Abstract
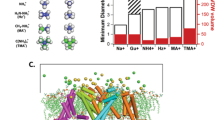
THE main route of ion permeation across some epithelia, including that of the gallbladder, is by the so-called ‘tight’ junctions between adjacent cells1. In the case of the gallbladder, this pathway is much more permeable to cations than to anions, and it also discriminates markedly among different inorganic cations2,3. We have extended selective permeability measurements to a series of small amines in the form with one positive charge (compare ref. 4). The rationale behind these experiments is that permeability differences among cationic amines may help to identify the chemical nature and arrangement of ion-selective sites, as well as the possible existence of steric restraints in the permeation channel. The results indicate that gallbladder ‘tight’ junctions contain proton-acceptor sites which distinguish more markedly among cationic proton donors than does water.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frömter, E., and Diamond, J. M., Nature new Biol., 235, 9 (1972).
Barry, P. H., Diamond, J. M., and Wright, E. M., J. Membrane Biol., 4, 358 (1971).
Moreno, J. H., and Diamond, J. M., J. Membrane Biol. (in the press).
Hille, B., J. gen. Physiol., 58, 599 (1971).
Wright, E. M., Barry, P. H., and Diamond, J. M., J. Membrane Biol., 4, 331 (1971).
Eisenman, G., Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 148, 5 (1968).
Diamond, J. M., and Wright, E. M., A. Rev. Physiol., 31, 581 (1969).
Krishnam, C. V., and Friedman, H. L., J. phys. Chem., 74, 3900 (1970).
Eisenman, G., and Krasne, S., Biophys. J., 13, 244a (1973).
Eisenman, G., Biophys. J., 2, part 2, 259 (1962).
Diamond, J. M., and Wright, E. M., Proc. R. Soc. B, London, 172, 273 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MORENO, J., DIAMOND, J. Role of Hydrogen Bonding in Organic Cation Discrimination by Gallbladder Epithelium. Nature 247, 368–369 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1038/247368a0
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/247368a0
This article is cited by
-
Electro-oxidation of hydrazine shows marcusian electron transfer kinetics
Science China Chemistry (2021)
-
Nitrogenous cations as probes of permeation channels
The Journal of Membrane Biology (1975)
-
Blockage of cation permeability across the tight junctions of gallbladder and other leaky epithelia
Nature (1974)
-
Discrimination of monovalent inorganic cations by “tight” junctions of gallbladder epithelium
The Journal of Membrane Biology (1974)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.