Abstract
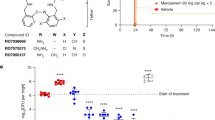
Inhibitors of the biosynthesis of peptidoglycan, the rigid layer of the bacterial cell wall which is responsible for the shape of the cell, are among the most effective antibacterial agents known. Both Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms are susceptible to the action of such compounds. As lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is an integral part of the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria, it is possible that a blockage of its biosynthesis might result in the arrest of cellular growth and eventually cell death, analogous to the effects seen with inhibitors of peptidoglycan biosynthesis. However, no antibacterial agent has been described which inhibits growth in this way. We present here experimental evidence which indicates that 1,2-dihydro-1-hydroxy-6-methyl-2-(propanesulphonyl)-thieno(3,2-D) (1,2,3)-diazaborine (code no. 84474), a heterocyclic, boron-containing substance, prevents bacterial proliferation by inhibiting LPS biosynthesis. There was a reduction in galactose incorporation into the LPS of whole cells, and no newly formed LPS chains appeared in whole bacteria in the presence of the compound, as demonstrated by electron microscopy. The 2-keto-3-deoxy-octonate metabolism seems to be the target of 84474 as arabinose 5-phosphate incorporation into macro-molecular material was affected.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gronowitz, S. et al. Acta pharm. suec. 8, 377–390 (1971).
Gronowitz, S. et al. Acta pharm. suec. 8, 623–638 (1971).
Florentin, D., Rogues, B.-P., Metzger, J. M. & Collin, J.-P. Bull. Soc. chim. Fr. 2620–2622 (1974).
Mayer, H., Rapin, A. M. C., Schmidt, G. & Boman, H. G. Eur. J. Biochem. 66, 357–368 (1976).
Prehm, P., Stirm, S., Jann, B. & Jann, K. Eur. J. Biochem. 66, 369–377 (1976).
Heller, K. B. & Wilson, T. H. J. Bact. 140, 395–399 (1979).
Westphal, O. & Jann, K. Meth. Carbohyd. Chem. 5, 83–91 (1965).
Mühlradt, P. F., Menzel, J., Golecki, J. & Speth, V. Eur. J. Biochem. 35, 471–481 (1973).
Eugvall, E. & Perlmann, P. Immunochemistry 8, 871–874 (1971).
Schmidt, G., Schlecht, S., Lüderitz, O. & Westphal, O. Zentbl. Bakt. ParasitKde 209, 483–496 (1969).
Rick, D. & Osborn, M. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 69, 3756–3760 (1972).
Levine, D. H. & Racker, E. J. biol. Chem. 234, 2532–2539 (1959).
Berger, H. & Hammerschmid, F. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 3, 1096–1097 (1975).
Ghalambor, M. A. & Heath, E. C. J. biol. Chem. 241, 3216–3221 (1966).
Hofstad, T. & Kristoffersen, T. J. gen. Microbiol. 61, 15–19 (1970).
Buttin, G. J. molec. Biol. 7, 183–205 (1963).
Miller, J. H. Experiments in Molecular Genetics, 431 (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, 1972).
Munson, R. S., Rasmussen, N. S. & Osborn, M. J. J. biol. Chem. 253, 1503–1511 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Högenauer, G., Woisetschläger, M. A diazaborine derivative inhibits lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis. Nature 293, 662–664 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1038/293662a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/293662a0
This article is cited by
-
Structural and Biochemical Studies on Klebsiella Pneumoniae Enoyl-ACP Reductase (FabI) Suggest Flexible Substrate Binding Site
The Protein Journal (2023)
-
A fatty-acid synthesis mechanism specialized for parasitism
Nature Reviews Microbiology (2007)
-
The use of a hybrid genetic system to study the functional relationship between prokaryotic and plant multi-enzyme fatty acid synthetase complexes
Plant Molecular Biology (1994)
-
A new class of synthetic antibacterials acting on lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis
Nature (1987)
-
Antibacterial agents specifically inhibiting lipopolysaccharide synthesis
Nature (1987)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.