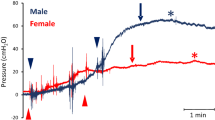
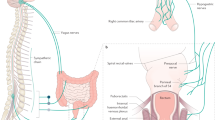
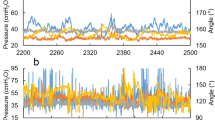
Abstract
Micturition, defecation and sexual function are all programmed through spinal reflexes that are under descending control from higher centres. Interaction between these reflexes can clearly be perceived, and evidence is accumulating the dysfunction in one reflex is often associated with dysfunction in another. In this article, we describe some of the basic properties and neural control of the smooth muscles mediating the reflexes, reviewing the common features that underlie these reflex functions, and what changes may be responsible for dysfunction. We propose that autonomic control within the pelvis predisposes pelvic and sexual organs to crosstalk, with the consequence that diseases and conditions of the pelvis are subject to convergence on a functional level. It should be expected that disturbance of the function of one system will inevitably impact adjacent systems.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Glina S, Santana AW, Azank F, Mello LF, Moreira Jr ED . Lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction are highly prevalent in ageing men. BJU Int 2006; 97: 763–765.
Macfarlane GJ, Botto H, Sagnier PP, Teillac P, Richard F, Boyle P . The relationship between sexual life and urinary condition in the French community. J Clin Epidemiol 1996; 49: 1171–1176.
Abrams P, Donovan JL, de la Rosette JJ, Schafer W . International Continence Society "Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia" Study: background, aims, and methodology. Neurourol Urodyn 1997; 16: 79–91.
Frankel SJ, Donovan JL, Peters TI, Abrams P, Dabhoiwala NF, Osawa D et al. Sexual dysfunction in men with lower urinary tract symptoms. J Clin Epidemiol 1998; 51: 677–685.
Vallancien G, Emberton M, Harving N, van Moorselaar RJ . Sexual dysfunction in 1,274 European men suffering from lower urinary tract symptoms. J Urol 2003; 169: 2257–2261.
Hoesl CE, Woll EM, Burkart M, Altwein JE . Erectile dysfunction (ED) is prevalent, bothersome and underdiagnosed in patients consulting urologists for benign prostatic syndrome (BPS). Eur Urol 2005; 47: 511–517.
Rosen R, Altwein J, Boyle P, Kirby RS, Lukacs B, Meuleman E et al. Lower urinary tract symptoms and male sexual dysfunction: the multinational survey of the aging male (MSAM-7). Eur Urol 2003; 44: 637–649.
Paick SH, Meehan A, Lee M, Penson DF, Wessells H . The relationship among lower urinary tract symptoms, prostate specific antigen and erectile dysfunction in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia: results from the proscar long-term efficacy and safety study. J Urol 2005; 173: 903–907.
Hanani M, Brading AF . Electrical coupling in smooth muscles. Is it universal? J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 2000; 11: 321–330.
Thuneberg L . One hundred years of interstitial cells of Cajal. Microsc Res Tech 1999; 47: 223–238.
Sanders KM, Koh SD, Ward SM . Interstitial Cells of Cajal as pacemakers in the gastrointestinal tract. Ann Rev Physiol 2006; 68: 17.11–17.37.
Brading AF, McCloskey KD . Mechanisms of disease: specialized interstitial cells of the urinary tract – an assessment of current knowledge. Nat Clin Pract Urol 2005; 2: 546–555.
Andersson KE . Pharmacology of penile erection. Pharmacol Rev 2001; 53: 417–450.
Fovaeus M, Andersson KE, Hedlund H . Effects of some calcium channel blockers on isolated human penile erectile tissues. J Urol 1987; 138: 1267–1272.
Hashitani H . Neuroeffector transmission to different layers of smooth muscle in the rat penile bulb. J Physiol 2000; 524: 549–563.
Hashitani H, Fukuta H, Dickens EJ, Suzuki H . Cellular mechanisms of nitric oxide-induced relaxation of corporeal smooth muscle in the guinea-pig. J Physiol 2002; 538: 573–581.
Christ GJ, Maayani S, Valcic M, Melman A . Pharmacological studies of human erectile tissue: characteristics of spontaneous contractions and alterations in alpha-adrenoceptor responsiveness with age and disease in isolated tissues. Br J Pharmacol 1990; 101: 375–381.
Hashitani H, Suzuki H . Identification of interstitial cells of Cajal in corporal tissues of the guinea-pig penis. Br J Pharmacol 2004; 141: 199–204.
Karkanis T, DeYoung L, Brock GB, Sims SM . Ca2+-activated Cl− channels in corpus cavernosum smooth muscle: a novel mechanism for control of penile erection. J Appl Physiol 2003; 94: 301–313.
Craven M, Sergeant GP, Hollywood MA, McHale NG, Thornbury KD . Modulation of spontaneous Ca2+-activated Cl− currents in the rabbit corpus cavernosum by the nitric oxide–cGMP pathway. J Physiol 2004; 556: 495–506.
Hashitani H, Yanai Y, Shirasawa N, Soji T, Tomita A, Kohri K et al. Interaction between spontaneous and neurally mediated regulation of smooth muscle tone in the rabbit corpus cavernosum. J Physiol 2005; 569(Part 3): 723–735.
Minhas S, Eardley I, Joyce AD, Morrison JB . The effect of cyclic GMP on rabbit corporal smooth muscle tone and its modulation by cyclo-oxygenase products. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 2000; 62: 153–160.
Azadzoi KM, Krane RJ, Saenz de Tejada I, Goldstein I, Siroky MB . Relative roles of cyclooxygenase and nitric oxide synthase pathways in ischemia-induced increased contraction of cavernosal smooth muscle. J Urol 1999; 161: 1324–1328.
Bivalacqua TJ, Champion HC, Usta MF, Cellek S, Chitaley K, Webb RC et al. RhoA/Rho-kinase suppresses endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the penis: a mechanism for diabetes-associated erectile dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 9121–9126.
Bramich NJ, Brading AF . Electrical properties of smooth muscle in the guinea-pig urinary bladder. J Physiol 1996; 492(Part 1): 185–198.
Hashitani H, Bramich NJ, Hirst GD . Mechanisms of excitatory neuromuscular transmission in the guinea-pig urinary bladder. J Physiol 2000; 524(Part 2): 565–579.
Hashitani H, Yanai Y, Suzuki H . Role of interstitial cells and gap junctions in the transmission of spontaneous Ca2+ signals in detrusor smooth muscles of the guinea-pig urinary bladder. J Physiol 2004; 559(Part 2): 567–581.
Brading AF . A myogenic basis for the overactive bladder. Urology 1997; 50: 57–67; discussion 68–73.
Brading AF, Turner WH . The unstable bladder: towards a common mechanism. Br J Urol 1994; 73: 3–8.
de Groat WC . A neurological basis for the overactive bladder. Urology 1997; 50: 36–52.
Hashitani H, Brading AF . Electrical properties of detrusor smooth muscles from the pig and human urinary bladder. Br J Pharmacol 2003; 140: 146–158.
Montgomery BS, Fry CH . The action potential and net membrane currents in isolated human detrusor smooth muscle cells. J Urol 1992; 147: 176–184.
McCloskey KD, Gurney AM . Kit positive cells in the guinea pig bladder. J Urol 2002; 168: 832–836.
Biers SM, Reynard JM, Doore T, Brading AF . The functional effects of a c-kit tyrosine inhibitor on guinea-pig and human detrusor. BJU Int 2006; 97: 612–616.
Kubota Y, Biers SM, Kohri K, Brading AF . Effects of imatinib mesylate (Glivec) as a c-kit tyrosine kinase inhibitor in the guinea-pig urinary bladder. Neurourol Urodyn 2006; 25: 205–210.
Kubota Y, Kajioka S, Biers SM, Yokota E, Kohri K, Brading AF . Investigation of the effect of the c-kit inhibitor Glivec on isolated guinea-pig detrusor preparations. Autonomic Neuroscience: Basic and Clinical 2004; 115: 64–73.
Sui GP, Wu C, Fry CH . Electrical characteristics of suburothelial cells isolated from the human bladder. J Urol 2004; 171: 938–943.
Gabella G, Davis C . Distribution of afferent axons in the bladder of rats. J Neurocytol 1998; 27: 141–155.
Drake MJ, Fry CH, Eyden B . Structural characterization of myofibroblasts in the bladder. BJU Int 2006; 97: 29–32.
Hashitani H, Edwards FR . Spontaneous and neurally activated depolarizations in smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig urethra. J Physiol 1999; 514(Part 2): 459–470.
Hashitani H, Van Helden DF, Suzuki H . Properties of spontaneous depolarizations in circular smooth muscle cells of rabbit urethra. Br J Pharmacol 1996; 118: 1627–1632.
Sergeant GP, Hollywood MA, McCloskey KD, Thornbury KD, McHale NG . Specialised pacemaking cells in the rabbit urethra. J Physiol 2000; 526(Part 2): 359–366.
Haefliger JA, Tissieres P, Tawadros T, Formenton A, Beny JL, Nicod P et al. Connexins 43 and 26 are differentially increased after rat bladder outlet obstruction. Exp Cell Res 2002; 274: 216–225.
Drake MJ, Gardner BP, Brading AF . Innervation of the detrusor muscle bundle in neurogenic detrusor overactivity. BJU Int 2003; 91: 702–710.
Ward SM, Morris G, Reese L, Wang XY, Sanders KM . Interstitial cells of Cajal mediate enteric inhibitory neurotransmission in the lower esophageal and pyloric sphincters. Gastroenterology 1998; 115: 314–329.
Hirst GD, Dickens EJ, Edwards FR . Pacemaker shift in the gastric antrum of guinea-pigs produced by excitatory vagal stimulation involves intramuscular interstitial cells. J Physiol 2002; 541: 917–928.
Smet PJ, Jonavicius J, Marshall VR, de Vente J . Distribution of nitric oxide synthase-immunoreactive nerves and identification of the cellular targets of nitric oxide in guinea-pig and human urinary bladder by cGMP immunohistochemistry. Neuroscience 1996; 71: 337–348.
Sui GP, Rothery S, Dupont E, Fry CH, Severs NJ . Gap junctions and connexin expression in human suburothelial interstitial cells. BJU Int 2002; 90: 118–129.
Wiseman OJ, Fowler CJ, Landon DN . The role of the human bladder lamina propria myofibroblast. BJU Int 2003; 91: 89–93.
Inoue R, Brading AF . The properties of the ATP-induced depolarization and current in single cells isolated from the guinea-pig urinary bladder. Br J Pharmacol 1990; 100: 619–625.
Hurt KJ, Musicki B, Palese MA, Crone JK, Becker RE, Moriarity JL et al. Akt-dependent phosphorylation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase mediates penile erection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 4061–4066.
Takahashi R, Nishimura J, Hirano K, Naito S, Kanaide H . Modulation of Ca2+ sensitivity regulates contractility of rabbit corpus cavernosum smooth muscle. J Urol 2003; 169: 2412–2416.
Daniel EE, Cowan W, Daniel VP . Structural bases for neural and myogenic control of human detrusor muscle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 1983; 61: 1247–1273.
Gabella G . Intramural neurons in the urinary bladder of the guinea-pig. Cell Tissue Res 1990; 261: 231–237.
Gabella G . The structural relations between nerve fibres and muscle cells in the urinary bladder of the rat. J Neurocytol 1995; 24: 159–187.
Brading AF, Williams JH . Contractile responses of smooth muscle strips from rat and guinea-pig urinary bladder to transmural stimulation: effects of atropine and α,β-methylene ATP. Br J Pharmacol 1990; 99: 493–498.
Sibley GNA . A comparison of spontaneous and nerve-mediated activity in bladder muscle from man, pig and rabbit. J Physiol (London) 1984; 354: 431–443.
Brading AF, Mostwin JL . Electrical and mechanical responses of guinea-pig bladder muscle to nerve stimulation. Br J Pharmacol 1989; 98: 1083–1090.
Fujii K . Evidence for adenosine triphosphate as an excitatory transmitter in guinea-pig, rabbit and pig urinary bladder. J Physiol 1988; 404: 39–52.
Inoue R, Brading AF . Human, pig and guinea-pig bladder smooth muscle cells generate similar inward currents in response to purinoceptor activation. Br J Pharmacol 1991; 103: 1840–1841.
Bayliss M, Wu C, Newgreen D, Mundy AR, Fry CH . A quantitative study of atropine-resistant contractile responses in human detrusor smooth muscle, from stable, unstable and obstructed bladders. J Urol 1999; 162: 1833–1839.
Levin RM, Ruggieri MR, Wein AJ . Functional effects of purinergic innervation of the rabbit urinary bladder. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1986; 236: 452–457.
Craggs MD, Rushton DN, Stephenson JD . A putative non-cholinergic mechanism in urinary bladders of new but not Old World primates. J Urol 1986; 136: 1348–1350.
Moon A . Influence of nitric oxide signalling pathways on pre-contracted human detrusor smooth muscle in vitro. BJU Int 2002; 89: 942–949.
Bridgewater M, MacNeil HF, Brading AF . Regulation of tone in pig urethral smooth muscle. J Urol 1993; 150: 223–228.
Werkstrom V, Persson K, Ny L, Bridgewater M, Brading AF, Andersson KE . Factors involved in the relaxation of female pig urethra evoked by electrical field stimulation. Br J Pharmacol 1995; 116: 1599–1604.
Waldeck K, Ny L, Persson K, Andersson KE . Mediators and mechanisms of relaxation in rabbit urethral smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol 1998; 123: 617–624.
Hashitani H, Yanai Y, Kohri K, Suzuki H . Heterogeneous CPA sensitivity of spontaneous excitation in smooth muscle of the rabbit urethra. Br J Pharmacol 2006; 148: 340–349.
Sergeant GP, Johnston L, McHale NG, Thornbury KD, Hollywood MA . Activation of the cGMP/PKG pathway inhibits electrical activity in rabbit urethral ICC by reducing the spatial spread of Ca2+ waves. J Physiol 2006; 574: 167–181.
Turner WH, Brading AF . Smooth muscle of the bladder in the normal and the diseased state: pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment. Pharmacol Ther 1997; 75: 77–110.
Mills IW, Greenland JE, McMurray G, McCoy R, Ho KM, Noble JG et al. Studies of the pathophysiology of idiopathic detrusor instability: the physiological properties of the detrusor smooth muscle and its pattern of innervation. J Urol 2000; 163: 646–651.
Drake MJ, Hedlund P, Mills IW, McCoy R, McMurray G, Gardener BP et al. Structural and functional denervation of human detrusor after spinal cord injury. Lab Invest 2000; 80: 1491–1499.
Mostwin JL, Karim OM, van Koeveringe G, Brooks EL . The guinea pig as a model of gradual urethral obstruction. J Urol 1991; 145: 854–858.
Pessina F, McMurray G, Wiggin A, Brading AF . The effect of anoxia and glucose-free solutions on the contractile response of guinea-pig detrusor strips to intrinsic nerve stimulation and the application of excitatory agonists. J Urol 1997; 157: 2375–2380.
Conners W, Whitebeck C, Chicester P, Legget R, Lin AD, Johnson A et al. L-NAME, a nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, diminishes oxidative damage in urinary bladder partial outlet obstruction. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2006; 290: F357–F363.
McVary KT, Rademaker A, Lloyd GL, Gann P . Autonomic nervous system overactivity in men with lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol 2005; 174: 1327–1433.
McVary KT . Erectile dysfunction and lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to BPH. Eur Urol 2005; 47: 838–845.
Heaton JP . Lower urinary tract disease: what are we trying to treat and in whom? Br J Pharmacol 2006; 147(Suppl 2): S2–S13.
Bloch W, Klotz T, Loch C, Schmidt G, Engelmann U, Addicks K . Distribution of nitric oxide synthase implies a regulation of circulation, smooth muscle tone, and secretory function in the human prostate by nitric oxide. Prostate 1997; 33: 1–8.
Luo J, Dunn T, Ewing C, Sauvageot J, Chen Y, Trent J et al. Gene expression signature of benign prostatic hyperplasia revealed by cDNA microarray analysis. Prostate 2002; 51: 189–200.
Crone JK, Burnett AL, Chamness SL, Strandberg JD, Chang TS . Neuronal nitric oxide synthase in the canine prostate: aging, sex steroid, and pathology correlations. J Androl 1998; 19: 358–364.
Sairam K, Kulinskaya E, McNicholas TA, Boustead GB, Hanbury DC . Sildenafil influences lower urinary tract symptoms. BJU Int 2002; 90: 836–839.
McVary KT, Razzaq A, Lee C, Venegas MF, Rademaker A, McKenna KE . Growth of the rat prostate gland is facilitated by the autonomic nervous system. Biol Reprod 1994; 51: 99–107.
Golomb E, Rosenzweig N, Eilam R, Abramovici A . Spontaneous hyperplasia of the ventral lobe of the prostate in aging genetically hypertensive rats. J Androl 2000; 21: 58–64.
Brading A, Pessina F, Esposito L, Symes S . Effects of metabolic stress and ischaemia on the bladder, and the relationship with bladder overactivity. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl 2004; 84–92.
Galvin DJ, Watson RW, O'Neill A, Coffey RN, Taylor C, Gillespie JI et al. Hypoxia inhibits human bladder smooth muscle cell proliferation: a potential mechanism of bladder dysfunction. Neurourol Urodyn 2004; 23: 342–348.
Berger AP, Deibl M, Leonhartsberger N, Bektic J, Horninger W, Fritsche G et al. Vascular damage as a risk factor for benign prostatic hyperplasia and erectile dysfunction. BJU Int 2005; 96: 1073–1078.
Brading AF, Greenland JE, Mills IW, McMurray G, Symes S . Blood supply to the bladder during filling. Scand J Urol Nephrol 1999; 201(Suppl): 25–31.
Greenland JE, Brading AF . Urinary bladder blood flow changes during the micturition cycle in a conscious pig model. J Urol 1996; 156: 1858–1861.
Keast JR, de Groat WC . Segmental distribution and peptide content of primary afferent neurons innervating the urogenital organs and colon of male rats. J Comp Neurol 1992; 319: 615–632.
Morgan C, Nadelhaft I, de Groat WC . The distribution within the spinal cord of visceral primary afferent axons carried by the lumbar colonic nerve of the cat. Brain Res 1986; 398: 11–17.
Dail WG . The pelvic plexus: innervation of pelvic and extrapelvic visceral tissues. Microsc Res Tech 1996; 35: 95–106.
Hanani M, Maudlej N . Intracellular recordings from intramural neurons in the guinea-pig urinary bladder. J Neurophysiol 1995; 74: 2358–2365.
Funakoshi K, Goris RC, Kadota T, Atobe Y, Nakano M, Kishida R . Prenatal development of peptidergic primary afferent projections to mouse lumbosacral autonomic preganglionic cell columns. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 2003; 144: 107–119.
Smet PJ, Edyvane KA, Jonavicius J, Marshall VR . Neuropeptides and neurotransmitter-synthesizing enzymes in intrinsic neurons of the human urinary bladder. J Neurocytol 1996; 25: 112–124.
Drake MJ . Structural, Pharmacological and Clinical Effects of Spinal Cord Injury on the Human Detrusor. Pharmacology. Oxford: Oxford, 2001, p 215.
Ho KMT . Structure and Innervation of the Urethral Sphincter. Pharmacology. Oxford: Oxford, 2000.
Gershon MD . Review article: serotonin receptors and transporters – roles in normal and abnormal gastrointestinal motility. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2004; 20(Supplement): 3–14.
Ferguson DR . Urothelial function. BJU Int 1999; 84: 235–242.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brading, A., Heaton, J. & Hashitani, H. A survey of commonalities relevant to function and dysfunction in pelvic and sexual organs. Int J Impot Res 20, 1–16 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901568
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901568
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Neural and Endocrine Factors Contribute to the Comorbidity of Urinary and Sexual Dysfunctions
Current Sexual Health Reports (2017)
-
The impact of hemorrhoidectomy on sexual function in women: a preliminary study
International Journal of Impotence Research (2009)