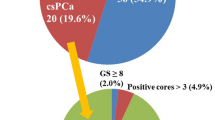
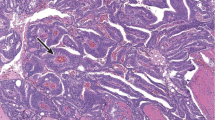
Abstract
High-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (HGPIN) is a premalignant lesion associated with increased risk of coexistent cancer or delayed progression to carcinoma. Extended biopsy schemes have improved the ability to rule out concurrent cancers, increased the detection of isolated HGPIN and removed the routine necessity for immediate repeat biopsy. As the natural history of HGPIN is poorly defined, and no non-invasive marker allows monitoring of progression to cancer, routine delayed interval biopsy should be considered in all patients. In this article, we present an overview of the existing literature on HGPIN and a proposed strategy for clinical management.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Epstein JI, Herawi M . Prostate needle biopsies containing prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia or atypical foci suspicious for carcinoma: implications for patient care. J Urol 2006; 175 (3 Part 1): 820–834.
Lefkowitz GK, Sidhu GS, Torre P, Lepor H, Taneja SS . Is repeat prostate biopsy for high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia necessary after routine 12-core sampling? Urology 2001; 58: 999–1003.
Abdel-Khalek M, El-Baz M, Ibrahiem el H . Predictors of prostate cancer on extended biopsy in patients with high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia: a multivariate analysis model. BJU Int 2004; 94: 528–533.
Bostwick DG, Qian J, Frankel K . The incidence of high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia in needle biopsies. J Urol 1995; 154: 1791–1794.
Feneley MR, Green JS, Young MP, Bose P, Kirby RS, Peeling WB et al. Prevalence of prostatic intra-epithelial neoplasia (PIN) in biopsies from hospital practice and pilot screening: clinical implications. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 1997; 1: 79–83.
Moore CK, Karikehalli S, Nazeer T, Fisher HA, Kaufman Jr RP, Mian BM . Prognostic significance of high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and atypical small acinar proliferation in the contemporary era. J Urol 2005; 173: 70–72.
Novis DA, Zarbo RJ, Valenstein PA . Diagnostic uncertainty expre ssed in prostate needle biopsies. A College of American Pathologists Q-probes Study of 15 753 prostate needle biopsies in 332 institutions. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1999; 123: 687–692.
O’Dowd GJ, Miller MC, Orozco R, Veltri RW . Analysis of repeated biopsy results within 1 year after a noncancer diagnosis. Urology 2000; 55: 553–559.
Renshaw AA, Santis WF, Richie JP . Clinicopathological characteristics of prostatic adenocarcinoma in men with atypical prostate needle biopsies. J Urol 1998; 159: 2018–2021; discussion 2022.
Lefkowitz GK, Taneja SS, Brown J, Melamed J, Lepor H . Followup interval prostate biopsy 3 years after diagnosis of high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia is associated with high likelihood of prostate cancer, independent of change in prostate specific antigen levels. J Urol 2002; 168 (4 Part t 1): 1415–1418.
Borboroglu PG, Sur RL, Roberts JL, Amling CL . Repeat biopsy strategy in patients with atypical small acinar proliferation or high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia on initial prostate needle biopsy. J Urol 2001; 166: 866–870.
Hom JJ, Coakley FV, Simko JP, Lu Y, Qayyum A, Westphalen AC et al. High-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia in patients with prostate cancer: MR and MR spectroscopic imaging features—initial experience. Radiology 2007; 242: 483–489.
McNeal JE, Bostwick DG . Intraductal dysplasia: a premalignant lesion of the prostate. Hum Pathol 1986; 17: 64–71.
Bostwick DG, Brawer MK . Prostatic intra-epithelial neoplasia and early invasion in prostate cancer. Cancer 1987; 59: 788–794.
Bostwick DG, Montironi R, Sesterhenn IA . Diagnosis of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia: Prostate Working Group/consensus report. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl 2000, 3–10.
Bostwick DG, Qian J . High-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Mod Pathol 2004; 17: 360–379.
Epstein JI, Grignon DJ, Humphrey PA, McNeal JE, Sesterhenn IA, Troncoso P et al. Interobserver reproducibility in the diagnosis of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Am J Surg Pathol 1995; 19: 873–886.
Srigley JR, Amin MB, Bostwick DG, Grignon DJ, Hammond ME . Updated protocol for the examination of specimens from patients with carcinomas of the prostate gland: a basis for checklists. Cancer Committee. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2000; 124: 1034–1039.
Allam CK, Bostwick DG, Hayes JA, Upton MP, Wade GG, Domanowski GF et al. Interobserver variability in the diagnosis of high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol 1996; 9: 742–751.
Algaba F . Evolution of isolated high-grade prostate intraepithelial neoplasia in a Mediterranean patient population. Eur Urol 1999; 35: 496–497.
Alsikafi NF, Brendler CB, Gerber GS, Yang XJ . High-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia with adjacent atypia is associated with a higher incidence of cancer on subsequent needle biopsy than high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia alone. Urology 2001; 57: 296–300.
Cheville JC, Reznicek MJ, Bostwick DG . The focus of ‘atypical glands, suspicious for malignancy’ in prostatic needle biopsy specimens: incidence, histologic features, and clinical follow-up of cases diagnosed in a community practice. Am J Clin Pathol 1997; 108: 633–640.
Fowler Jr JE, Bigler SA, Lynch C, Wilson SS, Farabaugh PB . Prospective study of correlations between biopsy-detected high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, serum prostate specific antigen concentration, and race. Cancer 2001; 91: 1291–1296.
Hoedemaeker RF, Kranse R, Rietbergen JB, Kruger AE, Schroder FH, van der Kwast TH . Evaluation of prostate needle biopsies in a population-based screening study: the impact of borderline lesions. Cancer 1999; 85: 145–152.
Horninger W, Volgger H, Rogatsch H, Strohmeyer D, Steiner H, Hobisch A et al. Predictive value of total and percent free prostate specific antigen in high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia lesions: results of the Tyrol prostate specific antigen screening project. J Urol 2001; 165: 1143–1145.
Hu JC, Palapattu GS, Kattan MW, Scardino PT, Wheeler TM . The association of selected pathological features with prostate cancer in a single-needle biopsy accession. Hum Pathol 1998; 29: 1536–1538.
Kahane H, Sharp JW, Shuman GB, Dasilva G, Epstein JI . Utilization of high molecular weight cytokeratin on prostate needle biopsies in an independent laboratory. Urology 1995; 45: 981–986.
Kamoi K, Troncoso P, Babaian RJ . Strategy for repeat biopsy in patients with high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. J Urol 2000; 163: 819–823.
Langer JE, Rovner ES, Coleman BG, Yin D, Arger PH, Malkowicz SB et al. Strategy for repeat biopsy of patients with prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia detected by prostate needle biopsy. J Urol 1996; 155: 228–231.
Lee F, Torp-Pedersen ST, Carroll JT, Siders DB, Christensen-Day C, Mitchell AE . Use of transrectal ultrasound and prostate-specific antigen in diagnosis of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Urology 1989; 34 (6 Suppl): 4–8.
Mettlin C, Lee F, Drago J, Murphy GP . The American cancer society national prostate cancer detection project. Findings on the detection of early prostate cancer in 2425 men. Cancer 1991; 67: 2949–2958.
Naya Y, Ayala AG, Tamboli P, Babaian RJ . Can the number of cores with high-grade prostate intraepithelial neoplasia predict cancer in men who undergo repeat biopsy? Urology 2004; 63: 503–508.
Postma R, Roobol M, Schroder FH, van der Kwast TH . Lesions predictive for prostate cancer in a screened population: first and second screening round findings. Prostate 2004; 61: 260–266.
Roscigno M, Scattoni V, Freschi M, Raber M, Colombo R, Bertini R et al. Monofocal and plurifocal high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia on extended prostate biopsies: factors predicting cancer detection on extended repeat biopsy. Urology 2004; 63: 1105–1110.
San Francisco IF, Olumi AF, Kao J, Rosen S, DeWolf WC . Clinical management of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia as diagnosed by extended needle biopsies. BJU Int 2003; 91: 350–354.
Tan PH, Tan HW, Tan Y, Lim CN, Cheng C, Epstein JI . Is high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia on needle biopsy different in an Asian population: a clinicopathologic study performed in Singapore. Urology 2006; 68: 800–803.
Weinstein MH, Greenspan DL, Epstein JI . Diagnoses rendered on prostate needle biopsy in community hospitals. Prostate 1998; 35: 50–55.
Wills ML, Hamper UM, Partin AW, Epstein JI . Incidence of high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia in sextant needle biopsy specimens. Urology 1997; 49: 367–373.
Sakr WA, Billis A, Ekman P, Wilt T, Bostwick DG . Epidemiology of high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl 2000, 11–18.
Skjorten FJ, Berner A, Harvei S, Robsahm TE, Tretli S . Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia in surgical resections: relationship to coexistent adenocarcinoma and atypical adenomatous hyperplasia of the prostate. Cancer 1997; 79: 1172–1179.
Aydin O, Cosar EF, Varinli S, Bugdayci R, Tansug Z . Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia in prostate specimens: frequency, significance and relationship to the sampling of the specimen (a retrospective study of 121 cases). Int Urol Nephrol 1999; 31: 687–697.
Gaudin PB, Sesterhenn IA, Wojno KJ, Mostofi FK, Epstein JI . Incidence and clinical significance of high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia in TURP specimens. Urology 1997; 49: 558–563.
Pacelli A, Bostwick DG . Clinical significance of high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia in transurethral resection specimens. Urology 1997; 50: 355–359.
Billis A . Age and race distribution of high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia: an autopsy study in Brazil (South America). J Urol Pathol 1996; 5: 175–181.
Oyasu R, Bahnson RR, Nowels K, Garnett JE . Cytological atypia in the prostate gland: frequency, distribution and possible relevance to carcinoma. J Urol 1986; 135: 959–962.
Sakr WA . Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia: a marker for high-risk groups and a potential target for chemoprevention. Eur Urol 1999; 35: 474–478.
Silvestri F, Bussani R, Pavletic N, Bassan F . Neoplastic and borderline lesions of the prostate: autopsy study and epidemiological data. Pathol Res Pract 1995; 191: 908–916.
Sakr WA, Grignon DJ, Haas GP, Schomer KL, Heilbrun LK, Cassin BJ et al. Epidemiology of high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Pathol Res Pract 1995; 191: 838–841.
Balaji KC, Rabbani F, Tsai H, Bastar A, Fair WR . Effect of neoadjuvant hormonal therapy on prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and its prognostic significance. J Urol 1999; 162 (3 Part 1): 753–757.
Cheng L, Cheville JC, Pisansky TM, Sebo TJ, Slezak J, Bergstralh EJ et al. Prevalence and distribution of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia in salvage radical prostatectomy specimens after radiation therapy. Am J Surg Pathol 1999; 23: 803–808.
Fujita MQ, Shin M, Yasunaga Y, Sekii K, Itatani H, Tsujimura T et al. Incidence of prostatic intra-epithelial neoplasia in Osaka, Japan. Int J Cancer 1997; 73: 808–811.
Kim HL, Yang XJ . Prevalence of high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and its relationship to serum prostate specific antigen. Int Braz J Urol 2002; 28: 413–416; discussion 417.
Qian J, Wollan P, Bostwick DG . The extent and multicentricity of high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia in clinically localized prostatic adenocarcinoma. Hum Pathol 1997; 28: 143–148.
Sakr WA, Grignon DJ . Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and atypical adenomatous hyperplasia. Relationship to pathologic parameters, volume and spatial distribution of carcinoma of the prostate. Anal Quant Cytol Histol 1998; 20: 417–423.
Shin M, Takayama H, Nonomura N, Wakatsuki A, Okuyama A, Aozasa K . Extent and zonal distribution of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia in patients with prostatic carcinoma in Japan: analysis of whole-mounted prostatectomy specimens. Prostate 2000; 42: 81–87.
Wiley EL, Davidson P, McIntire DD, Sagalowsky AI . Risk of concurrent prostate cancer in cystoprostatectomy specimens is related to volume of high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Urology 1997; 49: 692–696.
Troncoso P, Babaian RJ, Ro JY, Grignon DJ, von Eschenbach AC, Ayala AG . Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and invasive prostatic adenocarcinoma in cystoprostatectomy specimens. Urology 1989; 34 (6 Suppl): 52–56.
Sakr WA, Haas GP, Cassin BF, Pontes JE, Crissman JD . The frequency of carcinoma and intraepithelial neoplasia of the prostate in young male patients. J Urol 1993; 150 (2 Part 1): 379–385.
Brawer MK . Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia: an overview. Rev Urol 2005; 7 (Suppl 3): S11–S18.
Sakr WA, Grignon DJ, Haas GP . Pathology of premalignant lesions and carcinoma of the prostate in African-American men. Semin Urol Oncol 1998; 16: 214–220.
Kronz JD, Allan CH, Shaikh AA, Epstein JI . Predicting cancer following a diagnosis of high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia on needle biopsy: data on men with more than one follow-up biopsy. Am J Surg Pathol 2001; 25: 1079–1085.
Egevad L, Allsbrook WC, Epstein JI . Current practice of diagnosis and reporting of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and glandular atypia among genitourinary pathologists. Mod Pathol 2006; 19: 180–185.
Bostwick DG, Amin MB, Dundore P, Marsh W, Schultz DS . Architectural patterns of high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Hum Pathol 1993; 24: 298–310.
Bishara T, Ramnani DM, Epstein JI . High-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia on needle biopsy: risk of cancer on repeat biopsy related to number of involved cores and morphologic pattern. Am J Surg Pathol 2004; 28: 629–633.
Bostwick DG, Shan A, Qian J, Darson M, Maihle NJ, Jenkins RB et al. Independent origin of multiple foci of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia: comparison with matched foci of prostate carcinoma. Cancer 1998; 83: 1995–2002.
Wojno KJ, Epstein JI . The utility of basal cell-specific anti-cytokeratin antibody (34 beta E12) in the diagnosis of prostate cancer. A review of 228 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 1995; 19: 251–260.
Shah RB, Zhou M, LeBlanc M, Snyder M, Rubin MA . Comparison of the basal cell-specific markers, 34betaE12 and p63, in the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Am J Surg Pathol 2002; 26: 1161–1168.
McNeal JE, Villers A, Redwine EA, Freiha FS, Stamey TA . Microcarcinoma in the prostate: its association with duct-acinar dysplasia. Hum Pathol 1991; 22: 644–652.
Kronz JD, Shaikh AA, Epstein JI . High-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia with adjacent small atypical glands on prostate biopsy. Hum Pathol 2001; 32: 389–395.
Emmert-Buck MR, Vocke CD, Pozzatti RO, Duray PH, Jennings SB, Florence CD et al. Allelic loss on chromosome 8p12–21 in microdissected prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Cancer Res 1995; 55: 2959–2962.
Vukovic B, Park PC, Al-Maghrabi J, Beheshti B, Sweet J, Evans A et al. Evidence of multifocality of telomere erosion in high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (HPIN) and concurrent carcinoma. Oncogene 2003; 22: 1978–1987.
Qian J, Bostwick DG, Takahashi S, Borell TJ, Herath JF, Lieber MM et al. Chromosomal anomalies in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and carcinoma detected by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Cancer Res 1995; 55: 5408–5414.
Calvo A, Xiao N, Kang J, Best CJ, Leiva I, Emmert-Buck MR et al. Alterations in gene expression profiles during prostate cancer progression: functional correlations to tumorigenicity and down-regulation of selenoprotein-P in mouse and human tumors. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 5325–5335.
Harper ME, Glynne-Jones E, Goddard L, Mathews P, Nicholson RI . Expression of androgen receptor and growth factors in premalignant lesions of the prostate. J Pathol 1998; 186: 169–177.
Myers RB, Srivastava S, Oelschlager DK, Grizzle WE . Expression of p160erbB-3 and p185erbB-2 in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and prostatic adenocarcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 1994; 86: 1140–1145.
Nakashiro K, Hayashi Y, Oyasu R . Immunohistochemical expression of hepatocyte growth factor and c-Met/HGF receptor in benign and malignant human prostate tissue. Oncol Rep 2003; 10: 1149–1153.
Baltaci S, Orhan D, Ozer G, Tolunay O, Gogous O . Bcl-2 proto-oncogene expression in low- and high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. BJU Int 2000; 85: 155–159.
Luo J, Zha S, Gage WR, Dunn TA, Hicks JL, Bennett CJ et al. Alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase: a new molecular marker for prostate cancer. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 2220–2226.
Coogan CL, Bostwick DG, Bloom KJ, Gould VE . Glycoprotein A-80 in the human prostate: immunolocalization in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, carcinoma, radiation failure, and after neoadjuvant hormonal therapy. Urology 2003; 61: 248–252.
Hall RE, Horsfall DJ, Stahl J, Vivekanandan S, Ricciardelli C, Stapleton AM et al. Apolipoprotein-D: a novel cellular marker for HGPIN and prostate cancer. Prostate 2004; 58: 103–108.
Tsuji M, Kanda K, Murakami Y, Kurokawa Y, Kanayama H, Sano T et al. Biologic markers in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia: immunohistochemical and cytogenetic analyses. J Med Invest 1999; 46: 35–41.
Hampel OZ, Kattan MW, Yang G, Haidacher SJ, Saleh GY, Thompson TC et al. Quantitative immunohistochemical analysis of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in human prostatic adenocarcinoma: a prognostic study. J Urol 1998; 159: 2220–2225.
Koeneman KS, Pan CX, Jin JK, Pyle III JM, Flanigan RC, Shankey TV et al. Telomerase activity, telomere length, and DNA ploidy in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN). J Urol 1998; 160: 1533–1539.
Montironi R, Diamanti L, Thompson D, Bartels HG, Bartels PH . Analysis of the capillary architecture in the precursors of prostate cancer: recent findings and new concepts. Eur Urol 1996; 30: 191–200.
Steiner MS . High-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and prostate cancer risk reduction. World J Urol 2003; 21: 15–20.
Gonzalgo ML, Isaacs WB . Molecular pathways to prostate cancer. J Urol 2003; 170 (6 Part 1): 2444–2452.
Konishi N, Shimada K, Ishida E, Nakamura M . Molecular pathology of prostate cancer. Pathol Int 2005; 55: 531–539.
Aboseif S, Shinohara K, Weidner N, Narayan P, Carroll PR . The significance of prostatic intra-epithelial neoplasia. Br J Urol 1995; 76: 355–359.
Brawer MK, Bigler SA, Sohlberg OE, Nagle RB, Lange PH . Significance of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia on prostate needle biopsy. Urology 1991; 38: 103–107.
Weinstein MH, Epstein JI . Significance of high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia on needle biopsy. Hum Pathol 1993; 24: 624–629.
Raviv G, Janssen T, Zlotta AR, Descamps F, Verhest A, Schulman CC . Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia: influence of clinical and pathological data on the detection of prostate cancer. J Urol 1996; 156: 1050–1054; discussion 1054–1055.
Shepherd D, Keetch DW, Humphrey PA, Smith DS, Stahl D . Repeat biopsy strategy in men with isolated prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia on prostate needle biopsy. J Urol 1996; 156 (2 Part 1): 460–462; discussion 462–463.
Herawi M, Kahane H, Cavallo C, Epstein JI . Risk of prostate cancer on first re-biopsy within 1 year following a diagnosis of high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia is related to the number of cores sampled. J Urol 2006; 175: 121–124.
Epstein JI, Walsh PC, Carmichael M, Brendler CB . Pathologic and clinical findings to predict tumor extent of nonpalpable (stage T1c) prostate cancer. JAMA 1994; 271: 368–374.
Eggener SE, Roehl KA, Catalona WJ . Predictors of subsequent prostate cancer in men with a prostate specific antigen of 2.6 to 4.0 ng ml−1 and an initially negative biopsy. J Urol 2005; 174: 500–504.
Davidson D, Bostwick DG, Qian J, Wollan PC, Oesterling JE, Rudders RA et al. Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia is a risk factor for adenocarcinoma: predictive accuracy in needle biopsies. J Urol 1995; 154: 1295–1299.
Chan TY, Epstein JI . Follow-up of atypical prostate needle biopsies suspicious for cancer. Urology 1999; 53: 351–355.
Keetch DW, Humphrey P, Stahl D, Smith DS, Catalona WJ . Morphometric analysis and clinical followup of isolated prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia in needle biopsy of the prostate. J Urol 1995; 154 (2 Part 1): 347–351.
Park S, Shinohara K, Grossfeld GD, Carroll PR . Prostate cancer detection in men with prior high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia or atypical prostate biopsy. J Urol 2001; 165: 1409–1414.
Loeb S, Roehl KA, Yu X, Han M, Catalona WJ . Use of prostate-specific antigen velocity to follow up patients with isolated high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia on prostate biopsy. Urology 2007; 69: 108–112.
Brausi M, Castagnetti G, Dotti A, De Luca G, Olmi R, Cesinaro AM . Immediate radical prostatectomy in patients with atypical small acinar proliferation. Over treatment? J Urol 2004; 172: 906–908; discussion 908–909.
Steiner MS, Raghow S . Antiestrogens and selective estrogen receptor modulators reduce prostate cancer risk. World J Urol 2003; 21: 31–36.
Bullock MJ, Srigley JR, Klotz LH, Goldenberg SL . Pathologic effects of neoadjuvant cyproterone acetate on nonneoplastic prostate, prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, and adenocarcinoma: a detailed analysis of radical prostatectomy specimens from a randomized trial. Am J Surg Pathol 2002; 26: 1400–1413.
Thompson IM, Goodman PJ, Tangen CM, Lucia MS, Miller GJ, Ford LG et al. The influence of finasteride on the development of prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 2003; 349: 215–224.
Yang XJ, Lecksell K, Short K, Gottesman J, Peterson L, Bannow J et al. Does long-term finasteride therapy affect the histologic features of benign prostatic tissue and prostate cancer on needle biopsy? PLESS study group. Proscar Long-Term Efficacy and Safety Study. Urology 1999; 53: 696–700.
Bosland MC . Hormonal factors in carcinogenesis of the prostate and testis in humans and in animal models. Prog Clin Biol Res 1996; 394: 309–352.
Raghow S, Hooshdaran MZ, Katiyar S, Steiner MS . Toremifene prevents prostate cancer in the transgenic adenocarcinoma of mouse prostate model. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 1370–1376.
Price D, Stein B, Sieber P, Tutrone R, Bailen J, Goluboff E et al. Toremifene for the prevention of prostate cancer in men with high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia: results of a double-blind, placebo controlled, phase IIB clinical trial. J Urol 2006; 176: 965–970; discussion 970–961.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Godoy, G., Taneja, S. Contemporary clinical management of isolated high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 11, 20–31 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.pcan.4501014
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.pcan.4501014
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
What is the pathologist saying? Interpretation of the prostate pathology report
Current Urology Reports (2009)
-
What is the pathologist saying? Interpretation of the prostate pathology report
Current Prostate Reports (2009)
-
Precursor lesions to prostatic adenocarcinoma
Virchows Archiv (2009)