Abstract
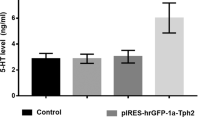
TRYPTOPHAN hydroxylation is the rate-limiting step in the biosynthesis of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) in central serotonergic neurones. In physiological states, tryptophan hydroxylase (EC 1.14.16.4), the key enzyme, is not saturated by its substrate1. Thus, three factors which modulate the concentration of tryptophan in brain—the levels of free tryptophan in plasma2,3, the ratio of total tryptophan levels to those of other neutral amino acids4, and the uptake process for tryptophan in brain tissues5,6—are important in the control of 5-HT synthesis. On the basis of indirect evidence7,8, it was suggested that tryptophan hydroxylase could also play a regulatory role. Among the mechanisms possibly involved, rapid changes in the enzyme affinity for its substrate and/or its cofactor may take place. Indeed, such changes are responsible for the activation of tyrosine hydroxylase seen in dopaminergic terminals after blockade of dopaminergic receptors by neuroleptics9. We used methiothepin(1-[10,11-dihydro-8-(methylthio)-dibenzo (b,f) thiepin-10-yl]-4-methylpiperazine maleate), a potent blocker of central serotonergic receptors10, to look for a similar activation of tryptophan hydroxylase. Our results indicate that the affinity of this enzyme for its substrate is markedly enhanced in methiothepin-treated tissue.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Friedman, P. A., Kappelman, A. H., and Kaufman, S., J. biol. Chem., 247, 4165–4173 (1972).
Tagliamonte, A., Biggio, G., Vargiu, L., and Gessa, G. L., Life Sci., 12, 277–287 (1973).
Knott, P. J., and Curzon, G., Nature, 239, 452–453 (1972).
Fernstrom, J. D., and Wurtman, R. J., Science, 178, 414–416 (1972).
Héry, F., Rouer, E., and Glowinski, J., Brain Res., 43, 445–465 (1972).
Hamon, M., and Glowinski, J., Life Sci., 15, 1533–1548 (1974).
Eccleston, D., Ritchie, I. M., and Roberts, M. H. T., Nature, 226, 84–85 (1970).
Carlsson, A., Lindqvist, M., Magnusson, T., and Atack, C., Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak., 277, 1–12, (1973).
Zivcovic, B., Guidotti, A., and Costa, E., Molec. Pharmac., 10, 727–735 (1974).
Jalfre, M., Ruch-Monachon, M. A., and Haefely, W., in Adv. Biochem. Psychopharmac., 10 (edit. by Costa, E., Gessa, G. L., and Sandler, M.), 121–134 (Raven, New York, 1974).
Hamon, M., Bourgoin, S., and Glowinski, J., J. Neurochem., 20, 1727–1745 (1973).
Gál, E. M., and Patterson, K., Analyt. Biochem., 52, 625–629 (1973).
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J., J. biol. Chem., 193, 265–275 (1951).
Snedecor, G. W., and Cochran, W. G., in Statistical Methods (Iowa State University, 1967).
Kuczenski, R., J. biol. Chem., 248, 2261–2265 (1973).
Kuczenski, R., Life Sci., 14, 2379–2384 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HAMON, M., BOURGOIN, S., HERY, F. et al. In vivo and in vitro activation of soluble tryptophan hydroxylase from rat brainstem. Nature 260, 61–63 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1038/260061a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/260061a0
This article is cited by
-
Studies on tryptophan accumulation in brain during methiothepin-induced enhancement of 5-hydroxyindole synthesis
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (1979)
-
Kinetics of tryptophan accumulation into synaptosomes of various regions of rat brain
Psychopharmacology (1979)
-
Conformational influences on brain tryptophan hydroxylase by submicromolar calcium: Opposite effects of equimolar lithium
Journal of Neural Transmission (1979)
-
Characteristics of the activation by dithiothreitol and Fe2+ of tryptophan hydroxylase from the rat brain
Neurochemical Research (1978)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.