Hepatology 2008; 48: 99–108.
Duramad P, McMahon CW, Hubbard A, Eskenazi B, Holland NT . Flow cytometric detection of intracellular TH1/TH2 cytokines using whole blood: validation of immunologic biomarker for use in epidemiologic studies. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2004; 13: 1452–8.
Liu W, Putnam AL, Zhou XY, Szot GL, Lee MR, Zhu S et al. CD127 expression inversely correlates with FoxP3 and suppressive function of human CD4+ T reg cells. J Exp Med 2006; 203: 1701–1711.
Lok AS, McMahon BJ . Chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2001; 34: 1225–1241.
Buster EH, Janssen HL . Antiviral treatment for chronic hepatitis B virus infection—immune modulation or viral suppression? Neth J Med 2006; 64: 175–185.
Gish RG, Lok AS, Chang TT, de Man RA, Gadano A, Sollano J et al. Entecavir therapy for up to 96 weeks in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2007; 133: 1437–1444.
Lee YS, Suh DJ, Lim YS, Jung SW, Kim KM, Lee HC et al. Increased risk of adefovir resistance in patients with lamivudine-resistant chronic hepatitis B after 48 weeks of adefovir dipivoxil monotherapy. Hepatology 2006; 43: 1385–1391.
Leung N, Peng CY, Sollano J, Lesmana L, Yuen MF, Jeffers L et al. Entecavir (ETV) results in higher HBV DNA reduction versus adefovir (ADV) in antiviral-naive HBeAg+ adults with high HBV DNA: week 96 results (E.A.R.L.Y. Study) [abstract]. J Hepatol 2008; 48 (Suppl 2) S373–S374.
Xu D, Fu J, Jin L, Zhang H, Zhou C, Zou Z et al. Circulating and liver resident CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells actively influence the antiviral immune response and disease progression in patients with hepatitis B. J Immunol 2006; 177: 739–747.
Ren FY, Jin H, Piao XX, Piao FS . Ribavirin and IFN-alpha combination therapy induces CD4+ T-cell proliferation and Th1 cytokine secretion in patients with chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13: 5440–5445.
McClary H, Koch R, Chisari FV, Guidotti LG . Relative sensitivity of hepatitis B virus and other hepatotropic viruses to the antiviral effects of cytokines. J Virol 2000; 74: 2255–2264.
Niederau C, Heintges T, Lange S, Goldmann G, Niederau CM, Mohr L et al. Long-term follow-up of HBeAg-positive patients treated with interferon alfa for chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 1996; 334: 1422–1427.
Puro R, Schneider RJ . Tumor necrosis factor activates a conserved innate antiviral response to hepatitis B virus that destabilizes nucleocapsids and reduces nuclear viral DNA. J Virol 2007; 81: 7351–7362.
Guidotti LG, Guilhot S, Chisari FV . Interleukin-2 and alpha/beta interferon down-regulate hepatitis B virus gene expression in vivo by tumor necrosis factor-dependent and -independent pathways. J Virol 1994; 68: 1265–1270.
Marcellin P, Chang TT, Lim SG, Tong MJ, Sievert W, Shiffman ML et al. Adefovir dipivoxil for the treatment of hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 808–816.
Marcellin P, Chang TT, Lim SG, Sievert W, Tong M, Arterburn S et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of adefovir dipivoxil for the treatment of hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2008; 48: 750–758.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge Dr Voo (The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, USA) for technical assistance and help in developing the content of the manuscript. This work was supported by grants from the Eleventh Five-Year Plan for AIDS and viral hepatitis, prevention and treatment of infectious diseases and other major science and technology (No. 2008ZX10002-004), the Ministry of Health Clinical Disciplines (No. 20073531), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30771912, 30972610 and 30972611), Jilin Province Science and Technology Agency (No. 200705128) and a BMS grant for manuscript development.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Li, W., Yu, L. et al. Enhancing the antihepatitis B virus immune response by adefovir dipivoxil and entecavir therapies. Cell Mol Immunol 8, 75–82 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2010.37
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2010.37
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Characterization of the liver-draining lymph nodes in mice and their role in mounting regional immunity to HBV
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2013)
-
Polymorphism of estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) is associated with virological response to entecavir (ETV) in nucleoside-naïve adult patients with chronic hepatitis B
Infection (2013)