Abstract
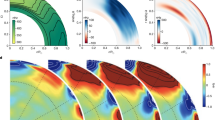
MAGNETIC fields pervade spiral galaxies1—at least all those searched so far; these fields have a substantial energy density, and hence could play an important role in galaxy evolution. Dynamo theory has been used for many years to explain the presence and overall structure of galactic magnetic fields, through the amplification of a weak seed field2,3. Here we report the observation of two 'magnetic spiral arms' in the nearby galaxy NGC6946, lying between the optical spiral arms. This is surprising because dynamo action is thought to be related to star formation activity4, which is concentrated within or in the leading edges of the optical spiral arms. The magnetic spiral arms are about 500–1,000 parsecs wide and more than 12 kiloparsecs long, and have greater symmetry than the optical arms. This organized structure probably reflects the signature of some global mechanism relating to magnetic field generation, but no current theory—in particular dynamo theory in its present form—is able to explain this phenomenon.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beck, R. in The Cosmic Dynamo (eds Krause, F., Rädler, K. H. & Rüdiger, G.) 283–297 (IAU Symp. No. 157, Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, 1993).
Ruzmaikin, A., Sokoloff, D. & Shukurov, A. Nature 336, 341–347 (1988).
Elstner, D., Meinel, R. & Beck, R. Astr. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 94, 587–600 (1992).
Ko, C. M. & Parker, E. N. Astrophys J. 341, 828–831 (1989).
Klein, U., Beck, R., Buczilowski, U. R. & Wielebinski, R. Astr. Astrophys. 108, 176–187 (1982).
Harnett, J. I., Beck, R. & Buczilowski, U. Astr. Astrophys. 208, 32–38 (1989).
Ehle, M. & Beck, R. Astr. Astrophys. 273, 45–64 (1993).
Beck, R. Astr. Astrophys. 251, 15–26 (1991).
Schlegel, E. M. Astrophys. J. 434, 523–535 (1994).
Cornwell, T. J., Briggs, D. S. & Holdaway, M. A. User's Guide to SDE (NRAO, Socorro, 1995).
Holdaway, M. A. Mosaicing with Very High Dynamic Range (Millimeter Array Memo No. 73, NRAO, Socorro, 1992).
Krause, M. in The Cosmic Dynamo (eds Krause, F., Rädler, K. H. & Rüdiger, G.) 305–310 (IAU Symp. No. 157, Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, 1993).
Krause, M., Hummel, E. & Beck, R. Astr. Astrophys. 217, 4–16 (1989).
Sukumar, S. & Allen, R. J. Nature 340, 537–539 (1989).
Rosso, F. & Pelletier, G. Astr. Astrophys. 270, 416–425 (1993).
Kleeorin, N. I. & Rogachevskii, I. V. in Plasma Astrophysics 21–23 (ESA SP-311, European Space Agency, Paris, 1990).
Lesch, H. & Reich, W. Astr. Astrophys. 264, 493–499 (1992).
Lesch, H. & Pohl, M. Astr. Astrophys. 254, 29–38 (1992).
Moss, D., Brandenburg, A., Donner, K. J. & Thomasson, M. Astrophys. J. 409, 179–189 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beck, R., Hoernes, P. Magnetic spiral arms in the galaxy NGC6946. Nature 379, 47–49 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/379047a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/379047a0
This article is cited by
-
Structure of the magnetic field near the galactic plane
Astrophysics (2011)
-
Distribution of free electrons in the galactic plane
Astrophysics (2006)
-
A large-scale, interstellar Faraday-rotation feature of unknown origin
Nature (1998)
-
Magnetic fields in galaxies and beyond
Nature (1997)
-
Origin of the magnetic spiral arms in the galaxy NGC6946
Nature (1996)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.