Abstract
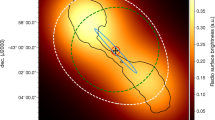
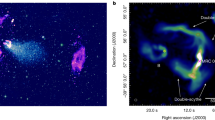
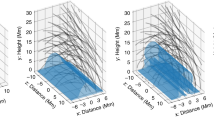
Extragalactic radio sources display a wide range of complex structures. The weaker sources have twin jets emerging from the nucleus of the parent galaxy, which bend and twist as they interact with the intergalactic medium (IGM); extreme examples are the radio-trail sources, such as NGC1265 (ref. 1) and 3C129 (ref. 2). More powerful sources typically show double structures with lobes and hotspots, but even these (such as Cygtius A (R. A. Perley, personal communication)) contain curved jets. Although our theoretical understanding of sources in terms of twin plasma-jets has advanced, numerical simulations3,4 have concentrated on axisym-metric models, whereas the investigation of radio-trail and complex sources demands three-dimensional simulations, despite the obvious computational difficulties. It is now generally accepted that radio-trail galaxies are produced by the motion of active galactic nuclei through the IGM in clusters of galaxies5. Models were initially proposed in which the ejected material consisted of independent blobs or plasmons6–8, but most evidence9,10 now supports ejection in a quasi-continuous jet9,11. Here we adopt the jet model and study the formation of twin-tail sources by the motion of the active nucleus through intra-cluster gas, using three dimensional fluid-dynamical simulations of a supersonic jet in a cross-wind.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miley, G. K., Wellington, K. J. & van der Laan, H. Astr. Astrophys. 38, 381–390 (1975).
Downes, A. J. B. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 190, 261–268 (1980).
Norman, M.L., Smarr, L., Winkler, K.-H.A. & Smith, M. D. Astr. Astrophys. 113, 285–302 (1982)
Wilson, M. J. & Scheuer, P. A. G. Mon. Not. R. astr. soc. 205, 449–463 (1983).
Miley, G. K., Perola, G. G., van der Kruit, P. C. & van der Laan, H. Nature 237, 269–272 (1972).
Cowie, L. L. & McKee, C. F. Astr. Astrophys. 43, 337–343 (1975).
Jaffe, W. J. & Perola, G. C. Astr. Astrophys. 26, 423–435 (1973).
Pacholczyk, A. G. & Scott, J. S. Astrophys. J. 203, 313–322 (1976).
Jones, T. W. & Owen, F. N. Astrophys. J. 234, 818–824 (1979).
Owen, F. N., Burns, J. O. & Rudnick, L. Astrophys. J. Lett. 226, L119–L123 (1978).
Begelman, M. C., Rees, M. J. & Blandford, R. D. Nature 279, 770–773 (1979).
Gentry, R. A., Martin, R. E. & Daly, B. J. J. computat. Phys. 1, 87–118 (1966).
Book, D. L., Boris, J. P. & Hain, K. J computat. Phys. 18, 248–283 (1975).
Sod, G. A. J. computat. Phys. 27, 1–31 (1978).
Strang, G. SIAM J numer. Analysis 5, 507–517 (1968).
Kamotani, Y. & Greber, I. Am. inst. Aeronaut, Astronaut. J. 10, 1425–1429 (1972).
Fanaroff, B. L. & Riley, J. M. Mon. Not. R. astr. Soc. 167, 31P–35P (1974).
Vallee, J. P., Bridle, A. H. & Wilson, A. S. Astrophys. J. 250, 66–78 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Williams, A., Gull, S. A three-dimensional model of the fluid dynamics of radio-trail sources. Nature 310, 33–36 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1038/310033a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/310033a0
This article is cited by
-
Instabilities in astrophysical jets
Astrophysics and Space Science (1996)
-
DrosophilaP element: Transposition, regulation and evolution
Genetica (1994)
-
Internal structure and polarization of the optical jet of the quasar 3C273
Nature (1993)
-
Vortex rings in the working surface of radio jets
Journal of Astrophysics and Astronomy (1988)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.