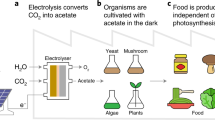
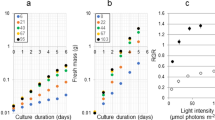
Abstract
The large amounts of microalgae produced in waste treatment ponds during sewage purification are a potential source of methane and fertiliser. If techniques can be developed for the selective cultivation of filamentous or colonial microalgae, harvesting of microalgal biomass could be accomplished by low-cost straining or sedimentation methods.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayers, E.A. & Scarlott, C.A. Energy Sources—The Wealth of the World (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1952).
Odum, H. T. Environment Power and Society (Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1971).
Kok, B. in Physiology of Plant Growth and Development (ed. Wilkins, M. B.) 335–379 (McGraw Hill, London, 1969).
Ryther, J. H. Science 130, 602–608 (1900).
Zelitch, I. Science 188, 626–633 (1975).
Hall, D. O., FEBS Lett. 67, 6–16 (1976).
Bassham, J. A. Proc. Symp. Clean Fuels from Biomass, Sewage, Urban Refuse, and Agricultural Wastes, 205 (Institute of Gas Technology, Chicago, 1976).
Calvin, M. Amer. Sci. 64, 424–429 (1976).
Burlew, J. S.(ed.) Algal Culture from Laboratory to Pilot Plant Pub. 600 (Carnegie Institute of Washington, Washington, DC, 1953).
Durand-Chastel, H. and Clement, G. Proc. 9th Int. Congr. Nutrition, Mex. (1972) 3, 85–90 (Karger, Basel, 1975).
Oswald, W. J. Progress in Water Technology, Water Quality Management, and Pollution Control 3, 153 (Pergamon, Oxford, 1973).
Oswald, W. J., Gotaas, H. B., Golueke, C. G. & Kellen, W. R. Sew. and Indus. Wastes 29, 437–457 (1957).
Oswald, W. J. Proc. ASCE San. Eng. Div. SA 4, 71–95 (1960).
Golueke, C. G. & Oswald, W. J. J. Water Poll. Cont. Fed. 37, 471–498 (1965).
Parker, D. S., Tyler, J. B. & Dosh, T. J. Water and Wastes Engineering 10, 26–29 (1973).
Palmer, C. M. Rev. Microbial (Sao Paulo) 5, 75–80 (1974).
Goldman, J. C. & Ryther, J. H. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 18, 1125–1144 (1976).
Benemann, J. R. Living Systems as Energy Converters (eds Buvet, R. et al. (Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical, Amsterdam, 1977).
Fay, P., Stewart, W. D. P., Walsby, A. E. & Fogg, G. E. Nature 220, 810–812 (1968).
Golueke, C. G., Oswald, W. J. & Gotaas, H. B. Applied Microbiol. 5, 47 (1957).
Uziel, M., Oswald, W. J. & Golueke, C. G. Proc. Am. Meeting, Am. Ass. Adv. Science (SERL, University of California, Berkeley, 1975).
Golueke, C. G. & Oswald, W. J. App. Microbiol. 7, 219 (1959).
Eloff, J. N., Steinitz, Y. & Shilo, M. Appl. environ. Microbiol. 31, 119 (1976).
Lewis, C. W. Process Biochem. p.29 (Nov. 1976).
Oswald, W. J. & Golueke, C. G. Adv. appl. Microbiol. 2, 223 (1960).
Oswald, W. J. & Benemann, J. R. in Handbook of Microbiology (CRC Press, Cleveland, in the press).
Oswald, W. J. & Benemann, J. R. Proc. U.S. Japan Conf. on Photosynthetic Energy Conversion (Academic, New York, in the press).
Benemann, J. R. & Weare, N. M. Science 184, 174–75 (1974).
Weissman, J. C. & Benemann, J. R. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 33, 123–131 (1977).
Benemann, J. R. & Weissman, J. C. Proc. Conf. on Microbial Energy Conversion eds Schlegel, H. G. & Bamen, J.) (Erich Koltze KG, Göttingen, Germany, (1976).
Gest, H. & Kamen, M. D. Science 109, 558 (1949).
Benemann, J. R. Living Systems as Energy Converters (eds R. Buvet et al.) 285 (Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical, Amsterdam, 1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benemann, J., Weissman, J., Koopman, B. et al. Energy production by microbial photosynthesis. Nature 268, 19–23 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1038/268019a0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/268019a0
This article is cited by
-
Response of Cyanobacterial Photosynthetic Rate to Different Conditions of Pulsed Light
BioEnergy Research (2023)
-
Microalgal–Bacterial Flocs and Extracellular Polymeric Substances: Two Essential and Valuable Products of Integrated Algal Pond Systems
Water, Air, & Soil Pollution (2019)
-
Dependency of Microalgal Production on Biomass and the Relationship to Yield and Bioreactor Scale-up for Biofuels: a Statistical Analysis of 60+ Years of Algal Bioreactor Data
BioEnergy Research (2017)
-
Changes in growth and composition of the marine microalgae Phaeodactylum tricornutum and Nannochloropsis salina in response to changing sodium bicarbonate concentrations
Journal of Applied Phycology (2016)
-
Engineering solutions for open microalgae mass cultivation and realistic indoor simulation of outdoor environments
Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering (2015)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.