Abstract
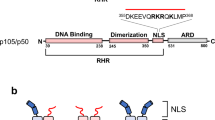
THE transcription factor NF-κB is a heterodimer consisting of two proteins encoded by different members of the rel gene family (p50 and p65)1–7. The p50 subunit is unusual among DNA-binding proteins in that its functional form is encoded in an open reading frame of relative molecular mass 105,000 (p105; ref. 4). The N-terminal region of this open reading frame encodes p50, whereas the remaining C terminus contains ankyrin repeats. Although p50 binds to DNA, full-length p105 translated in vitro does not4,5. The mechanism by which p50 is generated in vivo, and the fate of the C-terminal region of p105 have not been established. Here we show that functional p50 is produced by ATP-dependent pro-teolysis of p105. Moreover, we find that the C-terminal half of p105 is not required for processing in vivo, and is rapidly degraded on processing. We propose that the C-terminal region of p105 is involved in the cytoplasmic assembly of the complex between the p50/p65 heterodimer and the inhibitor IkB.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kawakami, K., Scheidereit, C. & Roeder, R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 4700–4704 (1988).
Baeuerle, P. A. & Baltimore, D. Genes Dev. 3, 1689–1699 (1989).
Lenardo, M. J. & Baltimore, D. Cell 58, 227–229 (1989).
Kieran, M. et al. Cell 62, 1007–1018 (1990).
Ghosh, S. et al. Cell 62, 1019–1029 (1990).
Nolan, G. et al. Cell 64, 961–969 (1991).
Ruben, S. M. et al. Science 251, 1490–1492 (1991).
Riviere, Y. et al. Nature 350, 625–626 (1991).
Munro, S. & Pelham, H. R. B. Cell 48, 899–907 (1987).
Field, J. et al. Molec. cell. Biol. 8, 2159–2165 (1988).
Lenardo, M. J., Fan, C.-M., Maniatis, T. & Baltimore, D. Cell 57, 287–294 (1989).
Fan, C.-M. & Maniatis, T. EMBO J. 8, 101–110 (1989).
Hershko, A. J. biol. Chem. 263, 15237–15240 (1988).
Rechsteiner, M. Cell 66, 615–618 (1991).
Haskill, S. et al. Cell 65, 1281–1289 (1991).
Ballard, D. W. et al. Cell 63, 803–814 (1990).
Inoue, J. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 3715–3719 (1991).
Tanaka, M. & Herr, W. Cell 60, 375–386 (1990).
Harlow, E. & Lane, D. Antibodies, A Laboratory Manual (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, 1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, CM., Maniatis, T. Generation of p50 subunit of NF-kB by processing of p105 through an ATP-dependent pathway. Nature 354, 395–398 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1038/354395a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/354395a0
This article is cited by
-
Systematic identification of 20S proteasome substrates
Molecular Systems Biology (2024)
-
Long non-coding RNA NKILA regulates expression of HSP90α, NF-κB and β-catenin proteins in the MCF-7 breast cancer cell line
Molecular Biology Reports (2021)
-
Role of the ubiquitin ligase KPC1 in NF-κB activation and tumor suppression
Journal of Analytical Science and Technology (2016)
-
One more wheel for a processing machine
Cell Death & Differentiation (2015)
-
Mechanical stretch induces angiotensinogen expression through PARP1 activation in kidney proximal tubular cells
In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Animal (2015)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.