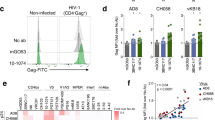
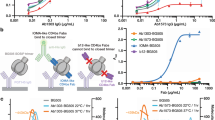
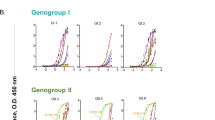
Abstract
CD4, a cell-surface glycoprotein expressed on a subset of T-cells and macrophages, serves as the receptor for the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) (reviewed in ref. 1), binding to the HIV envelope glycoprotein, gp120 with high affinity2,3. Attempts to block infection in vivo by raising antibodies against gp120 have failed, probably because these antibodies have insufficient neutralizing activity4. In addition, because of the extensive polymorphism of gp120 in different isolates of HIV, antibodies raised against one HIV isolate are only weakly effective against others5. Because interaction with CD4 is essential for infectivity by all isolates of HIV, an agent that could mimic CD4 in its ability to bind to gp120, such as a peptide or monoclonal antibody, might block infection by a wide spectrum of isolates. To aid the identification of such a ligand we have defined regions of CD4 that are required for binding to gp120. Although human CD4 is similar to mouse CD4 in amino-acid sequence (55 % identity, ref. 6) and structure7,8, we have found that the murine protein fails to bind detectably to gp120 and have exploited this finding to study binding of gp120 to mouse-human chimaeric CD4 molecules. These studies show that amino-acid residues within the amino-terminal immunoglobulin-like domain of human CD4 are involved in binding to gp120 as well as to many anti-CD4 monoclonal antibodies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sattentau Q. J. & Weiss, R. A. Cell 52, 631–633 (1988).
McDougal, J. S. et al. Science 231, 382–385 (1986).
Lasky, L. A. et al. Cell 50, 975–985 (1987).
Berman, P. W. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (in the press).
Weiss, R. A. et al. Nature 324, 572–575 (1986).
Littman, D. R. & Gettner, S. N. Nature 325, 453–455 (1987).
Littman, D. R. A. Rev. Immun. 5, 561–584 (1987).
Classon, B. J., Tsagaratos, J., McKenzie, I. F. C. & Walker, I. D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 4499–4503 (1986).
Traunecker, A., Luke, W. & Karjalainen, K. Nature 331, 84–86 (1988).
Bedinger, P. et al. Nature (in the press).
Gething, M. J., McCammon, K. & Sambrook, J. Cell 46, 939–950 (1986).
Horejsi, V. & Angelisova, P. in Leukocyte Typing III (ed. McMichael, A. J.) 234 (Oxford University Press, 1987).
McClure, M. O. et al. Nature 330, 487–489 (1987).
Sattentau, Q. J., Dalgleish, A. G., Weiss, R. A. & Beverly, P. C. Science 234, 1120–1123 (1986).
McDougal, S. J. et al. J. Immun. 137, 2937–2944 (1986).
Chanh, T. C., Dreesman, G. & Kennedy, R. C. Proc. natn. Acad. SCi. U.S.A. 84, 3891–3895 (1987).
Maddon, P. J. et al. Cell 42, 93–104 (1985).
Kunkel, T. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 488–492 (1985).
Stuve, L. L. et al. J. Virol. 61, 326–335 (1987).
Lasky, L. A. et al. Science 233, 209–233 (1986).
Graham, F. L. & van der Eb, A. J. Virology 52, 456–467 (1973).
Mitchell, P. J. et al. Molec. cell. Biol. 6, 425–440 (1986).
Nunberg, J. H., Kaufman, R. J., Schimke, R. T. Urlaub, G. & Chasin, L. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75, 5553–5556 (1978).
Thomas, E. K. et al. AIDS 2, 25–29 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Landau, N., Warton, M. & Littman, D. The envelope glycoprotein of the human immunodeficiency virus binds to the immunoglobulin-like domain of CD4. Nature 334, 159–162 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1038/334159a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/334159a0
This article is cited by
-
Human cyclin T1 expression ameliorates a T-cell-specific transcriptional limitation for HIV in transgenic rats, but is not sufficient for a spreading infection of prototypic R5 HIV-1 strains ex vivo
Retrovirology (2009)
-
Mouse T-cells restrict replication of human immunodeficiency virus at the level of integration
Retrovirology (2008)
-
Cellular receptor for pixuna virus in chicken embryonic fibroblasts
Medical Microbiology and Immunology (2006)
-
Structural mapping of CD134 residues critical for interaction with feline immunodeficiency virus
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2005)
-
Chemokines and HIV–1 second receptors
Nature Medicine (1996)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.