Abstract
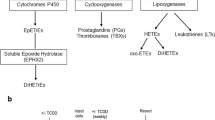
MICROSOMAL mixed-function oxygenases metabolise a variety of exogenous compounds, including drugs, pesticides and carcinogens, as well as endogenous substances such as steroids1,2. One oxygenase, aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase (AHH), is important in both the detoxification of some carcinogenic polycyclic hydrocarbons and the activation of others to more carcinogenic forms1–4. Hydroxylase activity and cytochrome P-450 have been found in various tissues of animals1,2 and man5–12. AHH activity increases in many tissues after treatment with polycyclic hydrocarbons. In certain inbred mouse strains this increase appears to be regulated by a single autosomal dominant gene13, and a correlation between enzyme levels and susceptibility to methylcholanthrene-induced tumorigenesis has been reported14. Data obtained by Shaw and his colleagues point to genetic regulation of AHH in human populations15.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Conney, A. H., Pharmacl. Rev., 19, 317–366 (1967).
Gelboin, H. V., Adv. Cancer Res., 10, 1–81 (1967).
Gelboin, H. V., Kinoshita, N., and Weibel, F. J., Fedn. Proc., 31, 1298–1308 (1972).
Kinoshita, N., Gelboin, H. V., Cancer Res., 23, 1329–1339 (1972).
Czygan, P., Greim, H., Garro, A. J., Hutterer, F., Rudick, J., Schaffner, F., and Popper, H., J. natn. Cancer Inst., 51, 1761–1764 (1973).
Grover, P. L., Hewer, A., and Sims, P., FEBS Lett., 34, 63–68 (1973).
Levin, W., Conney, A. H., Alvares, A. P., Markath, I., and Kappas, A., Science, 176, 419–420 (1972).
Juchau, M. R., Pederson, M. G., and Symms, K. G., Biochem. Pharmac., 21, 2269–2272 (1972).
Conney, A. H., Welch, R., Kuntzman, R., et al., Ann N.Y. Acad. Sci., 179, 155–172 (1971).
Cantrell, E. T., Wall, G. A., Busbee, D. L., and Martin, R. R., J. clin. Invest., 52, 1881–1884 (1973).
Whitlock, jun., J. P., Cooper, H. C., and Gelboin, H. V., Science, 117, 618–619 (1972).
Busbee, K. L., Shaw, C. R., and Cantrell, E. T., Science, 178, 315–316 (1972).
Nebert, D. W., Goujon, F. M., and Gielen, J. E., Nature new Biol., 236, 107–110 (1972).
Kouri, R. E., Ratrie, H., and Whitmire, C. E., J. natn. Cancer Inst., 51, 197–200 (1973).
Kellerman, G., Luyten-Kellerman, M., and Shaw, C. R., Am. J. Human Genet., 25, 327–331 (1973).
Cantrell, E., and Bresnick, F., J. Cell Biol., 52, 316–321 (1972).
Bast, jun., R. C., Shears, B. W., Rapp, H. J., and Gelboin, H. V., J. natn. Cancer Inst., 51, 675–678 (1973).
Boyum, A., Scand. J. clin. Invest., 21, Suppl., 77–89 (1968).
Nebert, D. W., and Gelboin, H. V., J. biol. Chem., 243, 6242–6249 (1968).
Diamond, L., and Gelboin, H. V., Science, 166, 1023–1025 (1969).
Roser, B. J., Reticuloendothelial Soc., 8, 139–161 (1970).
Bast, jun., R. C., Zbar, B., Borsos, T., and Rapp, H. J., New Engl. J. Med. 290, 1413–1420, (1974).
Pomeranz, J. R., J. natn. Cancer Inst., 48, 1513–1517 (1972).
Unanue, E. R., Adv. Immun., 15, 95–165 (1972).
Kellerman, G., Shaw, C. R., and Luyten-Kellerman, M., New Engl. J. Med., 289, 934–937 (1973).
Davidsohn, I., and Nelson, D. A., (ed.) Clinical diagnosis by laboratory methods, fourteenth ed., 176 (Sanders, Philadelphia, 1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BAST, R., WHITLOCK, J., MILLER, H. et al. Aryl hydrocarbon (benzo(a)pyrene) hydroxylase in human peripheral blood monocytes. Nature 250, 664–665 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1038/250664a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/250664a0
This article is cited by
-
32P-postlabelling analysis of DNA adducts in monocytes of smokers and passive smokers
International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health (1990)
-
Activation of xenobiotics by monooxygenases: cultures of mammalian cells as analytical tool
Archives of Toxicology (1977)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.