Abstract
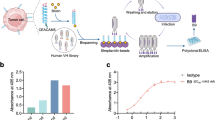
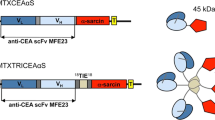
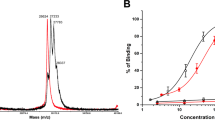
Irinotecan (CPT-11) is a key drug for the treatment of various cancers. CPT-11 can be considered to be a prodrug, since it needs to be activated into the toxic drug SN-38 by the enzyme carboxylesterase. However, CPT-11 may induce severe diarrhea and bone marrow suppression as adverse effects, thus leading to treatment interruption. The tumor-specific activation of CPT-11 is a possible strategy to avoid the severe toxicities by reducing the serum concentration of CPT-11. In this study, we constructed human liver carboxylesterase-2 fused with anticarcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) scFv as a targeting molecule. The recombinant enzyme anchors onto the tumor cell surface CEA, and thus metabolize CPT-11 extracellularly. In addition a secreted tumor-targeted form of carboxylesterase should help prevent the leakage of the enzyme from the site of the tumor into the circulation. This fusion protein showed CPT-11 activation to SN-38 and specific binding to CEA-expressing cells. In combination with CPT-11, the recombinant carboxylesterase protein exerted antiproliferative effects on human cancer cells. This recombinant enzyme is, therefore, a promising new tool in enzyme prodrug therapy for the treatment of carcinoma with CPT-11.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
Abbreviations
- Ad:
-
adenovirus
- ADEPT:
-
antibody-directed enzyme prodrug therapy
- ALT:
-
alanine aminotransferase
- CE:
-
carboxylesterase
- CEA:
-
carcinoembryonic antigen
- CMV:
-
cytomegalovirus
- DLT:
-
dose limiting toxicity
- FCS:
-
fetal calf serum
- IgG:
-
immunoglobulin G
- MOI:
-
multiplicity of infection
- NSCLC:
-
non-small cell lung cancer
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- scFv:
-
single chain variable fragment
References
Xu G, McLeod HL . Strategies for enzyme/prodrug cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 2001; 7: 3314–3324.
Syrigos KN, Epenetos AA . Antibody directed enzyme prodrug therapy (ADEPT): a review of the experimental and clinical considerations. Anticancer Res 1999; 19: 605–613.
Bagshawe KD . Antibody directed enzymes revive anti-cancer prodrugs concept. Br J Cancer 1987; 56: 531–532.
Satoh T, Hosokawa M, Atsumi R, Suzuki W, Hakusui H, Nagai E . Metabolic activation of CPT-11, 7-ethyl-10-[4-(1-piperidino)-1-piperidino]carbonyloxycamptothecin, a novel antitumor agent, by carboxylesterase. Biol Pharm Bull 1994; 17: 662–664.
Kudoh S, Fujiwara Y, Takada Y, Yamamoto H, Kinoshita A, Ariyoshi Y et al. Phase II study of irinotecan combined with cisplatin in patients with previously untreated small-cell lung cancer. West Japan Lung Cancer Group. J Clin Oncol 1998; 16: 1068–1074.
Irvin WP, Price FV, Bailey H, Gelder M, Rosenbluth R, Durivage HJ et al. A phase II study of irinotecan (CPT-11) in patients with advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix. Cancer 1998; 82: 328–333.
Noda K, Nishiwaki Y, Kawahara M, Negoro S, Sugiura T, Yokoyama A et al. Irinotecan plus cisplatin compared with etoposide plus cisplatin for extensive small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2002; 346: 85–91.
Kawato Y, Aonuma M, Hirota Y, Kuga H, Sato K . Intracellular roles of SN-38, a metabolite of the camptothecin derivative CPT-11, in the antitumor effect of CPT-11. Cancer Res 1991; 51: 4187–4191.
Tanizawa A, Fujimori A, Fujimori Y, Pommier Y . Comparison of topoisomerase I inhibition, DNA damage, and cytotoxicity of camptothecin derivatives presently in clinical trials. J Natl Cancer Inst 1994; 86: 836–842.
Khanna R, Morton CL, Danks MK, Potter PM . Proficient metabolism of irinotecan by a human intestinal carboxylesterase. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 4725–4728.
Hecht JR . Gastrointestinal toxicity or irinotecan. Oncology (Huntingt) 1998; 12: 72–78.
Hammarstrom S . The carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) family: structures, suggested functions and expression in normal and malignant tissues. Semin Cancer Biol 1999; 9: 67–81.
Goldenberg DM, DeLand F, Kim E, Bennett S, Primus FJ, van Nagell Jr JR et al. Use of radiolabeled antibodies to carcinoembryonic antigen for the detection and localization of diverse cancers by external photoscanning. N Engl J Med 1978; 298: 1384–1386.
Kuroki M, Arakawa F, Haruno M, Murakami M, Wakisaka M, Higuchi H et al. Biochemical characterization of 25 distinct carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) epitopes recognized by 57 monoclonal antibodies and categorized into seven groups in terms of domain structure of the CEA molecule. Hybridoma 1992; 11: 391–407.
Abe H, Kuroki M, Tachibana K, Li T, Awasthi A, Ueno A et al. Targeted sonodynamic therapy of cancer using a photosensitizer conjugated with antibody against carcinoembryonic antigen. Anticancer Res 2002; 22: 1575–1580.
Kurita A, Kaneda N . High-performance liquid chromatographic method for the simultaneous determination of the camptothecin derivative irinotecan hydrochloride, CPT-11, and its metabolites SN-38 and SN-38 glucuronide in rat plasma with a fully automated on-line solid-phase extraction system, PROSPEKT. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 1999; 724: 335–344.
Raben D, Buchsbaum DJ, Khazaeli MB, Rosenfeld ME, Gillespie GY, Grizzle WE et al. Enhancement of radiolabeled antibody binding and tumor localization through adenoviral transduction of the human carcinoembryonic antigen gene. Gene Ther 1996; 3: 567–580.
Guesdon JL, Ternynck T, Avrameas S . The use of avidin-biotin interaction in immunoenzymatic techniques. J Histochem Cytochem 1979; 27: 1131–1139.
Takayama K, Ueno H, Nakanishi Y, Sakamoto T, Inoue K, Shimizu K et al. Suppression of tumor angiogenesis and growth by gene transfer of a soluble form of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor into a remote organ. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 2169–2177.
Minagawa Y, Kigawa J, Ishihara H, Itamochi H, Terakawa N . Synergistic enhancement of cisplatin cytotoxicity by SN-38, an active metabolite of CPT-11, for cisplatin-resistant HeLa cells. Jpn J Cancer Res 1994; 85: 966–971.
Shayakhmetov DM, Gaggar A, Ni S, Li Z-Y, Lieber A . Adenovirus binding to blood factors results in liver cell infection and hepatotoxicity. J Virol 2005; 79: 7478–7491.
Dubowchik GM, Walker MA . Receptor-mediated and enzyme-dependent targeting of cytotoxic anticancer drugs. Pharmacol Ther 1999; 83: 67–123.
Deonarain MP, Epenetos AA . Targeting enzymes for cancer therapy: old enzymes in new roles. Br J Cancer 1994; 70: 786–794.
Wierdl M, Morton CL, Weeks JK, Danks MK, Harris LC, Potter PM . Sensitization of human tumor cells to CPT-11 via adenoviral-mediated delivery of a rabbit liver carboxylesterase. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 5078–5082.
Sanghani SP, Quinney SK, Fredenburg TB, Davis WI, Murry DJ, Bosron WF . Hydrolysis of irinotecan and its oxidative metabolites, 7-ethyl-10-[4-N-(5-aminopentanoic acid)-1-piperidino] carbonyloxycamptothecin and 7-ethyl-10-[4-(1-piperidino)-1-amino]-carbonyloxycamptothecin, by human carboxylesterases CES1A1, CES2, and a newly expressed carboxylesterase isoenzyme, CES3. Drug Metab Dispos 2004; 32: 505–511.
Oosternhoff D, Overmeer RM, de Graaf M, van der Meulen IH, Gaiconne G, van Beusechem VW et al. Adenoviral vector-mediated expression of a gene encoding secreted, EpCAM-trageted carboxylesterase-2 sensitises colon cancer spheroids to CPT-11. Br J Cancer 2005; 92: 882–887.
Oosternhoff D, Pinedo HM, van der Meulen IH, de Graaf M, Sone T, Kruyt FA et al. Secreted and tumour targeted human carboxylesterase for activation of irinotecan. Br J Cancer 2002; 87: 659–664.
Acknowledgements
We thank Mr J Suzuki, from the Yakult Central Institute for Microbiological Research who provided the technical assistance throughout this study. The study was supported by grant-in-aid scientific research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology in Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uchino, J., Takayama, K., Harada, A. et al. Tumor targeting carboxylesterase fused with anti-CEA scFv improve the anticancer effect with a less toxic dose of irinotecan. Cancer Gene Ther 15, 94–100 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7701100
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7701100
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Irinotecan-Induced Toxicity: A Pharmacogenetic Study Beyond UGT1A1
Clinical Pharmacokinetics (2023)
-
Heterogenous chemosensitivity of a panel of organoid lines derived from small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the uterine cervix
Human Cell (2021)
-
Individualization of Irinotecan Treatment: A Review of Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Pharmacogenetics
Clinical Pharmacokinetics (2018)
-
Carboxylesterase 2 production and characterization in human cells: new insights into enzyme oligomerization and activity
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2013)