Abstract
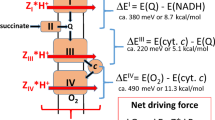
METABOLISING mammalian mitochondria normally will take up a considerable (30–80 nmol per mg protein) quantity of Ca2+ when no anion, such as phosphate or acetate, has been added to move in and balance the charges on the Ca2+ accumulated1,2. This has been attributed to reaction of the Ca2+ with membrane components. Recently3,4 the importance of adventitious phosphate, always present in mitochondrial suspensions3, has been recognised, and it has been shown that inhibition of phosphate movement lessens3,5, or can abolish, Ca2+ uptake4. Carbon dioxide is a further source of anion to accumulate with Ca2+ in mitochondria possessing carbonic anhydrase activity6. The importance of this process, which readily proceeds using the dissolved CO2 already present in the system, is now illustrated using a sensitive indicator of Ca2+ movement. Also, the production of 2H+ per Ca2+ accumulated as CaCO3 can account for the increase in the ratio H+: Ca2+, which is observed when phosphate uptake is inhibited.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chance, B. J. biol. Chem, 240, 2729–2747 (1965).
Carafoli, E. & Lehninger, A. L. Biochem. J. 122, 681–690 (1971).
Brand, M., Chen, C-H. & Lehninger, A. L. J. biol. Chem. 251, 968–974 (1976).
Harris, E. J. & Zaba, B. N. FEBS Lett. 79, 284–290 (1977).
Bygrave, F. L., Ramchandran, C. & Smith, R. L. FEBS Lett. 83, 155–158 (1977).
Elder, J. A. & Lehninger, A. L. Biochemistry 12, 976–982 (1973).
Rossi, C. S., Azzone, G. F. & Azzi, A. Eur. J. Biochem. 1, 141–146 (1967).
Carafoli, E., Rossi, C. S. & Lehninger, A. L. J. biol. Chem. 239, 3055–3061 (1964).
Rossi, C. S. & Lehninger, A. L. Biochem. Z. 338, 698–713 (1963).
Brand, M. D., Reynafarje, B. & Lehninger, A. L. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 73, 431–441 (1976).
Pozzan, T., Bragadin, M. & Azzone, G. F. Eur. J. Biochem. 71, 93–99 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HARRIS, E. The importance of CO2 for Ca2+ uptake by some mitochondria. Nature 274, 820–821 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1038/274820a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/274820a0
This article is cited by
-
Carbon dioxide or bicarbonate ions release Ca2+ from internal stores in crustacean myofibrillar bundles
The Journal of Membrane Biology (1981)
-
Aspartate and glutamate as possible transmitters at the ?slow? and ?fast? neuromuscular junctions of the body wall muscles ofMusca larvae
Journal of Comparative Physiology ? A (1980)
-
Cytochemical gradients and mitochondrial exclusion in the apices of vegetative hyphae
Experientia (1979)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.