Abstract
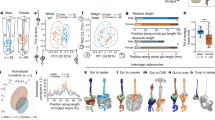
RECONSTRUCTION of a severed mammalian spinal cord with restoration of function has so far not been achieved1–12, although structural and functional restitution after spinal transection has been successful in some lower vertebrates12–14. In quail–chick and chick–chick chimaeras, spinal cord segments were found to be functional after replacement by isotopic and isochronic grafting of the neural tube15,16. Here we achieve such a replacement in neonatal rats under less restricted topological and temporal conditions than were necessary for the avian chimaeras. The replaced segments united with the host spinal cord and promoted robust growth and regrowth of axons across the graft, enabling neural connections to be reconstructed that were hardly distinguishable from normal. The animals with replaced segments could walk, run and climb with almost normal hind–forelimb coordination. This functional restoration in these animals appeared to be permanent, raising the possibility of therapeutic application in humans.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramón y Cajal, S. Degeneration and Regeneration of the Nervous System (Hafner, New York, 1959).
Björklund, A. Trends Neurosci. 14, 319–322 (1991).
Richardson, P. M., McGuinness, U. M. & Aguayo, A. J. Nature 284, 264–265 (1980).
Kao, C. C., Chang, L. W. & Bloodworth, J. M. B. Jr Expl Neurol. 54, 591–615 (1977).
Schnell, L. & Schwab, M. E. Nature 343, 269–272 (1990).
Reier, P. J., Bregman, B. S. & Wujek, J. R. J. comp. Neurol. 247, 275–296 (1986).
Bregman, B. S., Kunkel-Bagden, E., McAtee, M. & O'Neill, A. J. comp. Neurol. 282, 355–370 (1989).
Bregman, B. S. & Bernstein-Goral, H. Expl Neurol. 112, 49–63 (1991).
Sieradzan, K. & Vrbová, G. Neuroscience 31, 115–130 (1989).
Kunkel-Bagden, E. & Bregman, B. S. Expl Brain Res. 81, 25–34 (1990).
Das, G. D. in Neural Transplantation and Regeneration (eds Das, G. D. & Wallace, R. B.) 1–61 (Springer, New York, 1986).
Guth, L., Reier, P. J., Barrett, C. P. & Donati, E. J. Trends Neurosci. 6, 20–24 (1983).
Selzer, M. E. J. Physiol., Lond. 277, 395–408 (1978).
Singer, M., Nordlander, R. H. & Egar, M. J. comp. Neurol. 185, 1–22 (1979).
Kinutani, M. & Le Douarin, N. M. Devl Biol. 111, 243–255 (1985).
Le Douarin, N. M. Trends Neurosci. 16, 64–72 (1993).
Grillner, S. Physiol. Rev. 55, 247–304 (1975).
Harris, W. A. Nature 339, 218–221 (1989).
Tessier-Lavigne, M., Placzek, M., Lumsden, A. G. S., Dodd, J. & Jessell, T. M. Nature 336, 775–778 (1988).
Bolz, J., Götz, M., Hübener, M. & Novak, N. Trends Neurosci. 16, 310–316 (1993).
Kessel, M. & Gruss, P. Science 249, 374–379 (1990).
Itasaki, N. & Nakamura, H. Neuron 8, 787–798 (1992).
Kalil, K. & Reh, T. Science 205, 1158–1161 (1979).
Kawaguchi, S., Miyata, H. & Kato, N. J. comp. Neurol. 245, 258–273 (1986).
Leong, S. K., Shieh, J. Y. & Wong, W. C. J. comp. Neurol. 228, 18–23 (1984).
Schreyer, D. J. & Jones, E. G. Neuroscience 7, 1837–1853 (1982).
Bernstein, D. R. & Stelzner, D. J. J. comp. Neurol. 221, 382–400 (1983).
Matsushita, M. & Hosoya, Y. Brain Res. 173, 185–200 (1979).
Giesler, G. J. Jr, Spiel, H. R. & Willis, W. D. J. comp. Neurol. 195, 243–252 (1981).
Amassian, V. E., Waller, H. J. & Macy, J. Jr Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 112, 5–32 (1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iwashita, Y., Kawaguchi, S. & Murata, M. Restoration of function by replacement of spinal cord segments in the rat. Nature 367, 167–170 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/367167a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/367167a0
This article is cited by
-
New insights into glial scar formation after spinal cord injury
Cell and Tissue Research (2022)
-
Transplantation of adult spinal cord grafts into spinal cord transected rats improves their locomotor function
Science China Life Sciences (2019)
-
Transplantation of adult spinal cord tissue: Transection spinal cord repair and potential clinical translation
Science China Life Sciences (2019)
-
Characterization of neuron-like cells derived from canine bone marrow stromal cells
Veterinary Research Communications (2013)
-
Cellular and paracellular transplants for spinal cord injury: a review of the literature
Child's Nervous System (2011)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.