Abstract
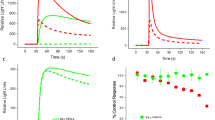
Calcium channels, controlling the influx of extracellular Ca2+ and hence neurotransmitter release, exist in the brain1. However, drugs classed as calcium antagonists and which inhibit Ca2+ entry through voltage-activated Ca2+ channels in heart and smooth muscle2, seem not to affect any aspect of neuronal function in the brain at pharmacologically relevant concentrations3–6. Yet the dihydropyridine calcium antagonists (for example, nitrendipine) bind stereospecifically with high affinity to a recognition site on brain-cell membranes thought to represent the Ca2+ channel4,7,8 and consequently, the physiological relevance of these sites has been questioned9. However, activation of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels can increase cytoplasmic Ca2+ and neurotransmitter release in neuronal tissue10. We show here that Bay K 8644, a dihydrophyridine Ca2+-channel activator11,12, can augment K+-stimulated release of serotonin from rat frontal cortex slices and that these effects can be antagonized by low concentrations of calcium antagonists. As 3H-dihydropyridine binding to cortical membrane preparations resembles the binding in heart and smooth muscle where there are good functional correlates8,13 we conclude that the dihydropyridine binding sites in the brain represent functional Ca2+ channels that can be unmasked under certain circumstances.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nelson, M. T., French, R. J. & Krueger, B. K. Nature 308, 77–80 (1984).
Fleckenstein, A. Calcium Antagonism in Heart and Smooth Muscle (Wiley, New York, 1983).
Daniell, L. C., Barr, E. M. & Leslie, S. W. J. Neurochem. 41, 1455–1459 (1983).
Snyder, S. H. Science 224, 22–31 (1984).
Miller, R. J. & Freedman, S. B. Life Sci. 34, 1205–1221 (1984).
Starke, K., Späth, L. & Wichmann, T. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archs Pharmak. 325, 124–130 (1984).
Glossmann, H., Ferry, D. R., Lübbecke, F., Mewes, R. & Hofmann, F. Trends pharmac. Sci. 3, 431–437 (1982).
Janis, R. A. & Scriabine, A. Biochem. Pharmac. 32, 3499–3507 (1983).
Triggle, D. J. Trends pharmac. Sci. 5, 4–5 (1984).
Ashley, R. H., Brammer, M. J. & Marchbanks, R. Biochem. J. 219, 149–158 (1984).
Schramm, M., Thomas, G., Towart, R. & Franckowiak, G. Nature 309, 535–537 (1983).
Schramm, M., Thomas, G., Towart, R. & Franckowiak, G. Arzneimittel-Forsch. 33, 1268–1272 (1983).
Bolger, G. T. et al. J. Pharmac. exp. Ther. 225, 291–309 (1983).
Göthert, M. Trends pharmac. Sci. 3, 437–440 (1982).
Spedding, M. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Archs Pharmak. 318, 234–240 (1982).
Anderson, C. L., Scriabine, A. & Janis, R. A. Fedn Proc. 43, 550 (1984).
Bellemann, P. FEBS Lett. 167, 88–92 (1984).
Spedding, M. & Berg, C. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archs Pharmak. 328, 69–75 (1984).
Albus, U., Habermann, E., Ferry, D. R. & Glossmann, H. J. Neurochem. 42, 1186–1189 (1984).
Toll, L. J. biol Chem. 257, 13189–13192 (1982).
Takahashi, M. & Ogwa, A. FEBS Lett. 152, 191–194 (1983).
Garcia, A. G. et al. Nature 309, 69–71 (1984).
Docherty, J. R., Hyland, L. & Warnock, P. B. J. Pharmac. 82, 213P (1984).
Venter, J. C. et al. J. biol. Chem. 258, 9344–9348 (1983).
Ferry, D. R., Rombusch, M., Goll, A. & Glossmann, H. FEBS Lett. 169, 112–119 (1984).
Glossmann, H. & Ferry, D. R. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archs Pharmak. 323, 279–291 (1983).
Goll, A., Ferry, D. R. & Glossmann, H. FEBS Lett. 157, 63–69 (1983).
Nayler, W. G. & Sturrock, W. J. J. molec. cell. Cardiol. 16, 331–344 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Middlemiss, D., Spedding, M. A functional correlate for the dihydropyridine binding site in rat brain. Nature 314, 94–96 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1038/314094a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/314094a0
This article is cited by
-
Influence of nicardipine, nimodipine and flunarizine on the anticonvulsant efficacy of antiepileptics against pentylenetetrazol in mice
Journal of Neural Transmission (1996)
-
Organic calcium antagonists verapamil and riodipine prevent elevation of free calcium level in rat brain synaptosomes during metrazol kindling
Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine (1992)
-
Evidence for verapamil-induced functional inhibition of noradrenergic neurotransmission in vivo
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (1992)
-
Role of calcium channels in effects of antidepressant drugs on responsiveness to pain
Psychopharmacology (1991)
-
Two components of long-term potentiation induced by different patterns of afferent activation
Nature (1990)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.