Abstract
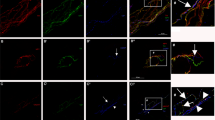
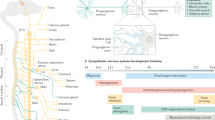
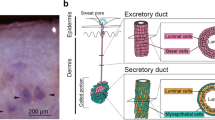
Mammalian sympathetic neurons in vivo may express either a noradrenergic or cholinergic phenotype. In view of the opposing effect of noradrenaline and acetv Icholine on most autonomic target organs, the target-appropriate expression of neurotransmitter is critical. We have examined the maturation of the sympathetic innervation of rat sweat glands to define the developmental mechanisms regulating neurotransmitter choice in vivo1–5. Eccrine sweat glands and their sympathetic innervation develop together post-natally in the rat. Early postnatal innervation expresses only noradrenergic properties, but as the glands and their innervation mature, noradrenergic properties decrease dramatically and cholinergic features appear in the same population of neurons. To investigate the role of the sweat gland in this change we have used a transplantation paradigm which allows sweat glands to be innervated by sympathetic neurons that would normally innervate noradrenergic target organs and remain noradrenergic throughout life. We observe that the sympathetic neurons that innervate the novel cholinergic target alter their neurotransmitter properties and develop a cholinergic phenotype. These results indicate that target organs are able to induce appropriate neurotransmitter traits in the neurons that innervate them.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Landis, S. C. & Keefe, D. Devl Biol. 98, 349–372 (1983).
Yodlowski, M. L., Fredieu, J. R. & Landis, S. C. J. Neurosci. 4, 1535–1548 (1984).
Leblanc, G. & Landis, S. J. Neurosci. 6, 260–265 (1986).
Landis, S. C., Siegel, R. E. & Schwab, M. Devl Biol. 126, 129–140 (1988).
Stevens, L. M. & Landis, S. C. Devl Biol. 123, 179–190 (1987).
Gabella, G. in Structure of the Autonomic Nervous System 150–159 (Chapman and Hall, London, 1976).
Angeletti, P. U. & Levi-Montalcini, R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 65, 114–121 (1970).
Finch, L., Haeusler, G. & Thoenen, H. Br. J. Pharmac. 47, 249–260 (1973).
Patterson, P. H. & Chun, L. L. Y. Devl Biol. 56, 263–280 (1977).
Johnson, M. I., Ross, C. D., Meyers, M., Spitznagel, E. L. & Bunge, R. P. J. cell. Biol. 84, 680–691 (1980).
Potter, D. D., Landis S. C., Matsumoto, S. G. & Furshpan, E. J. J. Neurosci. 6, 1080–1098 (1986).
Fukada, K. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 8795–8799 (1985).
Kessler, J. A., Conn, G. & Hatcher, V. B. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 3528–3532 (1986).
Raynaud, B., Clarous, D., Vidal, S., Ferrand, C. & Weber, M. J. Devl Biol. 121, 548–558 (1987).
Steinmuller, D. in Transplantation of Tissues and Cells (eds Billingham, R. E. & Silvers, W. K.) 27–29 (Wistar, Philadelphia, 1961).
Steinmuller, D. Meth. Enzym. 108, 20–28 (1984).
De la Torre, J. C. J. Neurosci. Meth. 3, 1–5 (1980).
Fonnum, F. J. Neurochem. 24, 407–409 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schotzinger, R., Landis, S. Cholinergic phenotype developed by noradrenergic sympathetic neurons after innervation of a novel cholinergic target in vivo. Nature 335, 637–639 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1038/335637a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/335637a0
This article is cited by
-
A century of exercise physiology: concepts that ignited the study of human thermoregulation. Part 4: evolution, thermal adaptation and unsupported theories of thermoregulation
European Journal of Applied Physiology (2024)
-
A century of exercise physiology: concepts that ignited the study of human thermoregulation. Part 3: Heat and cold tolerance during exercise
European Journal of Applied Physiology (2024)
-
A century of exercise physiology: concepts that ignited the study of human thermoregulation. Part 2: physiological measurements
European Journal of Applied Physiology (2023)
-
The diversity of neuronal phenotypes in rodent and human autonomic ganglia
Cell and Tissue Research (2020)
-
Transcytosis of TrkA leads to diversification of dendritic signaling endosomes
Scientific Reports (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.