Abstract
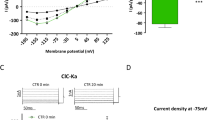
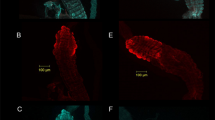
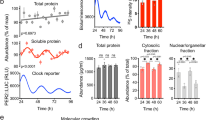
The contents of endocytic vesicles and other intracellular organ-elles (such as Golgi and microsomes) are acidified by an elec-trogenic proton-translocating ATPase that is remarkably similar to that found in urinary epithelia1–10. We recently found that the number of H+ ATPases in the apical plasma membrane of these epithelia is regulated by exocytotic insertion of endocytic vesicles whose membranes contain this H+ pump2,10. Carbon dioxide, a major stimulus for urinary acidification, causes rapid fusion of these vesicles with the luminal membrane, thereby inserting these pumps there and increasing the rate of net transepithelial H+ secretion; CO2 also inhibits endocytic retrieval of the pumps from the luminal membrane11. Such reciprocal regulation of endocytosis and exocytosis by a physiological modulator makes this system particularly attractive for studying the cellular events regulating membrane fusion. Here we present evidence that CO2 induces exocytosis by a cascade of events, the first step of which is cytoplas-mic acidification. Cell acidification then increases calcium activity, which causes the fusion event.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tycko, B. & Maxfield, F. R. Cell 28, 643–651 (1982).
Gluck, S., Cannon, C. & Al-Awqati, Q. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 4327–4331 (1982).
Gluck, S., Kelly, S. & Al-Awqati, Q. J. biol. Chem. 257, 9230–9233 (1982).
Forgac, M., Cantley, L., Wiedemann, B., Altstiel, L. & Branton, D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 1300–1303 (1983).
Stone, D. K., Xie, X.-S. & Racker, E. J. biol. Chem. 258, 4059–5062 (1983).
Galloway, C. J., Dean, G. E., Marsh, M., Rudnick, G. & Mellman, I. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 3334–3338 (1983).
Glickman, J., Croen, K., Kelly, S. & Al-Awqati, Q. J. Cell Biol. 97, 1303–1308 (1983).
Rees-Jones, R. & Al-Awqati, Q. Biochemistry 23, 2336–2340 (1984).
Gluck, S. & Al-Awqati, Q. J. clin. Invest. 73, 1704–1710 (1984).
Schwartz, G. J. & Al-Awqati, Q. J. clin. Invest. (in the press).
Reeves, W., Gluck, S. & Al-Awqati, Q. Kidney Int. 23, 232 (Abstr.) (1983).
Steinmetz, P. R. Physiol. Rev. 54, 890–956 (1974).
Baker, P. F. & Honerjager, P. Nature 273, 160 (1978).
Lea, T. J. & Ashley, C. C. Nature 175, 236–238 (1978).
Lorenzen, M., Lee, C. O. & Windhager, E. E. Fedn Proc. 41, 1350 (1982).
Alvarez-Leefmans, F. J., Rink, T. J. & Tsein, R. Y. J. Physiol., Lond. 315, 531–548 (1981).
Tsien, R. Y. Biochemistry 19, 2396–2403 (1980).
Tsien, R. Y., Pozzan, T. & Rink, T. J. J. Cell Biol. 94, 325–334 (1982).
van Adelsberg, J. S. & Al-Awqati, Q. Kidney Int. 27, 290 (abstr.) (1985).
Roos, A. & Boron, W. Physiol. Rev. 61, 296–434 (1981).
Cook, D. L., Ikeuchi, M. & Fujimoto, W. Y. Nature 311, 269–271 (1984).
Lorentzen, M., Taylor, A. & Windhager, E. E. Am. J. Physiol. 245, F188–F197 (1983).
Rossier, M., Rossier, B. C., Pfeiffer, J. & Kraehenbuhl, J. P. J. Membrane Biol. 48, 141–166 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cannon, C., van Adelsberg, J., Kelly, S. et al. Carbon-dioxide-induced exocytotic insertion of H+ pumps in turtle-bladder luminal membrane: role of cell pH and calcium. Nature 314, 443–446 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1038/314443a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/314443a0
This article is cited by
-
Kinetics of receptor-mediated endocytosis of albumin in cells derived from the proximal tubule of the kidney (opossum kidney cells): influence of Ca2+ and cAMP
Pfl�gers Archiv European Journal of Physiology (1995)
-
Plasma membrane protein composition and synthesis in soybean hypocotyl segments undergoing auxin-induced elongation
Protoplasma (1994)
-
Immunolocalization of 15-kDa membrane proteins in the kidneys of normal and acidotic rats
Pfl�gers Archiv European Journal of Physiology (1991)
-
Activation of latent Ca2+ channels in renal epithelial cells by parathyroid hormone
Nature (1990)
-
Madin-Darby canine kidney cells
Pfl�gers Archiv European Journal of Physiology (1990)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.