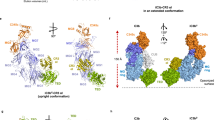
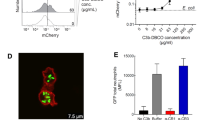
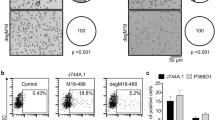
Abstract
RECEPTORS on the surface at B cells for the fixed C3 component of complement have previously been studied by investigating the adherence to lymphocytes of complement-coated immune complexes and their function interpreted in the light of this reaction1–10. Other nucleated cells, however, notably macrophages, in the secondary lymphoid organs, also have receptors for fixed C3 (refs 3 and 4). It is therefore possible that alexinated complexes might mediate mixed adherence of different cell types which could have more significant functional consequences for complement receptor lymphocytes than just direct binding to their C3 receptors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Uhr, J. W., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci., U.S.A., 54, 1599 (1965).
Uhr, J. W., and Phillips, J. M., Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 129, 792 (1966).
Lay, W. H., and Nussenzweig, V., J. exp. Med., 128, 991 (1968).
Henson, P. M., Immunology, 16, 107 (1969).
Bianco, C., Patrick, R., and Nussenzweig, V., J. exp. Med., 132, 702 (1970).
Bianco, C., and Nussenzweig, V., Science, 173, 154 (1971).
Dukor, P., Bianco, C., and Nussenzweig, V., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci., U.S.A., 67, 991 (1970).
Dukor, P., Bianco, C., and Nussenzweig, V., Eur. J. Immun., 1, 491 (1971).
Eden, A., Bianco, C., and Nussenzweig, V., Cell. Immun., 2, 658 (1971).
Nussenzweig, V., Bianco, C., Dukor, P., and Eden, A., Prog. Immun., 1, 73 (1971).
Pepys, M. B., Nature new Biol., 237, 157 (1972).
Janossy, G., Humphrey, J. H., Pepys, M. B., and Greaves, M. F., Nature new Biol., 245, 108 (1973).
Feldman, M., and Pepys, M. B., Nature (in the press).
Feldmann, M., and Nossal, G. J. V., Transplantn Rev., 13, 3 (1972).
Ballow, M., and Cochrane, C. G., J. Immun., 103, 944 (1969).
Muller-Eberhard, H. J., and Fjellstrom, K.-E., J. Immun., 107, 1666 (1971).
Dukor, P., Suter, E. R., Dietrich, F. M., and Probst, H., Proc. 4th Int. Conf. Lymphatic Tissue Germinal Centres Immune Reactions, (Plenum Press, 1972).
Miller, G., and Nussenzweig, V., J. Immun., 111, 299 (1973).
Eden, A., Bianco, C., Nussenzweig, V., and Mayer, M. M., J. Immun., 110, 1452 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
PEPYS, M. Complement-mediated mixed aggregation of murine spleen cells. Nature 249, 51–53 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1038/249051a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/249051a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.