Abstract
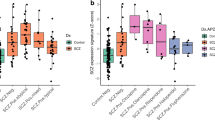
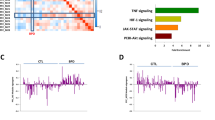
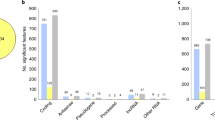
Post-mortem studies conducted over the past 15 years suggest that apoptosis could play a role in the pathophysiology of bipolar disorder (BD) and, to a lesser degree, schizophrenia (SZ). To test this hypothesis, we have performed a post hoc analysis of an extant gene expression profiling database obtained from the hippocampus using a novel methodology with improved sensitivity. Consistent with the working hypothesis, BDs showed a marked upregulation of 19 out of 44 apoptosis genes; however, contrary to the hypothesis, the SZ group showed a downregulation of genes associated with apoptotic injury and death. These changes in the regulation of apoptosis genes were validated using quantitative RT–PCR. Additionally, antioxidant genes showed a marked downregulation in BDs, suggesting that accumulation of free radicals might occur in the setting of a previously reported decrease of the electron transport chain in this disorder. Overall, the changes seen in BDs and SZs do not appear to be related to exposure to either neuroleptics or mood stabilizers. We conclude that fundamental differences in the genetic regulation of apoptosis and antioxidant genes may help discriminate between the pathophysiology of BD and SZ and potentially point to new treatment strategies that are specific for each disorder.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Benes FM, Walsh J, Bhattacharyya S, Sheth A, Berretta S . DNA fragmentation decreased in schizophrenia but not bipolar disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2003; 60: 359–364.
Margolis RL, Chuang DM, Post RM . Programmed cell death: implications for neuropsychiatric disorders. Biol Psychiatry 1994; 35: 946–956.
Konradi C, Eaton M, Walsh J, Benes FM, Heckers S . Molecular evidence for mitochondrial dysfunction in bipolar disorder. Archives of General Psychiatry 2004; 61: 300–308.
Jarskog LF, Gilmore JH, Selinger ES, Lieberman JA . Cortical bcl-2 protein expression and apoptotic regulation in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 2000; 48: 641–650.
Benes FM, McSparren J, Bird ED, Vincent SL, SanGiovanni JP . Deficits in small interneurons in prefrontal and anterior cingulate cortex of schizophrenic and schizoaffective patients. Arch Gen Psychiat 1991; 48: 996–1001.
Benes FM, Vincent SL, Todtenkopf M . The density of pyramidal and nonpyramidal neurons in anterior cingulate cortex of schizophrenic and bipolar subjects. Biol Psychiatry 2001; 50: 395–406.
Todtenkopf MS, Vincent SL, Benes FM . A cross-study meta-analysis and three-dimensional comparison of cell counting in the anterior cingulate cortex of schizophrenic and bipolar brain. Schizophr Res 2005; 73: 79–89.
Benes FM, Burke RE, Walsh J, Matzilevich D, Berretta S, Minns M, Konradi C . Acute amygdalar activation induces an upregulation of multiple monoamine G protein coupled pathways in rat hippocampus. Molecular Psychiatry 2004; 9: 932–945.
Tsunoda T, Yamada R, Tanaka T, Ohnishi Y, Kamatani N . Environmental factor dependent maximum likelihood method for association study targeted to personalized medicine. Genome Inform 2000; 11: 96–105.
Asyali MH, Shoukri MM, Demirkaya O, Khabar KSA . Assessment of reliability of microarray data and estimation of signal thresholds using mixture modeling. Nucleic Acids Res 2004; 32: 2323–2335.
Raffelsberger W, Dembele D, Neubauer MG, Gottardis MM, Gronemeyer H . Quality indicators increase the reliability of microarray data. Genomics 2002; 80: 385–394.
Li CX, Wong WH . Model-based analysis of oligonucleotide arrays: expression index computation and outlier detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2001; 98: 31–36.
Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW, Dempfle L . Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 2002; 30: e36.
Hu WH, Johnson H, Shu HB . Activation of NF-kappaB by FADD, Casper, and caspase-8. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 10838–10844.
Shin SW, Park JW, Suh MH, Suh SI, Choe BK . Persistent expression of Fas/FasL mRNA in the mouse hippocampus after a single NMDA injection. J Neurochem 1998; 71: 1773–1776.
Ohara T, Morishita T, Suzuki H, Masaoka T, Ishii H . Perforin and granzyme B of cytotoxic T lymphocyte mediate apoptosis irrespective of Helicobacter pylori infection: possible act as a trigger of peptic ulcer formation. Hepatogastroenterology 2003; 50: 1774–1779.
Thome M, Hofmann K, Burns K, Martinon F, Bodmer JL, Mattmann C, Tschopp J . Identification of CARDIAK, a RIP-like kinase that associates with caspase-1. Curr Biol 1998; 8: 885–888.
Mielke K, Brecht S, Dorst A, Herdegen T . Activity and expression of JNK1, p38 and ERK kinases, c-Jun N-terminal phosphorylation, and c-jun promoter binding in the adult rat brain following kainate-induced seizures. Neuroscience 1999; 91: 471–483.
Alarcon-Vargas D, Tansey WP, Ronai Z . Regulation of c-myc stability by selective stress conditions and by MEKK1 requires aa 127-189 of c-myc. Oncogene 2002; 21: 4384–4391.
Viktorsson K, Ekedahl J, Lindebro MC, Lewensohn R, Zhivotovsky B, Linder S, Shoshan MC . Defective stress kinase and Bak activation in response to ionizing radiation but not cisplatin in a non-small cell lung carcinoma cell line. Exp Cell Res 2003; 289: 256–264.
Ferrer I, Lopez E, Blanco R, Rivera R, Krupinski J, Marti E . Differential c-Fos and caspase expression following kainic acid excitotoxicity. Acta Neuropathol (Berlin) 2000; 99: 245–256.
Northington FJ, Ferriero DM, Martin LJ . Neurodegeneration in the thalamus following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia is programmed cell death. Dev Neurosci 2001; 23: 186–191.
Micheau O, Lens S, Gaide O, Alevizopoulos K, Tschopp J . NF-kappaB signals induce the expression of c-FLIP. Mol Cell Biol 2001; 21: 5299–5305.
Adams JM, Cory S . The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science 1998; 281: 1322–1326.
Yang DD, Kuan CY, Whitmarsh AJ, Rincon M, Zheng TS, Davis RJ et al. Absence of excitotoxicity-induced apoptosis in the hippocampus of mice lacking the Jnk3 gene. Nature 1997; 389: 865–870.
Bouchard VJ, Rouleau M, Poirier GG . PARP-1, a determinant of cell survival in response to DNA damage. Exp Hematol 2003; 31: 446–454.
Warner DS, Sheng H, Batinic-Haberle I . Oxidants, antioxidants and the ischemic brain. J Exp Biol 2004; 207: 3221–3231.
Sun J, Bird CH, Thia KY, Matthews AY, Trapani JA, Bird PI . Granzyme B encoded by the commonly-occurring human RAH allele retains pro-apoptotic activity. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 16907–16911.
Wang CY, Guttridge DC, Mayo MW, Baldwin Jr AS . NF-kappaB induces expression of the Bcl-2 homologue A1/Bfl-1 to preferentially suppress chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 1999; 19: 5923–5929.
Boldt S, Weidle UH, Kolch W . The kinase domain of MEKK1 induces apoptosis by dysregulation of MAP kinase pathways. Exp Cell Res 2003; 283: 80–90.
Benes FM, Burke RE, Walsh J, Matzilevich D, Berretta S, Minns M, Konradi C . Amygdalar activation induces an upregulation of multiple monoamine and peptide G-coupled protein receptors occurs in rat hippocampus. Mol Psychiatry 2004; 9: 932–944.
Benes FM, McSparren J, Bird ED, SanGiovanni JP, Vincent SL . Deficits in small interneurons in prefrontal and cingulate cortices of schizophrenic and schizoaffective patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1991; 48: 996–1001.
Benes FM, Kwok EW, Vincent SL, Todtenkopf MS . A reduction of nonpyramidal cells in sector CA2 of schizophrenics and manic depressives [see comments]. Biol Psychiatry 1998; 44: 88–97.
Benes FM, Berretta S . GABAergic interneurons: implications for understanding schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. TPG-1-27. Neuropsychopharmacology 2001; 25: 1–27.
Woo TW, Walsh JP, Benes FM . Density of glutamate acid decarboxylase 67 messenger RNA-containing neurons that express the N-methyl-D-aspartate subunit NR2a is decreased in the anterior cingulate cortex in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2004; 61: 649–657.
Achour A, Lu W, Arlie M, Cao L, Andrieu JMT . Cell survival/proliferation reconstitution by trifluoperazine in human immunodeficiency virus-1 infection. Virology 2003; 315: 245–258.
Wei Z, Bai O, Richardson JS, Mousseau DD, Li XM . Olanzapine protects PC12 cells from oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide. J Neurosci Res 2003; 73: 364–368.
Qing H, Xu H, Wei Z, Gibson K, Li XM . The ability of atypical antipsychotic drugs vs. haloperidol to protect PC 12 cells: against, MPP+-induced apoptosis. Eur J Neurosci 2003; 17: 1563–1570.
Gil-ad I, Shtaif B, Shiloh R, Weizman A . Evaluation of the neurotoxic activity of typical and atypical neuroleptics: relevance to iatrogenic extrapyramidal symptoms. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2001; 21: 705–716.
Haack MJ, Bak ML, Beurskens R, Maes M, Stolk LM, Delespaul PA . I. Toxic rise of clozapine plasma concentrations in relation to inflammation. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2003; 13: 381–385.
Kang UG, Seo MS, Roh MS, Kim Y, Yoon SC, Kim YS . The effects of clozapine on the GSK-3-mediated signaling pathway. FEBS Lett 2004; 560: 115–119.
Li X, Bijur GN, Jope RS . Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta, mood stabilizers, and neuroprotection. Bipolar Disord 2002; 4: 137–144.
Manji HK, Moore GJ, Chen G . Clinical and preclinical evidence for the neurotrophic effects of mood stabilizers: implications for the pathophysiology and treatment of manic-depressive illness. Biol Psychiatry 2000; 48: 740–754.
Manji HK, Moore GJ, Rajkowska G, Chen G . Neuroplasticity and cellular resilience in mood disorders. Mol Psychiatry 2000; 5: 578–593.
Manji HK, Etcheberrigaray R, Chen G, Olds JL . Lithium decreases membrane-associated protein kinase C in hippocampus: selectivity for the alpha isozyme. J Neurochem 1993; 61: 2303–2310.
Chen G, Masana MI, Manji HK . Lithium regulates PKC-mediated intracellular cross-talk and gene expression in the CNS in vivo. Bipolar Disord 2000; 2: 217–236.
Pollack M, Leeuwenburgh C . Apoptosis and aging: role of the mitochondria. J Gerontol A 2001; 56: B475–B482.
Tanaka T, Nangaku M, Miyata T, Inagi R, Ohse T, Ingelfinger JR, Fujita T . Blockade of calcium influx through l-type calcium channels attenuates mitochondrial injury and apoptosis in hypoxic renal tubular cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 2004; 15: 2320–2333.
Yagami T, Ueda K, Sakaeda T, Itoh N, Sakaguchi G, Okamura N, et al. Protective effects of a selective L-type voltage-sensitive calcium channel blocker, S-312-d, on neuronal cell death. Biochem Pharmacol 2004; 67: 1153–1165.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (MH42261, MH62822 and MH/NS31862) and the generosity of Menachem and Carmella Abraham, John and Virginia Taplin and Anne Allen.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benes, F., Matzilevich, D., Burke, R. et al. The expression of proapoptosis genes is increased in bipolar disorder, but not in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 11, 241–251 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001758
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001758
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Metabolic regulation to treat bipolar depression: mechanisms and targeting by trimetazidine
Molecular Psychiatry (2023)
-
In vitro effects of antidepressants and mood-stabilizing drugs on cell energy metabolism
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2020)
-
Downregulation of the psychiatric susceptibility gene Cacna1c promotes mitochondrial resilience to oxidative stress in neuronal cells
Cell Death Discovery (2018)
-
Perturbations in the apoptotic pathway and mitochondrial network dynamics in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from bipolar disorder patients
Translational Psychiatry (2017)
-
The Neurobiology of Depression: an Integrated Overview from Biological Theories to Clinical Evidence
Molecular Neurobiology (2017)