Abstract
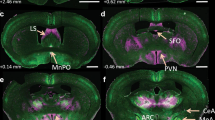
Atrial natriuretic peptides, produced in the mammalian cardiac atrium, are released into the general circulation and may be actively involved in the control of blood pressure and in fluid homeostasis as antagonists of the peripheral angiotensin system1–4. Certain cardiovascular effects of atrial natriuretic peptides may be centrally mediated, as binding sites for atrial natriuretic factor (8–33) (ANF) have been localized to the subfornical organ5. This circumventricular structure lacks a blood–brain barrier and is therefore accessible to circulating peptides. It contains large numbers of angiotensin II (AII) binding sites, and has been suggested as the main central site of action for circulating AII in the regulation of blood pressure and fluid metabolism6,7. Here we have studied binding sites for rat atrial natriuretic peptide(6–33) (rANP) and AII in the brains of spontaneously (genetic) hypertensive rats (SHR) and their normotensive controls, Wistar Kyoto (WKY) rats8, by quantitative autoradiography5,9–11. Binding sites for both peptides were highly localized in the subfornical organ. The number of rANP binding sites was decreased in the subfornical organ of both young (4 weeks old) and adult (14 weeks old) SHR compared with age-matched normotensive controls. Conversely, the number of AII binding sites was higher in both young and adult SHR compared with WKY rats. Our results suggest a central role for rANP and AII in genetic hypertension; they may act as mutual antagonists in brain areas involved in control of blood pressure and fluid regulation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cantin, M. & Genest, J. Endocr. Rev. 6, 107–127 (1985).
de Bold, A. J., Borenstein, H. B., Veress, A. T. & Sonnenberg, H. Life Sci. 28, 89–94 (1981).
Kleinert, H. D. et al. Hypertension 6 (Suppl. I), I-143–I-147 (1984).
Campbell, W. B., Currie, M. G. & Needleman, P. Circulation Res. 57, 113–118 (1985).
Quirion, R. et al. Peptides 5, 1167–1172 (1984).
Simpson, J. B. Neuroendocrinology 32, 248–256 (1981).
Mangiapane, M. L. & Simpson, J. B. Am. J. Physiol. 239, R382–R389 (1980).
Okamoto, K. & Aoki, K. Jap. Circulation J. 27, 282–293 (1963).
Mendelsohn, F. A. O., Quirion, R., Saavedra, J. M., Aguilera, G. & Catt, K. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 1575–1579 (1984).
Israel, A., Correa, F. M. A., Niwa, M. & Saavedra, J. M. Brain Res. 322, 341–345 (1984).
Israel, A., Plunkett, L. M. & Saavedra, J. M. Cell molec. Neurobiol. 5, 211–222 (1985).
Flynn, T. G., de Bold, M. L. & de Bold, A. J. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 117, 859–865 (1983).
Garcia, R. et al. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med. 178, 155–159 (1985).
Garcia, R. et al. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med. 179, 396–401 (1985).
Folkow, B., Hallback, M., Lungren, Y. & Weiss, L. Acta physiol. Scand. 79, 373–378 (1970).
Saavedra, J. M., Grobecker, H. & Axelrod, J. Circulation Res. 42, 529–534 (1978).
Saavedra, J. M., Grobecker, H. & Axelrod, J. Science 191, 483–484 (1976).
Plunkett, L. M. & Saavedra, J. M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 7721–7724 (1985).
Mangiapane, M. L., Thrasher, T. N., Keil, L. C., Simpson, J. B. & Ganong, W. F. Brain Res. Bull. 13, 43–47 (1984).
Hartle, D. K. & Brody, M. J. Circulation Res. 54, 355–366 (1984).
Jacobowitz, D. M., Skofitsch, G., Keiser, H. R., Eskay, R. L. & Zamir, N. Neuroendocrinology 40, 92–94 (1985).
Lind, R. W., Swanson, L. W. & Ganten, D. Neuroendocrinology 40, 2–24 (1985).
Saavedra, J. M. & Chevillard, C. Neurosci. Lett. 29, 123–127 (1982).
Correa, F. M. A., Plunkett, L. M., Saavedra, J. M. & Hichens, M. Brain Res. 347, 192–195 (1985).
Chevillard, C. & Saavedra, J. M. Regul. Peptides 5, 333–341 (1983).
Shioni, K. & Sokabe, H., Am. J. Physiol. 231, 1295–1299 (1976).
Polsky-Cynkin, R., Reichlin, S. & Fauburg, B. L. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med. 164, 242–247 (1980).
Niwa, M., Israel, A. & Saavedra, J. M., Eur. J. Pharmac. 110, 133–136 (1985).
Stamler, J. F., Brody, M. J. & Phillips, M. I. Brain Res. 186, 499–503 (1980).
Weyhenmeyer, J. A. & Phillips, M. I. Hypertension 4, 514–523 (1982).
Phillips, M. I. Neuroendocrinology 25, 354–377 (1978).
Sonnenberg, H. & Samson, W. K. Neuroendocrinology 40, 277–279 (1985).
Crofton, J. T., Share, L., Shade, R. E., Allen, C. & Tarnowski, D. Am. J. Physiol. 235, H361–H366 (1978).
Samson, W. K. Neuroendocrinology 40, 277–279 (1985).
Seymour, A. A., Marsh, E. A., Mazack, E. K., Stabilito, I. I. & Baine, E. H. Hypertension 7 (Suppl. I), I-35–I-42 (1985).
Milojevic, S., Chong, C. K. & Veress, A. T. Hypertension 5, 672–672 (1983).
Ganten, D., Hermann, K., Bayer, C., Unger, T. & Lang, R. E. Science 221, 869–871 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saavedra, J., Correa, F., Plunkett, L. et al. Binding of angiotensin and atrial natriuretic peptide in brain of hypertensive rats. Nature 320, 758–760 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/320758a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/320758a0
This article is cited by
-
Decreased expression of natriuretic peptide a receptors and decreased cGMP production in the choroid plexus of spontaneously hypertensive rats
Molecular and Chemical Neuropathology (1998)
-
Is blood pressure in later life affected by events in infancy?
Pediatric Nephrology (1995)
-
Quantitative receptor autoradiographic analysis for angiotensin II receptors in bovine retinal microvessels: quantitation with radioluminography
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (1993)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.