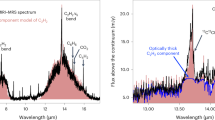
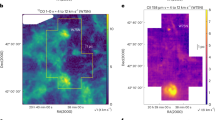
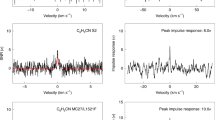
Abstract
THE diffuse interstellar lines, seen in the optical spectra of stars which lie behind fairly low density interstellar clouds, have remained unidentified for many years. It has recently been suggested1 that the diffuse interstellar lines are the absorption bands of long chain carbon molecules, Cn, where n may be in the range 5–15. As one possible source for these molecules, Douglas1 proposes that long chain hydrocarbons are synthesised in dense interstellar clouds. After cloud disruption, the hydrocarbons may lose their hydrogen atoms by photodissociation and exist as pure carbon chains. While the shortest of the chains (C2, C3, C4) will themselves be photodissociated, Douglas1 argues that chains beyond a certain length are stable against photodissociation and will persist in the low density clouds in which the diffuse interstellar lines are formed. As a first step in evaluating the feasibility of this route, we estimate here the abundances of chain hydrocarbon molecules which would be expected in dense interstellar clouds as a result of gas-phase chemistry alone. The rather high abundances of hydrocarbons which we predict support the identification of carbon chains as the source of the diffuse interstellar spectral features.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Douglas, A. E. Nature 269, 130–132 (1977).
Huntress, W. T., Jr Astrophys. J. Suppl. 33, 495–514 (1977).
Bohme, D. K. & Schiff, H. I. preprint (1978).
Huntress, W. T., Jr & Mitchell, G. F. Astrophys. J. (in the press).
Guélin, M., Langer, W. D., Snell, R. L. & Wootten, H. A. Astrophys. J. 217, L165–L168 (1977).
Langer, W. D., Wilson, R. W., Henry, P. S. & Guélin, M. Astrophys. J. 225, L139–L142 (1978).
Smith, D. & Adams, N. G. Astrophys. J. 220, L87–L92 (1978).
Fox, K. & Jennings, D. E. Astrophys. J. 226, L43–L47 (1978).
Broten, N. W., Oka, T., Avery, L. W. & MacLeod, J. M. Astrophys. J. 223, L105–L107 (1978).
Mitchell, G. F. Astr. J. 83, 1612–1613 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MITCHELL, G., HUNTRESS, W. Long chain carbon molecules and diffuse interstellar lines. Nature 278, 722–723 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1038/278722a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/278722a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.