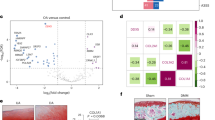
Abstract
The achondroplasia class of chondrodysplasias comprises the most common genetic forms of dwarfism in humans and includes achondroplasia, hypochondroplasia and thanatophoric dysplasia types I and II (TDI and TDII), which are caused by different mutations in a fibroblast growth-factor receptor FGFR3 (ref. 1). The molecular mechanism and the mediators of these FGFR3-related growth abnormalities are not known. Here we show that mutant TDII FGFR3 has a constitutive tyrosine kinase activity which can specifically activate the transcription factor Statl (for signal transducer and activator of transcription)2,3. Furthermore, expression of TDII FGFR3 induced nuclear translocation of Statl, expression of the cell-cycle inhibitor p21WAF1/CIP1 , and growth arrest of the cell. Thus, TDII FGFR3 may use Statl as a mediator of growth retardation in bone development. Consistent with this, Statl activation and increased p21WAF1/CIP1 expression was found in the cartilage cells from the TDII fetus, but not in those from the normal fetus. Thus, abnormal STAT activation and p21WAF1/CIP1 expression by the TDII mutant receptor may be responsible for this FGFR3-related bone disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Muenke, M. & Schell, U. Fibroblast-growth-factor receptor mutaitons in human skeletal disorders. Trends Genet. 11, 308–313 (1995).
Darnell, J. E. Jr, Kerr, I. M. & Stark, G. R. Jak–STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 264, 1415–1421 (1994).
Ihle, J. N. & Kerr, I. M. Jaks and Stats in signaling by the cytokine receptor superfamily. Trends Genet. 11, 69–74 (1995).
Mason, I. J. The ins and outs of fibroblast growth factors. Cell 78, 547–552 (1994).
Tavormina, P. L. et al. Thanatophoric dysplasia (types I and II) caused by distinct mutations in fibroblast growth factor receptor 3. Nature Genet. 9, 321–328 (1995).
Sillence, D. O., Horton, W. A. & Rimoin, D. L. Morphologic studies in the skeletal dysplasia. Am. J. Pathol. 96, 813–859 (1979).
Deng, C., Wynshaw-Boris, A., Zhou, F., Kuo, A. & Leder, P. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 is a negative regulator of bone growth. Cell 84, 911–921 (1996).
Colvin, J. S., Bohne, B. A., Harding, G. W., McEwen, D. G. & Ornitz, D. M. Skeletal overgrowth and deafness in mice lacking fibroblast growth factor receptor 3. Nature Genet. 12, 390–397 (1996).
Webster, K. M., D'avis, P. Y., Robertson, S. C. & Donoghue, D. J. Profound ligand-independent kinase activation of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 by the activation loop mutation responsible for a lethal skeletal dysplasia, thanatophoric dysplasia type II. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16, 4081–4087 (1996).
Naski, M. C., Wang, Q., Xu, J. & Ornitz, D. M. Graded activation of FGFR3 by mutations causing achondroplasia and thanatophoric dysplasia. Nature Genet. 13, 233–237 (1996).
Fu, X.-Y. A transcription factor with SH2 and SH3 domains is directly activated by an interferon α-induced cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinase(s). Cell 70, 323–335 (1992).
Shuai, K., Schindler, C., Prezioso, V. R. & Darnell, J. E. Jr Activation of transcription by IFN-γ tyrosine phosphorylation of a 91 kDa DNA binding protein. Science 259, 1808–1812 (1992).
Velazquez, L., Fellous, M., Stark, G. R. & Pellegrini, S. A protein tyrosine kinase in the interferon α/β signaling pathway. Cell 70, 313–322 (1992).
Sadowski, H. B. & Gilman, M. Z. Cell-free activation of a DNA binding protein by epidermal growth factor. Nature 362, 79–83 (1993).
Larner, A. C. et al. Tyrosine phosphorylation of DNA binding proteins by multiple cytokines. Science 261, 1730–1733 (1993).
Fu, X.-Y. & Zhang, J.-J. Transcription factor p91 interacts with the epidermal growth factor receptor and mediates activation of the c-fos gene promoter. Cell 74, 1135–1145 (1993).
Ruff-Jamison, S., Chen, K. & Cohen, S. Epidermal growth factor induces the tyrosine phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of Stat 5 in mouse liver. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 4215–4218 (1995).
Chin, Y. E. et al. Cell growth arrest and induction of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21WAFI/CIPI mediated by STAT1 Science 272, 719–722 (1996).
Ornitz, D. M. & Leder, P. Ligand specificity and heparin dependence of fibroblast growth factor receptors 1 and 3. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 16305–16311 (1992).
Schindler, C., Shuai, K., Prezioso, V. R. & Darnell, J. E. Jr Interferon-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of a latent cytoplasmic transcription factor. Science 257, 809–813 (1992).
Ko, L. O. & Prives, C. p53: Puzzle and paradigm. Genes Dev. 10, 1054–1072 (1996).
Schlessinger, J. & Ullrich, A. Growth factor signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Neuron 9, 383–391 (1992).
van der Geer, P., Hunter, T. & Lindberg, R. Receptor protein tyrosine kinases and their signal transduction pathways. Annu. Rev. Cell. Biol. 10, 251–337 (1994).
Peters, K., Ornitz, D., Werner, S. & Williams, L. Unique expression pattern of the FGF receptor 3 gene during mouse organogenesis. Dev. Biol. 155, 423–430 (1993).
Marshall, C. J. Specificity of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling: transient versus sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Cell 80, 179–185 (1995).
Meraz, M. A. et al. Targeted disruption of the Stat1 gene in mice reveals unexpected physiologic specificity in the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Cell 84, 431–442 (1996).
Durbin, J. E., Hackenmiller, R., Simon, M. C. & Levy, D. E. Targeted disruption of the mouse Stat1 gene results in compromised innate immunity to viral disease. Cell 84, 443–450 (1996).
Mizushima, S. & Nagata, S. pEF-BOS, a powerful mammalian expression vector. Nucleic Acids Res. 18, 5332 (1990).
Webster, M. K. & Donoghue, D. J. Constitutive activation of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 by the transmembrane domain point mutation found in achondroplasia. EMBO J. 15, 520–527 (1996).
Yamamoto, H., Crow, M., Cheng, L., Lakatta, E. & Kinsella, J. PDGF receptor-to-nucleus signaling of p91 (STAT1 alpha) transcription factor in rat smooth muscle cells. Exp. Cell Res. 222, 125–130 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, WC., Kitagawa, M., Xue, N. et al. Activation of Statl by mutant fibroblast growth-factor receptor in thanatophoric dysplasia type II dwarfism. Nature 386, 288–292 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/386288a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/386288a0
This article is cited by
-
Anti-fibrotic effects of pharmacologic FGF-2: a review of recent literature
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2022)
-
The Indispensable Role of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 1 in Skeletal Development
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Transcriptional profiling of PRKG2-null growth plate identifies putative down-stream targets of PRKG2
BMC Research Notes (2015)
-
Role of FGF/FGFR signaling in skeletal development and homeostasis: learning from mouse models
Bone Research (2014)
-
Functional roles of fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs) signaling in human cancers
Apoptosis (2013)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.