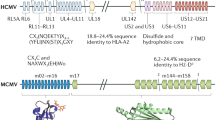
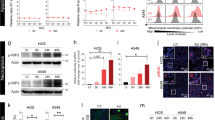
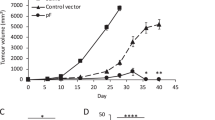
Abstract
STUDIES of mechanisms of resistance to herpes simplex virus (HSV) in mice have demonstrated antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (AD-CMC) of HSV-infected cells exposed in suspension cultures to anti-HSV sera and normal mouse peritoneal cells (PC) or human peripheral blood leukocytes. In this system it was impossible to demonstrate T-cell-mediated cytotoxicity1–3. In an attempt to adjust the assay conditions to permit detection of such cytotoxicity by immune spleens or PC, the “monolayer” system of Gardner et al.4 was examined in syngeneic, allogeneic and xenogeneic combinations. Target cell monolayers were infected with HSV and exposed to immune or normal mouse PC. The latter produced unexpectedly high levels of nonspecific release of 51Cr by the monolayer HSV-infected cells. Because nonspecific or non-selective killing of human tumour cells5 by lymphocytes from normal patients has been a major problem in human tumour immunology, we have investigated the mechanism of this nonspecific cell-mediated cytotoxicity in the HSV system. Our results indicate that selective nonspecific killing is a consequence of the cross linking of effector and target cells through aggregated immunoglobulins.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rager-Zisman, B., and Bloom, B. R., Nature, 251, 542–543 (1974).
Shore, S. L., Nahmias, A. J., Starr, S. E., Wood, P. A., and McFarlin, D. F., Nature, 251, 350–352 (1974).
Ramshaw, I. A., Infect. Immun., 11, 767–769 (1975).
Gardner, I., Bowern, N. A., and Blanden, R. V., Eur. J. Immun., 4, 63–67 (1974).
Bean, M. A., et al., Cancer Res., 35, 2902–2913 (1975).
Schubert, D., Humphreys, S., Baroni, C., and Cohn, M., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 64, 316–323 (1969).
Julius, M. H., Simpson, E., and Herzenberg, L. A., Eur. J. Immun., 3, 645–649 (1973).
Allison, A. C., Harington, J. S., and Birbeck, M., J. exp. Med., 124, 141–154 (1966).
Westmoreland, D., and Watkins, J. F., J. gen. Virol., 24, 167–178 (1974).
Westmoreland, D., Watkins, J. F., and Rapp, F., J. gen. Virol., 25, 167–170 (1974).
Ishizaka, T., Ishizaka, K., Salmon, S., and Fundenberg, H., J. Immun., 99, 82–91 (1967).
Paraskevas, F., Lee, S.-T., Orr, K. B., and Israels, L. G., J. Immun., 108, 1319–1327 (1972).
Takasugi, M., Mickey, M. R., and Terasaki, P. I., Cancer Res., 33, 2898–2902 (1973).
Hersey, P., et al., J. Cancer, 16, 173–183 (1975).
Tønder, O., Morse, P. A., and Humphrey, L. J., J. Immun., 113, 1162–1169 (1974).
Svedmyr, E., and Jondal, M., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 72, 1622–1626 (1975).
Stott, E. J., Probert, M., and Thomas, L. H., Nature, 255, 710–712 (1975).
Kiessling, R., Klein, E., Pross, H., and Wigzell, H., Eur. J. Immun., 5, 117–121 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
RAGER-ZISMAN, B., GROSE, C. & BLOOM, B. Mechanism of selective nonspecific cell-mediated cytotoxicity of virus-infected cells. Nature 260, 369–370 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1038/260369a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/260369a0
This article is cited by
-
Interferon production and activity in mouse neuroblastoma cells
Archives of Virology (1978)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.