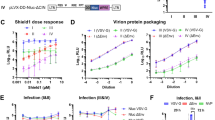
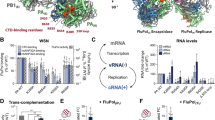
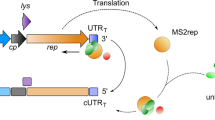
Abstract
THE discovery of reverse transcriptase1,2 offered the possibility of using in vitro synthesis to study the replication of RNA tumour virus genomes in molecular detail. Attempts to study DNA provirus formation in vitro, however, have encountered serious obstacles: poor efficiency of transcription, small DNA products, and unequal representation of the viral RNA sequences in the DNA product have been common findings3. These difficulties in copying RNA into DNA have led to suggestions that cellular factors, such as ligases or unwinding proteins might be necessary to assist reverse transcriptase in copying the viral RNA genome into a complete DNA transcript4,5. Binding (unwinding) proteins involved in DNA synthesis are well known in bacteria6,7 and have also been described in mammalian systems8. We reported previously the isolation of a DNA binding protein from transformed chicken cells and its stimulating effect on reverse transcriptase activities5. Here we present evidence that, in the presence of the binding protein, purified reverse transcriptase from Rous sarcoma virus (RSV) synthesised an extensive, possibly complete complementary transcript of DNA from the viral RNA genome in a totally reconstituted reaction system.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baltimore, D. Nature 226, 1209–1211 (1970).
Temin, H. M. & Mizutani, S. Nature 226, 1211–1213 (1970).
Green, M. & Gerard, S. F. Prog. Nucleic Acids Res. molec. Biol. 14, 187–334 (1974).
Temin, H. M. & Baltimore, D. Adv. Virus Res. 17, 129–186 (1972).
Hung, P. P. & Lee, S. G. Nature 259, 499–502 (1976).
Sigal, N., Dalius, H., Kornberg, T., Gefter, M. L. & Alberts, B. M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 69, 3534–3541 (1972).
Alberts, B. M. & Frey, L. Nature 227, 1313–1318 (1970).
Herrick, G. & Alberts, B. W. J. biol. Chem. 251, 2124–2132 (1976).
Tsai, R. L. & Green, H. J. molec. Biol. 73, 307–316 (1973).
Gradgenett, D. P., Gerard, G. F. & Green, M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 70, 230–234 (1973).
Aposhian, H. V. & Kornberg, A. J. biol. Chem. 237, 516–525 (1962).
Holloman, W. K. & Holliday, R. J. biol. Chem. 248, 8107–8113 (1973).
Delius, H., Duesberg, P. H. & Mangel, W. F. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 39, 835–843 (1975).
Marmur, J. & Doty, P. Nature 183, 1427–1429 (1959).
Staskus, K. A., Colletti, M. S. & Faras, A. J. Virology 71, 162–168 (1976).
Taylor, J. M. & Illmensee, R. J. Virol. 16, 553–558 (1975).
Taylor, J. M. et al. Biochemistry 12, 460–467 (1973).
Robinson, W. S., Robinson, H. L. & Duesberg, P. H. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 58, 825–834 (1967).
Rothenberg, E. & Baltimore, D. J. Virol. 21, 168–178 (1977).
Ando, T. Biochim. biophys. Acta 114, 158–168 (1966).
Junghans, P., Duesberg, P. H. & Knight, C. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 72, 4895–4899 (1975).
Collett, M. S. & Faras, A. J. J. Virol. 16, 1220–1228 (1975).
Haseltine, W. A., Kleid, D. G., Panet, A., Rothenberg, E. & Baltimore, D. J. molec. Biol. 106, 109–131 (1976).
Sen, A., Sherr, C. J. & Todaro, G. J. Cell 7, 21–32 (1976).
Adesnik, M. Meth. Virol. 5, 125–177 (1971).
Canaani, E. & Duesberg, P. J. Virol. 10, 23–31 (1972).
Maizel, J. V. Jr, Meth. Virol. 5, 179–245 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LEE, S., HUNG, P. Extensive reverse transcription of RSV genome by nucleic acid-binding protein. Nature 270, 366–369 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1038/270366a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/270366a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.