Abstract
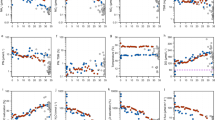
IT has recently been suggested that the deposition of mineral aerosol particles, primarily transported from Africa during sporadic but intense events1,2, may have a profound influence on the geochemistry and the sedimentology of the Mediterranean Sea1-3. Several studies in the open ocean4-7 have shown that such particles, with radii generally less than 5 μm, are removed from the surface waters within a few weeks, together with large organic particles produced by biological packaging7. Here we report data from time-series measurements of both atmospheric inputs and water-column participate fluxes at 200m depth obtained from sediment traps, which show that such a biological control also prevails in northwestern Mediterranean waters. On short time-scales, concentrations and fluxes in the upper water column can increase significantly following dust transport and deposition events, with a response time of the order of one week. Such non-steady-state behaviour must be taken into account when assessing the impact of pulsed atmospheric inputs on particulate trace element concentrations and fluxes in the water column.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergametti, G. et al. in Paleoclimatology and Paleometeorology: Modern and Past Patterns of Global Atmospheric Transport (eds Leinen, M. & Sarntheim, M.) (Reidel, Dordrecht, in the press).
Loÿe-Pilot, M. D., Martin, J. M. & Morelli, J. Nature 321, 427–428 (1986).
Buat-Ménard, P. in The Role of Air-Sea Exchange in Geochemical Cycling (ed. Buat-Ménard, P.) 477–496 (Reidel, Dordrecht, 1986).
Honjo, S. Science 218, 883–884 (1982).
Wallace, G. T., Mahoney, O. M., Dulmage, R., Storti, F. & Dudek, N., Nature 293, 729–731 (1981).
Deuser, W. G., Brewer, P. G., Jickells, T. D. & Commeau, R. F. Science 219, 388–391 (1983).
Fowler, S. W. & Knauer, G. A. Progr. Oceanogr. 16, 147–194 (1986).
Fowler, S. W. et al. Nature 329, 56–58 (1987).
Monaco, A. et al. in Particle Flux in the Oceans (ed. Degens, E. T., Izdar, E. & Honjo S.) 109–125 (SCOPE/UNEP, 1987).
Delmas, R., Dulac, F., Lambert, C. E. & Revel, G. J. radioanalyst. Nucl. Chem. 111, 371–383 (1987).
Lambert, C. E., Jehanno, C., Silverberg, J. S., Brun-Cottan, J. C. & Chesselet, R. J. mar. Res. 39, 77–98 (1981).
Eppley, R. W. & Peterson, B. J. Nature 282, 677–680 (1979).
Hargrave, B. T. Ecol. Model. 30, 229–246 (1986).
Jacques, G. Oceanol. Acta. Spec. Iss. No. 9, 143–148 (1988).
Taylor, S. R. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 28, 1273–1285 (1964).
Copin-Montégut, C., Oceanol. Acta Spec. Iss. No. 9, 95–102 (1988).
Buat-Ménard, P. et al. in Radionuclides, a Tool for Oceanography (ed. Guary, J. C. Guegueniat, P. & Pentreath, R. J.) 121–130 (Elsevier, London, 1988).
Uematsu, M., Duce, R. A., Nakaya, S. & Tsunogai, S. J. geophys. Res. 90, 1167–1172 (1985).
Chester, R. in The Role of Air-Sea Exchange in Geochemical Cycling (ed. Buat-Menard, P.) 443–476 (Reidel, Dordrecht, 1986).
Andersen, V. & Nival, P. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 44, 37–50 (1988).
Ruiz-Pino, D., Lambert, C. E., Jeandel, C. & Buat-Ménard, P. Chem. Geol. 70, 198 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buat-Ménard, P., Davies, J., Remoudaki, E. et al. Non-steady-state biological removal of atmospheric particles from Mediterranean surface waters. Nature 340, 131–134 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1038/340131a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/340131a0
This article is cited by
-
Low sedimentary accumulation of lead caused by weak downward export of organic matter in Hudson Bay, northern Canada
Biogeochemistry (2017)
-
A mesocosm experiment coupled with optical measurements to assess the fate and sinking of atmospheric particles in clear oligotrophic waters
Geo-Marine Letters (2012)
-
Seasonal variability of deep ocean particle fluxes and particle composition in the north open sea of Prydz Bay
Frontiers of Earth Science in China (2008)
-
Aluminum in the macrotidal Yalujiang estuary: Partitioning of Al along the estuarine gradients and flux
Estuaries (2002)
-
Saharan dust and the atmospheric inputs of elements and alkalinity to mediterranean ecosystems
Water, Air, and Soil Pollution (1993)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.