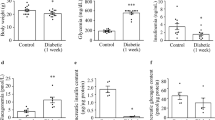
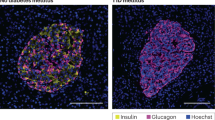
Abstract
Autoantibodies to cytoplasmic and surface antigens on pancreatic islet cells have been found in many newly diagnosed cases of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM)1–9. Various autoantibodies (for example, against islet cells, adrenals, thyroid, gastric mucosa and intrinsic factor) have also been found in patients with polyendocrine disease1,2,8,9. What triggers the production of these antibodies and their importance in the pathogenesis of these diseases are still unclear. Recently, we found in an animal model for studing polyendocrine disease10 that reovirus type 1 (reo-1) infected cells in both the pancreas and pituitary, and produced a disease characterized by hyperglycaemia and retarded growth10. Moreover, autoantibodies that reacted with antigens in pancreatic islets, the anterior pituitary and gastric mucosa were found, one of which reacted with insulin and another with growth hormone (GH). Using recombinant viruses11 we showed that the S1 gene segment from reo-1 was required for the induction of auto-antibodies to GH. We report here our search for additional autoantibodies, especially against surface antigens, and our efforts to evaluate the pathological contributions of the lytic effect of the virus on cells compared with the immunopathological response of the host. Our experiments showed that reo-1 induced autoantibodies that reacted with antigens on the surface of islet cells, thymocytes and a GH-producing cell line. In addition, we found that treatment with immunosuppressive agents depressed autoantibody production and prevented development of the polyendocrine disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bottazzo, G. F., Florin-Christensen, A. & Doniach, D. Lancet ii, 1279–1282 (1974).
MacCuish, A. C., Irvine, W. J., Barnes, E. W. & Duncan, L. J. P. Lancet ii, 1529–1531 (1974).
Irvine, W. J., Gray, R. S. & McCallum, C. J. Lancet ii, 1097–1102 (1976).
Lendrum, R., Walker, G. & Gamble, D. R. Lancet i, 880–883 (1975).
Doniach, D. & Bottazzo, G. F. in Pathobiology Annual (ed. Joachim, H. L.) 327–346 (Appleton-Century-Crofts, New York, 1977).
Lernmark, A. et al. New Engl. J. Med. 299, 375–380 (1978).
Dobersen, M. J., Scharff, J. E., Ginsberg-Fellner, F. & Notkins, A. L. New Engl. J. Med. 303, 1493–1498 (1980).
Cahill, G. F. & McDevitt, H. O. New Engl. J. Med. 304, 1454–1465 (1981).
Doniach, D. & Bottazzo, G. F. in Clinical Immunology Update (ed. Franklin, E. D.) 96–121 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1981).
Onodera, T. et al. J. exp. Med. 153, 1457–1473 (1981).
Weiner, H. L., Drayana, D., Averill, D. R. Jr & Fields, B. N. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 5744–5748 (1977).
Openshaw, H., Asher, L. V. S., Wohlenberg, C., Sekizawa, T. & Notkins, A. L. J. gen. Virol 44, 205–215 (1979).
Birge, C. A., Peake, G. T., Mariz, I. K. & Daughaday, W. H. Endocrinology 81, 195–204 (1967).
Weiner, H. L., Powers, M. L. & Fields, B. N. J. infect. Dis. 141, 609–616 (1980).
Bancroft, F. C. & Tashjian, A. H. Jr Expl Cell Res. 64, 125–128 (1971).
Ledbetter, J. A., Rouse, R. V., Micklem, H. S. & Herzenberg, L. A. J. exp. Med. 152, 280–295 (1980).
Notkins, A. L. (ed.) Viral Immunology and Immunopathology (Academic, New York, 1975).
Oldstone, M. B. A. Prog. med. Virol. 19, 84–119 (1975).
Zinkernagel, R. M. Compreh. Virol. 15, 171–204 (1979).
Finberg, R., Weiner, H. L., Fields, B. N., Benacerraf, B. & Burakoff, S. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76, 442–446 (1979).
Toniolo, A., Onodera, T., Yoon, J. W. & Notkins, A. L. Nature 288, 383–385 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onodera, T., Ray, U., Melez, K. et al. Virus-induced diabetes mellitus: autoimmunity and polyendocrine disease prevented by immunosuppression. Nature 297, 66–68 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1038/297066a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/297066a0
This article is cited by
-
IDDM: an islet or an immune disease?
Diabetologia (1994)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.