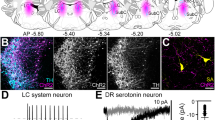
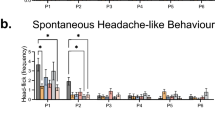
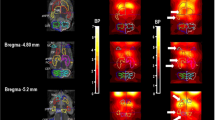
Abstract
SUBSTANCES which mimic or inhibit the actions of dopamine in the vertebrate central nervous system (CNS) have become of increasing interest since the discovery of their potential clinical importance1. It has been suggested that the receptors involved are closely associated with an adenylate cyclase responsible for the formation of cyclic AMP by homogenates of the neostriatum and limbic regions of the brain in the presence of dopamine2. In favour of this idea, substances believed to be agonists for central dopamine receptors also stimulate the production of cyclic AMP in such homogenates2,3, and neuroleptics, which are believed to act by blocking dopaminergic transmission, inhibit the action of dopamine on homogenates2,4. It is difficult, however, to obtain information about the physiological mode of action of these compounds at the cellular level in the CNS. We report here the effects of a dopamine-like agonist and a neuroleptic on an alternative system which enables investigation of intracellular responses. Our results are consistent with the idea that both substances act directly on postsynaptic dopamine receptors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iversen, L. L., Science, 188, 1084–1089 (1975).
Kebabian, J. M., Petzold, G. L., and Greengard, P., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 69, 2145–2149 (1972).
Miller, R., Horn, A., Iversen, L. L., and Pinder, R., Nature, 250, 238–241 (1974).
Miller, R. J., Horn, A. S., and Iversen, L. L., Molec. Pharmac., 10, 759–766 (1974).
Woodruff, G. N., Comp. gen. Pharmac., 2, 439–455 (1971).
Woodruff, G. N., Elkhawad, A. O., Crossman, A. R., and Walker, R. J., J. Pharm. Pharmac., 26, 740–741 (1974).
Møller-Nielsen, I., et al., Acta Pharmac. Toxic., 33, 353–362 (1973).
House, C. R., Ginsborg, B. L., and Silinsky, E. M., Nature new Biol., 245, 63 (1973).
Ginsborg, B. L., House, C. R., and Turnbull, K. W., Br. J. Pharmac. (in the press).
Seeman, P., and Lee, T., Science, 188, 1217–1219 (1975).
Ginsborg, B. L., House, C. R., and Silinsky, E. M., J. Physiol., Lond., 236, 723–731 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HOUSE, C., GINSBORG, B. Actions of a dopamine analogue and a neuroleptic at a neuroglandular synapse. Nature 261, 332–333 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1038/261332a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/261332a0
This article is cited by
-
Dopamine stimulates production of cyclic AMP by the salivary gland of the cockroach,Nauphoeta cinerea
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (1982)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.