Abstract
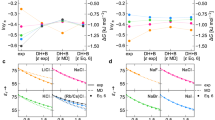
Measurements of the thermodynamic properties of electrolytes in hot water have a widespread practical and theoretical interest. The chemistry of many solutes changes rapidly as a solution is heated but the reasons for such changes have not been understood in terms of electrolyte theory. The temperature behaviour of the equilibrium thermodynamic properties is best seen by examining the ionic heat capacities of representative electrolytes, and we report here measurements just completed of C̄°p2 of NaCl(aq) and BaCl2 (aq) up to 300 °C. The values are so negative that we now believe that the properties of electrolytes at higher temperatures are determined primarily by the electrostatic field of the ions and the bulk dielectric constant of water, and not by structural arrangements of ions and water molecules which characterize solutions at lower temperatures. These new phenomena are summarized in Fig. 1, which not only illustrates the large values at 300 °C for C̄°p2 for NaCl (aq) and BaCl2 (aq) of −339 and −1,011 cal mol−1 deg−1, but also indicates a continued rapid change above 300 °C. The observations also suggest a need for reexamination of the theory of aqueous electrolytes at 25 °C, a temperature in the transition region between the two types of behaviour.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Criss, C. M. & Cobble, J. W. J. Am. chem. Soc. 83, 3223–3228 (1961).
Ellis, A. J. & McFadden, I. M. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 36, 413–426 (1972).
Kelley, K. K. U.S. Bur. Mines Bull. 584 (1960).
Gardner, W. L., Mitchell, R. E. & Cobble, J. W. J. phys. Chem. 73, 2025–2032 (1969).
Wood, R. W. & Smith-Magowan, D. Am. Chem. Soc. Ser. No. 133, 569–580 (1980).
Kavanau, J. Lee Water and Solute–Water Interactions (Holden-Day, San Francisco, 1964).
Eisenberg, D. & Kauzmann, W. The Structure and Properties of Water (Oxford University Press, 1969).
Narten, A. H. & Levy, H. A. Science 165, 447–454 (1969).
Frank, H. S. Science 169, 635–641 (1970).
Angell, C. A. J. phys. Chem. 75, 3698–3705 (1971).
Hagler, A. T., Scheraga, H. A. & Nemethy, G. J. phys. Chem. 76, 3229–3243 (1972).
Benson, S. W. J. Am. chem. Soc. 100, 5640–5644 (1978).
Frank, H. S. & Wen, W. Y. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 133–140 (1957).
Conway, B. E., Desnoyers, J. E. & Smith, A. C. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A256, 389–437 (1964).
Rosseinsky, D. R. Chem. Rev. 65, 467–490 (1965).
Bockris, J. O'M. & Saluja, P. P. S. J. phys. Chem. 76, 2298–2310 (1972).
Haggis, G. H., Hasted, J. B. & Buchanan, T. J. J. chem. Phys. 20, 1452–1465 (1952).
Cobble, J. W. Science 152, 1479–1485 (1966).
Bradley, D. H. & Pitzer, K. S. J. phys. Chem. 83, 1599–1603 (1979).
Born, M. Z. Phys. 1, 45–48 (1920).
Cobble, J. W. & Murray, R. C. Jr Trans. Faraday Soc. 64, 144–149 (1978).
Sweeton, F. H., Mesmer, R. E. & Baes, C. F. Jr J. Solut. Chem. 3, 191–214 (1974).
Hitch, B. F. & Mesmer, R. E. J. Solut. Chem. 5, 667–679 (1976).
Jones, M. E. J. phys. Chem. 67, 1113–1115 (1963).
Read, A. J. J. Solut. Chem. 4, 53–70 (1975).
Helgeson, H. A. J. phys. Chem. 71, 3121–3136 (1967).
Ellis, A. J. & Golding, R. M. Am. J. Sci. 261, 47–60 (1963).
Pearson, D., Copeland, C. S. & Benson, S. W. J. Am. chem. Soc. 85, 1047–1049 (1963).
Gardner, W. L., Jekel, E. C. & Cobble, J. W. J. phys. Chem. 73, 2017–2020 (1969).
Cobble, J. W., Stephens, H. P., McKinnon, I. R. & Westrum, E. F. Jr Inorg. Chem. 11, 1669–1674 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cobble, J., Murray, R. & Sen, U. Field and structure behaviour of electrolytes. Nature 291, 566–568 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1038/291566a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/291566a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.